我们得到一个大小为n的树作为数组父[0..n-1],其中父[]中的每个索引i代表一个节点,i处的值代表该节点的直接父节点。对于根节点,值将为-1。找到给定父链接的通用树的高度。 例如:
Input : parent[] = {-1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2}
Output : 2

Input : parent[] = {-1, 0, 1, 2, 3}
Output : 4

方法1: 一种解决方案是从节点向上遍历树,直到到达节点值为-1的根节点。当遍历每个节点时,存储最大路径长度。 这个解决方案的时间复杂性是 O(n^2) . 方法2: 在O(N)时间内为N元树构建图,并在O(N)时间内对存储的图应用BFS,同时执行BFS存储达到的最大级别。该解决方案通过两次迭代来确定N元树的高度。
C++
// C++ code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define MAX 1001 using namespace std; // Adjacency list to // store N-ary tree vector< int > adj[MAX]; // Build tree in tree in O(n) int build_tree( int arr[], int n) { int root_index = 0; // Iterate for all nodes for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // if root node, store index if (arr[i] == -1) root_index = i; else { adj[i].push_back(arr[i]); adj[arr[i]].push_back(i); } } return root_index; } // Applying BFS int BFS( int start) { // map is used as visited array map< int , int > vis; queue<pair< int , int > > q; int max_level_reached = 0; // height of root node is zero q.push({ start, 0 }); // p.first denotes node in adjacency list // p.second denotes level of p.first pair< int , int > p; while (!q.empty()) { p = q.front(); vis[p.first] = 1; // store the maximum level reached max_level_reached = max(max_level_reached, p.second); q.pop(); for ( int i = 0; i < adj[p.first].size(); i++) // adding 1 to previous level // stored on node p.first // which is parent of node adj[p.first][i] // if adj[p.first][i] is not visited if (!vis[adj[p.first][i]]) q.push({ adj[p.first][i], p.second + 1 }); } return max_level_reached; } // Driver Function int main() { // node 0 to node n-1 int parent[] = { -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 }; // Number of nodes in tree int n = sizeof (parent) / sizeof (parent[0]); int root_index = build_tree(parent, n); int ma = BFS(root_index); cout << "Height of N-ary Tree=" << ma; return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { static int MAX = 1001 ; // Adjacency list to // store N-ary tree static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); // Build tree in tree in O(n) static int build_tree( int arr[], int n) { int root_index = 0 ; // Iterate for all nodes for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { // if root node, store index if (arr[i] == - 1 ) root_index = i; else { adj.get(i).add(arr[i]); adj.get(arr[i]).add(i); } } return root_index; } // Applying BFS static int BFS( int start) { // map is used as visited array Map<Integer, Integer> vis = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>(); ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> q = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); int max_level_reached = 0 ; // height of root node is zero q.add( new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(start, 0 ))); // p.first denotes node in adjacency list // p.second denotes level of p.first ArrayList<Integer> p = new ArrayList<Integer>(); while (q.size() != 0 ) { p = q.get( 0 ); vis.put(p.get( 0 ), 1 ); // store the maximum level reached max_level_reached = Math.max(max_level_reached,p.get( 1 )); q.remove( 0 ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < adj.get(p.get( 0 )).size(); i++) { // adding 1 to previous level // stored on node p.first // which is parent of node adj[p.first][i] // if adj[p.first][i] is not visited if (!vis.containsKey(adj.get(p.get( 0 )).get(i))) { q.add( new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(adj.get(p.get( 0 )).get(i), p.get( 1 )+ 1 ))); } } } return max_level_reached; } // Driver Function public static void main (String[] args) { for ( int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) { adj.add( new ArrayList<Integer>()); } // node 0 to node n-1 int parent[] = { - 1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 }; // Number of nodes in tree int n = parent.length; int root_index = build_tree(parent, n); int ma = BFS(root_index); System.out.println( "Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma); } } // This code is contributed by rag2127 |
Python3
# Python3 code to find height # of N-ary tree in O(n) from collections import deque MAX = 1001 # Adjacency list to # store N-ary tree adj = [[] for i in range ( MAX )] # Build tree in tree in O(n) def build_tree(arr, n): root_index = 0 # Iterate for all nodes for i in range (n): # if root node, store # index if (arr[i] = = - 1 ): root_index = i else : adj[i].append(arr[i]) adj[arr[i]].append(i) return root_index # Applying BFS def BFS(start): # map is used as visited # array vis = {} q = deque() max_level_reached = 0 # height of root node is # zero q.append([start, 0 ]) # p.first denotes node in # adjacency list # p.second denotes level of # p.first p = [] while ( len (q) > 0 ): p = q.popleft() vis[p[ 0 ]] = 1 # store the maximum level # reached max_level_reached = max (max_level_reached, p[ 1 ]) for i in range ( len (adj[p[ 0 ]])): # adding 1 to previous level # stored on node p.first # which is parent of node # adj[p.first][i] # if adj[p.first][i] is not visited if (adj[p[ 0 ]][i] not in vis ): q.append([adj[p[ 0 ]][i], p[ 1 ] + 1 ]) return max_level_reached # Driver code if __name__ = = '__main__' : # node 0 to node n-1 parent = [ - 1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 3 ] # Number of nodes in tree n = len (parent) root_index = build_tree(parent, n) ma = BFS(root_index) print ( "Height of N-ary Tree=" , ma) # This code is contributed by Mohit Kumar 29 |
C#
// C# code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class GFG { static int MAX = 1001; // Adjacency list to // store N-ary tree static List<List< int >> adj = new List<List< int >>(); // Build tree in tree in O(n) static int build_tree( int [] arr, int n) { int root_index = 0; // Iterate for all nodes for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // if root node, store index if (arr[i] == -1) root_index = i; else { adj[i].Add(arr[i]); adj[arr[i]].Add(i); } } return root_index; } // Applying BFS static int BFS( int start) { // map is used as visited array Dictionary< int , int > vis = new Dictionary< int , int >(); List<List< int >> q= new List<List< int >>(); int max_level_reached = 0; // height of root node is zero q.Add( new List< int >(){start, 0}); // p.first denotes node in adjacency list // p.second denotes level of p.first List< int > p = new List< int >(); while (q.Count != 0) { p = q[0]; vis.Add(p[0], 1); // store the maximum level reached max_level_reached = Math.Max(max_level_reached, p[1]); q.RemoveAt(0); for ( int i = 0; i < adj[p[0]].Count; i++) { // adding 1 to previous level // stored on node p.first // which is parent of node adj[p.first][i] // if adj[p.first][i] is not visited if (!vis.ContainsKey(adj[p[0]][i])) { q.Add( new List< int >(){adj[p[0]][i], p[1] + 1 }); } } } return max_level_reached; } // Driver Function static public void Main () { for ( int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { adj.Add( new List< int >()); } // node 0 to node n-1 int [] parent = { -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 }; // Number of nodes in tree int n = parent.Length; int root_index = build_tree(parent, n); int ma = BFS(root_index); Console.Write( "Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma); } } // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 |
Javascript
<script> // JavaScript code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) let MAX = 1001; let adj = []; // Adjacency list to // store N-ary tree function build_tree(arr,n) { let root_index = 0; // Iterate for all nodes for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { // if root node, store index if (arr[i] == -1) root_index = i; else { adj[i].push(arr[i]); adj[arr[i]].push(i); } } return root_index; } // Applying BFS function BFS(start) { // map is used as visited array let vis = new Map(); let q = []; let max_level_reached = 0; // height of root node is zero q.push([start, 0 ]); // p.first denotes node in adjacency list // p.second denotes level of p.first let p = []; while (q.length != 0) { p = q[0]; vis.set(p[0],1); // store the maximum level reached max_level_reached = Math.max(max_level_reached,p[1]); q.shift(); for (let i = 0; i < adj[p[0]].length; i++) { // adding 1 to previous level // stored on node p.first // which is parent of node adj[p.first][i] // if adj[p.first][i] is not visited if (!vis.has(adj[p[0]][i])) { q.push([adj[p[0]][i], p[1]+1]); } } } return max_level_reached; } // Driver Function for (let i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { adj.push([]); } // node 0 to node n-1 let parent = [ -1, 0, 1, 2, 3 ]; // Number of nodes in tree let n = parent.length; let root_index = build_tree(parent, n); let ma = BFS(root_index); document.write( "Height of N-ary Tree=" + ma); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 </script> |
Height of N-ary Tree=4
这个解决方案的时间复杂性是 O(2n) 对于非常大的n,收敛到O(n)。 方法3: 我们可以在一次迭代中找到N元树的高度。我们迭代地访问从0到n-1的节点,如果以前没有访问过未访问的祖先,则递归地标记它们,直到我们到达一个被访问的节点,或者我们到达根节点。如果我们在使用父链接向上遍历树时到达被访问的节点,那么我们使用它的高度,在递归中不会进一步。 例1的解释:
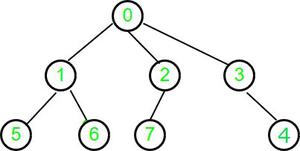
对于 节点0 :检查根节点是否为真, 将0返回为高度,将节点0标记为已访问 对于 节点1 :重现已访问的直接祖先,即0 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点0)+1 将节点1标记为已访问 对于 节点2 :重现已访问的直接祖先,即0 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点0)+1 将节点2标记为已访问 对于 节点3 :重现已访问的直接祖先,即0 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点0)+1 将节点3标记为已访问 对于 节点4 :重现已访问的直系祖先,即3 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点3)+1 将节点3标记为已访问 对于 节点5 :重现已访问的直系祖先,即1 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点1)+1 将节点5标记为已访问 对于 节点6 :重现已访问的直系祖先,即1 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点1)+1 将节点6标记为已访问 对于 节点7 :重现已访问的直系祖先,即2 因此,使用其高度和返回高度(节点2)+1 将节点7标记为已访问 因此,我们只处理N元树中的每个节点一次。
C++
// C++ code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) (Efficient Approach) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Recur For Ancestors of node and // store height of node at last int fillHeight( int p[], int node, int visited[], int height[]) { // If root node if (p[node] == -1) { // mark root node as visited visited[node] = 1; return 0; } // If node is already visited if (visited[node]) return height[node]; // Visit node and calculate its height visited[node] = 1; // recur for the parent node height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node], visited, height); // return calculated height for node return height[node]; } int findHeight( int parent[], int n) { // To store max height int ma = 0; // To check whether or not node is visited before int visited[n]; // For Storing Height of node int height[n]; memset (visited, 0, sizeof (visited)); memset (height, 0, sizeof (height)); for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // If not visited before if (!visited[i]) height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i, visited, height); // store maximum height so far ma = max(ma, height[i]); } return ma; } // Driver Function int main() { int parent[] = { -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 }; int n = sizeof (parent) / sizeof (parent[0]); cout << "Height of N-ary Tree = " << findHeight(parent, n); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) (Efficient Approach) import java.util.*; class GFG { // Recur For Ancestors of node and // store height of node at last static int fillHeight( int p[], int node, int visited[], int height[]) { // If root node if (p[node] == - 1 ) { // mark root node as visited visited[node] = 1 ; return 0 ; } // If node is already visited if (visited[node] == 1 ) return height[node]; // Visit node and calculate its height visited[node] = 1 ; // recur for the parent node height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node], visited, height); // return calculated height for node return height[node]; } static int findHeight( int parent[], int n) { // To store max height int ma = 0 ; // To check whether or not node is visited before int []visited = new int [n]; // For Storing Height of node int []height = new int [n]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { visited[i] = 0 ; height[i] = 0 ; } for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { // If not visited before if (visited[i] != 1 ) height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i, visited, height); // store maximum height so far ma = Math.max(ma, height[i]); } return ma; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int parent[] = { - 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 1 , 2 }; int n = parent.length; System.out.println( "Height of N-ary Tree = " + findHeight(parent, n)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar |
Python3
# Python3 code to find height of N-ary # tree in O(n) (Efficient Approach) # Recur For Ancestors of node and # store height of node at last def fillHeight(p, node, visited, height): # If root node if (p[node] = = - 1 ): # mark root node as visited visited[node] = 1 return 0 # If node is already visited if (visited[node]): return height[node] # Visit node and calculate its height visited[node] = 1 # recur for the parent node height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node], visited, height) # return calculated height for node return height[node] def findHeight(parent, n): # To store max height ma = 0 # To check whether or not node is # visited before visited = [ 0 ] * n # For Storing Height of node height = [ 0 ] * n for i in range (n): # If not visited before if ( not visited[i]): height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i, visited, height) # store maximum height so far ma = max (ma, height[i]) return ma # Driver Code if __name__ = = '__main__' : parent = [ - 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 3 , 1 , 1 , 2 ] n = len (parent) print ( "Height of N-ary Tree =" , findHeight(parent, n)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK |
C#
// C# code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) (Efficient Approach) using System; class GFG { // Recur For Ancestors of node and // store height of node at last static int fillHeight( int []p, int node, int []visited, int []height) { // If root node if (p[node] == -1) { // mark root node as visited visited[node] = 1; return 0; } // If node is already visited if (visited[node] == 1) return height[node]; // Visit node and calculate its height visited[node] = 1; // recur for the parent node height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node], visited, height); // return calculated height for node return height[node]; } static int findHeight( int []parent, int n) { // To store max height int ma = 0; // To check whether or not // node is visited before int []visited = new int [n]; // For Storing Height of node int []height = new int [n]; for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { visited[i] = 0; height[i] = 0; } for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // If not visited before if (visited[i] != 1) height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i, visited, height); // store maximum height so far ma = Math.Max(ma, height[i]); } return ma; } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { int []parent = { -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 }; int n = parent.Length; Console.WriteLine( "Height of N-ary Tree = " + findHeight(parent, n)); } } // This code contributed by Rajput-Ji |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript code to find height of N-ary // tree in O(n) (Efficient Approach) // Recur For Ancestors of node and // store height of node at last function fillHeight(p, node, visited, height) { // If root node if (p[node] == -1) { // mark root node as visited visited[node] = 1; return 0; } // If node is already visited if (visited[node] == 1) return height[node]; // Visit node and calculate its height visited[node] = 1; // recur for the parent node height[node] = 1 + fillHeight(p, p[node], visited, height); // return calculated height for node return height[node]; } function findHeight(parent,n) { // To store max height let ma = 0; // To check whether or not node is visited before let visited = new Array(n); // For Storing Height of node let height = new Array(n); for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { visited[i] = 0; height[i] = 0; } for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) { // If not visited before if (visited[i] != 1) height[i] = fillHeight(parent, i, visited, height); // store maximum height so far ma = Math.max(ma, height[i]); } return ma; } // Driver Code let parent = [ -1, 0, 0, 0, 3, 1, 1, 2 ]; let n = parent.length; document.write( "Height of N-ary Tree = " + findHeight(parent, n)); // This code is contributed by ab2127 </script> |
Height of N-ary Tree = 2
时间复杂性: O(n)


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



