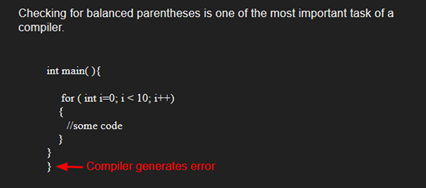
给定一个表达式字符串exp,编写一个程序来检查exp中的对和“{”、“}”、“(“,”)、“[”、“]”的顺序是否正确。
null
实例 :
输入 :exp=“[()]{}{[()()]()}” 输出 :平衡的
输入 :exp=“[(])” 输出 :不平衡
算法:
- 声明一个字符 堆栈 s
- 现在遍历表达式字符串exp。
- 如果当前字符是起始括号( “(”或“{”或“[” )然后把它推到堆栈上。
- 如果当前字符是右括号( “)”或“}”或“]” )然后从堆栈中弹出,如果弹出的字符是匹配的起始括号,则fine else括号不平衡。
- 完成遍历后,如果堆栈中还剩下一些起始括号,则“不平衡”
下图是上述方法的试运行:
![图片[2]-使用堆栈检查表达式中的平衡括号(格式良好)-yiteyi-C++库](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/cdn-uploads/20190626134001/ForBalancedParanthesisInanExoression1.png)
以下是上述方法的实施情况:
C++
// CPP program to check for balanced brackets. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // function to check if brackets are balanced bool areBracketsBalanced(string expr) { stack< char > s; char x; // Traversing the Expression for ( int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++) { if (expr[i] == '(' || expr[i] == '[' || expr[i] == '{' ) { // Push the element in the stack s.push(expr[i]); continue ; } // IF current current character is not opening // bracket, then it must be closing. So stack // cannot be empty at this point. if (s.empty()) return false ; switch (expr[i]) { case ')' : // Store the top element in a x = s.top(); s.pop(); if (x == '{' || x == '[' ) return false ; break ; case '}' : // Store the top element in b x = s.top(); s.pop(); if (x == '(' || x == '[' ) return false ; break ; case ']' : // Store the top element in c x = s.top(); s.pop(); if (x == '(' || x == '{' ) return false ; break ; } } // Check Empty Stack return (s.empty()); } // Driver code int main() { string expr = "{()}[]" ; // Function call if (areBracketsBalanced(expr)) cout << "Balanced" ; else cout << "Not Balanced" ; return 0; } |
C
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define bool int // structure of a stack node struct sNode { char data; struct sNode* next; }; // Function to push an item to stack void push( struct sNode** top_ref, int new_data); // Function to pop an item from stack int pop( struct sNode** top_ref); // Returns 1 if character1 and character2 are matching left // and right Brackets bool isMatchingPair( char character1, char character2) { if (character1 == '(' && character2 == ')' ) return 1; else if (character1 == '{' && character2 == '}' ) return 1; else if (character1 == '[' && character2 == ']' ) return 1; else return 0; } // Return 1 if expression has balanced Brackets bool areBracketsBalanced( char exp []) { int i = 0; // Declare an empty character stack struct sNode* stack = NULL; // Traverse the given expression to check matching // brackets while ( exp [i]) { // If the exp[i] is a starting bracket then push // it if ( exp [i] == '{' || exp [i] == '(' || exp [i] == '[' ) push(&stack, exp [i]); // If exp[i] is an ending bracket then pop from // stack and check if the popped bracket is a // matching pair*/ if ( exp [i] == '}' || exp [i] == ')' || exp [i] == ']' ) { // If we see an ending bracket without a pair // then return false if (stack == NULL) return 0; // Pop the top element from stack, if it is not // a pair bracket of character then there is a // mismatch. // his happens for expressions like {(}) else if (!isMatchingPair(pop(&stack), exp [i])) return 0; } i++; } // If there is something left in expression then there // is a starting bracket without a closing // bracket if (stack == NULL) return 1; // balanced else return 0; // not balanced } // Driver code int main() { char exp [100] = "{()}[]" ; // Function call if (areBracketsBalanced( exp )) printf ( "Balanced " ); else printf ( "Not Balanced " ); return 0; } // Function to push an item to stack void push( struct sNode** top_ref, int new_data) { // allocate node struct sNode* new_node = ( struct sNode*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct sNode)); if (new_node == NULL) { printf ( "Stack overflow n" ); getchar (); exit (0); } // put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // link the old list off the new node new_node->next = (*top_ref); // move the head to point to the new node (*top_ref) = new_node; } // Function to pop an item from stack int pop( struct sNode** top_ref) { char res; struct sNode* top; // If stack is empty then error if (*top_ref == NULL) { printf ( "Stack overflow n" ); getchar (); exit (0); } else { top = *top_ref; res = top->data; *top_ref = top->next; free (top); return res; } } |
JAVA
// Java program for checking // balanced brackets import java.util.*; public class BalancedBrackets { // function to check if brackets are balanced static boolean areBracketsBalanced(String expr) { // Using ArrayDeque is faster than using Stack class Deque<Character> stack = new ArrayDeque<Character>(); // Traversing the Expression for ( int i = 0 ; i < expr.length(); i++) { char x = expr.charAt(i); if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '{' ) { // Push the element in the stack stack.push(x); continue ; } // If current character is not opening // bracket, then it must be closing. So stack // cannot be empty at this point. if (stack.isEmpty()) return false ; char check; switch (x) { case ')' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '{' || check == '[' ) return false ; break ; case '}' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '(' || check == '[' ) return false ; break ; case ']' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '(' || check == '{' ) return false ; break ; } } // Check Empty Stack return (stack.isEmpty()); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { String expr = "([{}])" ; // Function call if (areBracketsBalanced(expr)) System.out.println( "Balanced " ); else System.out.println( "Not Balanced " ); } } |
蟒蛇3
# Python3 program to check for # balanced brackets. # function to check if # brackets are balanced def areBracketsBalanced(expr): stack = [] # Traversing the Expression for char in expr: if char in [ "(" , "{" , "[" ]: # Push the element in the stack stack.append(char) else : # IF current character is not opening # bracket, then it must be closing. # So stack cannot be empty at this point. if not stack: return False current_char = stack.pop() if current_char = = '(' : if char ! = ")" : return False if current_char = = '{' : if char ! = "}" : return False if current_char = = '[' : if char ! = "]" : return False # Check Empty Stack if stack: return False return True # Driver Code if __name__ = = "__main__" : expr = "{()}[]" # Function call if areBracketsBalanced(expr): print ( "Balanced" ) else : print ( "Not Balanced" ) # This code is contributed by AnkitRai01 and improved # by Raju Pitta |
C#
// C# program for checking // balanced Brackets using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class BalancedBrackets { public class stack { public int top = -1; public char [] items = new char [100]; public void push( char x) { if (top == 99) { Console.WriteLine( "Stack full" ); } else { items[++top] = x; } } char pop() { if (top == -1) { Console.WriteLine( "Underflow error" ); return ' ' ; } else { char element = items[top]; top--; return element; } } Boolean isEmpty() { return (top == -1) ? true : false ; } } // Returns true if character1 and character2 // are matching left and right brackets */ static Boolean isMatchingPair( char character1, char character2) { if (character1 == '(' && character2 == ')' ) return true ; else if (character1 == '{' && character2 == '}' ) return true ; else if (character1 == '[' && character2 == ']' ) return true ; else return false ; } // Return true if expression has balanced // Brackets static Boolean areBracketsBalanced( char [] exp) { // Declare an empty character stack */ Stack< char > st = new Stack< char >(); // Traverse the given expression to // check matching brackets for ( int i = 0; i < exp.Length; i++) { // If the exp[i] is a starting // bracket then push it if (exp[i] == '{' || exp[i] == '(' || exp[i] == '[' ) st.Push(exp[i]); // If exp[i] is an ending bracket // then pop from stack and check if the // popped bracket is a matching pair if (exp[i] == '}' || exp[i] == ')' || exp[i] == ']' ) { // If we see an ending bracket without // a pair then return false if (st.Count == 0) { return false ; } // Pop the top element from stack, if // it is not a pair brackets of // character then there is a mismatch. This // happens for expressions like {(}) else if (!isMatchingPair(st.Pop(), exp[i])) { return false ; } } } // If there is something left in expression // then there is a starting bracket without // a closing bracket if (st.Count == 0) return true ; // balanced else { // not balanced return false ; } } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { char [] exp = { '{' , '(' , ')' , '}' , '[' , ']' }; // Function call if (areBracketsBalanced(exp)) Console.WriteLine( "Balanced " ); else Console.WriteLine( "Not Balanced " ); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program for checking // balanced brackets // Function to check if brackets are balanced function areBracketsBalanced(expr) { // Using ArrayDeque is faster // than using Stack class let stack = []; // Traversing the Expression for (let i = 0; i < expr.length; i++) { let x = expr[i]; if (x == '(' || x == '[' || x == '{' ) { // Push the element in the stack stack.push(x); continue ; } // If current character is not opening // bracket, then it must be closing. // So stack cannot be empty at this point. if (stack.length == 0) return false ; let check; switch (x){ case ')' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '{' || check == '[' ) return false ; break ; case '}' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '(' || check == '[' ) return false ; break ; case ']' : check = stack.pop(); if (check == '(' || check == '{' ) return false ; break ; } } // Check Empty Stack return (stack.length == 0); } // Driver code let expr = "([{}])" ; // Function call if (areBracketsBalanced(expr)) document.write( "Balanced " ); else document.write( "Not Balanced " ); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script> |
输出
Balanced
时间复杂性: O(n) 辅助空间: O(n)表示堆栈。
如果您在上述代码/算法中发现任何错误,请写下评论,或者寻找其他方法来解决相同的问题
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



