计数排序 是一种基于特定范围内键的排序技术。它通过计算具有不同键值的对象的数量来工作(类似于散列)。然后做一些算法来计算输出序列中每个对象的位置。
让我们通过一个例子来理解它。
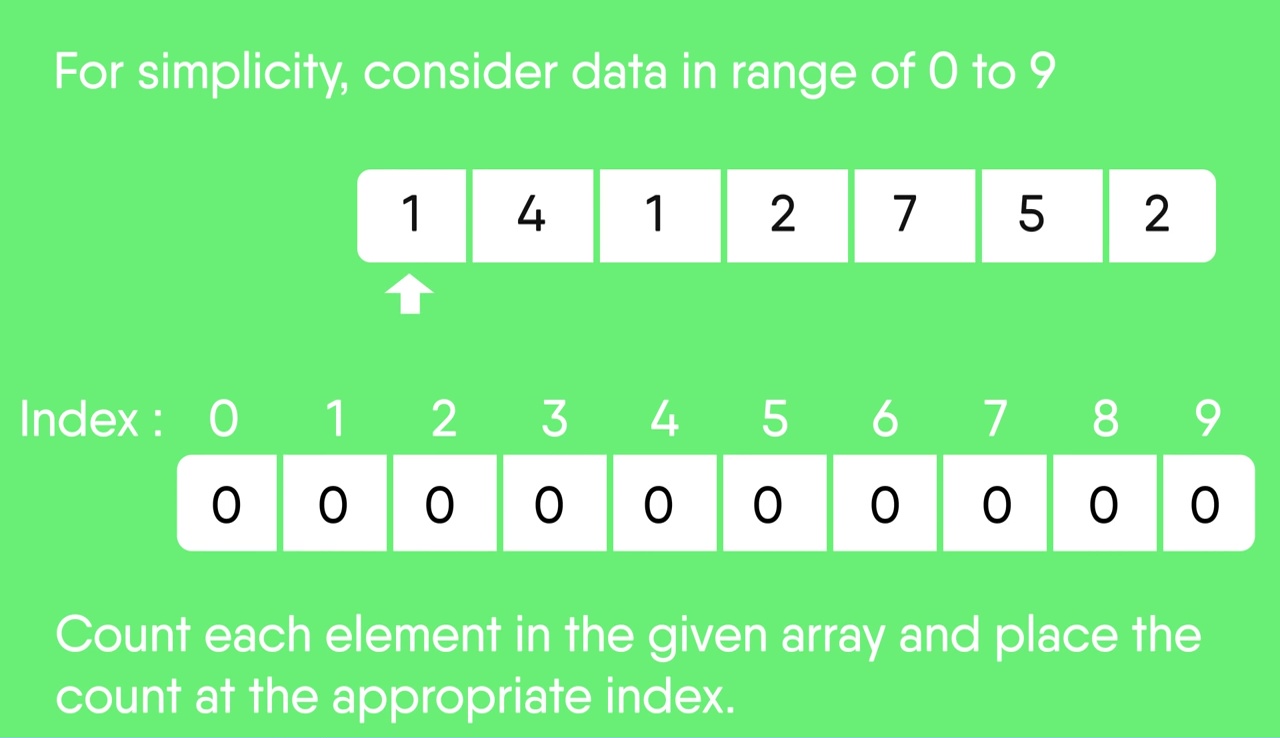
For simplicity, consider the data in the range 0 to 9. Input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2 1) Take a count array to store the count of each unique object. Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Count: 0 2 2 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 2) Modify the count array such that each element at each index stores the sum of previous counts. Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Count: 0 2 4 4 5 6 6 7 7 7 The modified count array indicates the position of each object in the output sequence. 3) Rotate the array clockwise for one time. Index: 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Count: 0 0 2 4 4 5 6 6 7 7 4) Output each object from the input sequence followed by increasing its count by 1. Process the input data: 1, 4, 1, 2, 7, 5, 2. Position of 1 is 0. Put data 1 at index 0 in output. Increase count by 1 to place next data 1 at an index 1 greater than this index.
下面是计数排序的实现。
C++
// C++ Program for counting sort #include <bits/stdc++.h> #include <string.h> using namespace std; #define RANGE 255 // The main function that sort // the given string arr[] in // alphabetical order void countSort( char arr[]) { // The output character array // that will have sorted arr char output[ strlen (arr)]; // Create a count array to store count of individual // characters and initialize count array as 0 int count[RANGE + 1], i; memset (count, 0, sizeof (count)); // Store count of each character for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) ++count[arr[i]]; // Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual // position of this character in output array for (i = 1; i <= RANGE; ++i) count[i] += count[i - 1]; // Build the output character array for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) { output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } /* For Stable algorithm for (i = sizeof(arr)-1; i>=0; --i) { output[count[arr[i]]-1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } For Logic : See implementation */ // Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now // contains sorted characters for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) arr[i] = output[i]; } // Driver code int main() { char arr[] = "geeksforgeeks" ; countSort(arr); cout << "Sorted character array is " << arr; return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
// C Program for counting sort #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define RANGE 255 // The main function that sort the given string arr[] in // alphabetical order void countSort( char arr[]) { // The output character array that will have sorted arr char output[ strlen (arr)]; // Create a count array to store count of individual // characters and initialize count array as 0 int count[RANGE + 1], i; memset (count, 0, sizeof (count)); // Store count of each character for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) ++count[arr[i]]; // Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual // position of this character in output array for (i = 1; i <= RANGE; ++i) count[i] += count[i - 1]; // Build the output character array for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) { output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } /* For Stable algorithm for (i = sizeof(arr)-1; i>=0; --i) { output[count[arr[i]]-1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } For Logic : See implementation */ // Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now // contains sorted characters for (i = 0; arr[i]; ++i) arr[i] = output[i]; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { char arr[] = "geeksforgeeks" ; //"applepp"; countSort(arr); printf ( "Sorted character array is %sn" , arr); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java implementation of Counting Sort class CountingSort { void sort( char arr[]) { int n = arr.length; // The output character array that will have sorted arr char output[] = new char [n]; // Create a count array to store count of individual // characters and initialize count array as 0 int count[] = new int [ 256 ]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < 256 ; ++i) count[i] = 0 ; // store count of each character for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) ++count[arr[i]]; // Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual // position of this character in output array for ( int i = 1 ; i <= 255 ; ++i) count[i] += count[i - 1 ]; // Build the output character array // To make it stable we are operating in reverse order. for ( int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { output[count[arr[i]] - 1 ] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } // Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now // contains sorted characters for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) arr[i] = output[i]; } // Driver method public static void main(String args[]) { CountingSort ob = new CountingSort(); char arr[] = { 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' , 'f' , 'o' , 'r' , 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' }; ob.sort(arr); System.out.print( "Sorted character array is " ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; ++i) System.out.print(arr[i]); } } /*This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */ |
Python3
# Python program for counting sort # The main function that sort the given string arr[] in # alphabetical order def countSort(arr): # The output character array that will have sorted arr output = [ 0 for i in range ( len (arr))] # Create a count array to store count of individual # characters and initialize count array as 0 count = [ 0 for i in range ( 256 )] # For storing the resulting answer since the # string is immutable ans = ["" for _ in arr] # Store count of each character for i in arr: count[ ord (i)] + = 1 # Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual # position of this character in output array for i in range ( 256 ): count[i] + = count[i - 1 ] # Build the output character array for i in range ( len (arr)): output[count[ ord (arr[i])] - 1 ] = arr[i] count[ ord (arr[i])] - = 1 # Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now # contains sorted characters for i in range ( len (arr)): ans[i] = output[i] return ans # Driver program to test above function arr = "geeksforgeeks" ans = countSort(arr) print ( "Sorted character array is % s" % ("".join(ans))) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh |
C#
// C# implementation of Counting Sort using System; class GFG { static void countsort( char [] arr) { int n = arr.Length; // The output character array that // will have sorted arr char [] output = new char [n]; // Create a count array to store // count of individual characters // and initialize count array as 0 int [] count = new int [256]; for ( int i = 0; i < 256; ++i) count[i] = 0; // store count of each character for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i) ++count[arr[i]]; // Change count[i] so that count[i] // now contains actual position of // this character in output array for ( int i = 1; i <= 255; ++i) count[i] += count[i - 1]; // Build the output character array // To make it stable we are operating in reverse order. for ( int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[arr[i]] - 1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i]]; } // Copy the output array to arr, so // that arr now contains sorted // characters for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i) arr[i] = output[i]; } // Driver method public static void Main() { char [] arr = { 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' , 'f' , 'o' , 'r' , 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' }; countsort(arr); Console.Write( "Sorted character array is " ); for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; ++i) Console.Write(arr[i]); } } // This code is contributed by Sam007. |
PHP
<?php // PHP Program for counting sort $RANGE = 255; // The main function that sort // the given string arr[] in // alphabetical order function countSort( $arr ) { global $RANGE ; // The output character array // that will have sorted arr $output = array ( strlen ( $arr )); $len = strlen ( $arr ); // Create a count array to // store count of individual // characters and initialize // count array as 0 $count = array_fill (0, $RANGE + 1, 0); // Store count of // each character for ( $i = 0; $i < $len ; ++ $i ) ++ $count [ord( $arr [ $i ])]; // Change count[i] so that // count[i] now contains // actual position of this // character in output array for ( $i = 1; $i <= $RANGE ; ++ $i ) $count [ $i ] += $count [ $i - 1]; // Build the output // character array // To make it stable we are operating // in reverse order. for ( $i = $len -1; $i >= 0 ; $i --) { $output [ $count [ord( $arr [ $i ])] - 1] = $arr [ $i ]; -- $count [ord( $arr [ $i ])]; } // Copy the output array to // arr, so that arr now // contains sorted characters for ( $i = 0; $i < $len ; ++ $i ) $arr [ $i ] = $output [ $i ]; return $arr ; } // Driver Code $arr = "geeksforgeeks" ; //"applepp"; $arr = countSort( $arr ); echo "Sorted character array is " . $arr ; // This code is contributed by mits ?> |
Javascript
Javas<script> // Javascript implementation of Counting Sort function sort(arr) { var n = arr.length; // The output character array that will have sorted arr var output = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => 0); // Create a count array to store count of individual // characters and initialize count array as 0 var count = Array.from({length: 256}, (_, i) => 0); // store count of each character for ( var i = 0; i < n; ++i) ++count[arr[i].charCodeAt(0)]; // Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual // position of this character in output array for ( var i = 1; i <= 255; ++i) count[i] += count[i - 1]; // Build the output character array // To make it stable we are operating in reverse order. for ( var i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[arr[i].charCodeAt(0)] - 1] = arr[i]; --count[arr[i].charCodeAt(0)]; } // Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now // contains sorted characters for ( var i = 0; i < n; ++i) arr[i] = output[i]; return arr; } // Driver method var arr = [ 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' , 'f' , 'o' , 'r' , 'g' , 'e' , 'e' , 'k' , 's' ]; arr = sort(arr); document.write( "Sorted character array is " ); for ( var i = 0; i < arr.length; ++i) document.write(arr[i]); // This code is contributed by shikhasingrajput </script> cript |
输出:
Sorted character array is eeeefggkkorss
时间复杂性: O(n+k),其中n是输入数组中的元素数,k是输入范围。 辅助空间: O(n+k)
以前的计数排序的问题是,如果元素中有负数,我们就无法对元素进行排序。因为没有负的数组索引。所以我们要做的是,找到最小元素,然后将最小元素的计数存储在零索引处。
C++
// Counting sort which takes negative numbers as well #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <vector> using namespace std; void countSort(vector< int >& arr) { int max = *max_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()); int min = *min_element(arr.begin(), arr.end()); int range = max - min + 1; vector< int > count(range), output(arr.size()); for ( int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) count[arr[i] - min]++; for ( int i = 1; i < count.size(); i++) count[i] += count[i - 1]; for ( int i = arr.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[arr[i] - min] - 1] = arr[i]; count[arr[i] - min]--; } for ( int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) arr[i] = output[i]; } void printArray(vector< int >& arr) { for ( int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) cout << arr[i] << " " ; cout << "" ; } int main() { vector< int > arr = { -5, -10, 0, -3, 8, 5, -1, 10 }; countSort(arr); printArray(arr); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Counting sort which takes negative numbers as well import java.util.*; class GFG { static void countSort( int [] arr) { int max = Arrays.stream(arr).max().getAsInt(); int min = Arrays.stream(arr).min().getAsInt(); int range = max - min + 1 ; int count[] = new int [range]; int output[] = new int [arr.length]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { count[arr[i] - min]++; } for ( int i = 1 ; i < count.length; i++) { count[i] += count[i - 1 ]; } for ( int i = arr.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { output[count[arr[i] - min] - 1 ] = arr[i]; count[arr[i] - min]--; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = output[i]; } } static void printArray( int [] arr) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { System.out.print(arr[i] + " " ); } System.out.println( "" ); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int [] arr = { - 5 , - 10 , 0 , - 3 , 8 , 5 , - 1 , 10 }; countSort(arr); printArray(arr); } } // This code is contributed by princiRaj1992 |
Python3
# Python program for counting sort # which takes negative numbers as well # The function that sorts the given arr[] def count_sort(arr): max_element = int ( max (arr)) min_element = int ( min (arr)) range_of_elements = max_element - min_element + 1 # Create a count array to store count of individual # elements and initialize count array as 0 count_arr = [ 0 for _ in range (range_of_elements)] output_arr = [ 0 for _ in range ( len (arr))] # Store count of each character for i in range ( 0 , len (arr)): count_arr[arr[i] - min_element] + = 1 # Change count_arr[i] so that count_arr[i] now contains actual # position of this element in output array for i in range ( 1 , len (count_arr)): count_arr[i] + = count_arr[i - 1 ] # Build the output character array for i in range ( len (arr) - 1 , - 1 , - 1 ): output_arr[count_arr[arr[i] - min_element] - 1 ] = arr[i] count_arr[arr[i] - min_element] - = 1 # Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now # contains sorted characters for i in range ( 0 , len (arr)): arr[i] = output_arr[i] return arr # Driver program to test above function arr = [ - 5 , - 10 , 0 , - 3 , 8 , 5 , - 1 , 10 ] ans = count_sort(arr) print ( "Sorted character array is " + str (ans)) |
C#
// Counting sort which takes negative numbers as well using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; class GFG { static void countSort( int [] arr) { int max = arr.Max(); int min = arr.Min(); int range = max - min + 1; int []count = new int [range]; int []output = new int [arr.Length]; for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { count[arr[i] - min]++; } for ( int i = 1; i < count.Length; i++) { count[i] += count[i - 1]; } for ( int i = arr.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[arr[i] - min] - 1] = arr[i]; count[arr[i] - min]--; } for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { arr[i] = output[i]; } } static void printArray( int [] arr) { for ( int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) { Console.Write(arr[i] + " " ); } Console.WriteLine( "" ); } // Driver code public static void Main( string [] args) { int [] arr = { -5, -10, 0, -3, 8, 5, -1, 10 }; countSort(arr); printArray(arr); } } // This code is contributed by rutvik_56. |
Javascript
<script> // Counting sort which takes negative numbers as well function countSort(arr) { var max = Math.max.apply(Math, arr); var min = Math.min.apply(Math, arr); var range = max - min + 1; var count = Array.from({length: range}, (_, i) => 0); var output = Array.from({length: arr.length}, (_, i) => 0); for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { count[arr[i] - min]++; } for (i = 1; i < count.length; i++) { count[i] += count[i - 1]; } for (i = arr.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { output[count[arr[i] - min] - 1] = arr[i]; count[arr[i] - min]--; } for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { arr[i] = output[i]; } } function printArray(arr) { for (i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { document.write(arr[i] + " " ); } document.write( '<br>' ); } // Driver code var arr = [ -5, -10, 0, -3, 8, 5, -1, 10 ]; countSort(arr); printArray(arr); // This code is contributed by Amit Katiyar </script> |
输出:
-10 -5 -3 -1 0 5 8 10
需要注意的要点: 1. 如果输入数据的范围不明显大于要排序的对象的数量,则计数排序是有效的。考虑输入序列在范围1到10K之间的情况,并且数据是10, 5、10K、5K。 2. 它不是基于比较的排序。它的运行时间复杂度为O(n),空间与数据范围成正比。 3. 它通常被用作另一种排序算法(如基数排序)的子程序。 4. 计数排序使用部分哈希计算O(1)中数据对象的出现次数。 5. 计数排序也可以扩展到负输入。
练习: 1. 修改上述代码,将输入数据排序在M到N之间。 2. 计数排序是否稳定且在线? 3. 关于计数排序算法并行化的思考。
快照:






计数排序测验
分类编码实践
GeekSforgeks/GeekSquick上的其他排序算法 选择排序 , 气泡排序 , 插入排序 , 合并排序 , 堆排序 , 快速排序 , 基数排序 , 计数排序 , 斗式分拣 , 贝壳类 , 梳排序 , 鸽子洞分拣 本文由 阿希什·巴恩瓦尔 。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



