在继续阅读本文之前,我们强烈建议参考下面的文章。 Push-Relabel算法|集1(简介和插图)
问题陈述: 给定一个表示流动网络的图,其中每条边都有一个容量。也给出了两个顶点 来源 “s”和 下沉 “t”在图中,找出从s到t的最大可能流量,并满足以下约束条件: (a) 边缘上的流量不会超过边缘的给定容量。 b) 除了s和t之外,每个顶点的输入流都等于输出流。
例如,从CLSR书中考虑下面的图表。
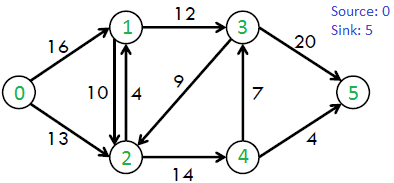
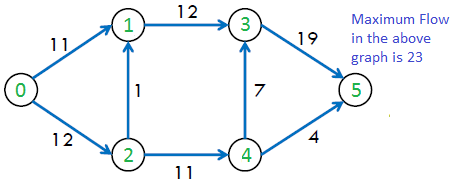
上图中的最大可能流量为23。
Push-Relabel Algorithm 1) Initialize PreFlow : Initialize Flows and Heights 2) While it is possible to perform a Push() or Relablel() on a vertex // Or while there is a vertex that has excess flow Do Push() or Relabel()// At this point all vertices have Excess Flow as 0 (Except source// and sink)3) Return flow.
以下是Push-Relabel算法中执行的主要操作。
Push-Relabel算法有三个主要操作
1.初始化预流() 它初始化所有顶点的高度和流动。
Preflow() 1) Initialize height and flow of every vertex as 0.2) Initialize height of source vertex equal to total number of vertices in graph.3) Initialize flow of every edge as 0.4) For all vertices adjacent to source s, flow and excess flow is equal to capacity initially.
2.推 用于从具有多余流的节点生成流。如果一个顶点有多余的流量,并且有一个高度较小的相邻点(在残差图中),我们将流量从顶点推到高度较低的相邻点。通过管道(边缘)的推动流量等于边缘的最小过剩流量和容量。
3.重新标记() 当一个顶点有多余的流量,且其相邻顶点都不在较低的高度时,将使用该操作。我们基本上增加了顶点的高度,这样我们就可以执行push()。为了增加高度,我们选择最小相邻高度(在残差图中,即我们可以添加流的相邻高度)并向其添加1。
实施
下面的实现使用下面的结构来表示流网络。
struct Vertex { int h; // Height of node int e_flow; // Excess Flow }
struct Edge { int u, v; // Edge is from u to v int flow; // Current flow int capacity; }
class Graph { Edge edge[]; // Array of edges Vertex ver[]; // Array of vertices }
下面的代码将给定的图本身用作流网络和残差图。我们没有为残差图创建单独的图,为了简单起见,我们使用了相同的图。
C++
// C++ program to implement push-relabel algorithm for // getting maximum flow of graph #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Edge { // To store current flow and capacity of edge int flow, capacity; // An edge u--->v has start vertex as u and end // vertex as v. int u, v; Edge( int flow, int capacity, int u, int v) { this ->flow = flow; this ->capacity = capacity; this ->u = u; this ->v = v; } }; // Represent a Vertex struct Vertex { int h, e_flow; Vertex( int h, int e_flow) { this ->h = h; this ->e_flow = e_flow; } }; // To represent a flow network class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices vector<Vertex> ver; vector<Edge> edge; // Function to push excess flow from u bool push( int u); // Function to relabel a vertex u void relabel( int u); // This function is called to initialize // preflow void preflow( int s); // Function to reverse edge void updateReverseEdgeFlow( int i, int flow); public : Graph( int V); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge( int u, int v, int w); // returns maximum flow from s to t int getMaxFlow( int s, int t); }; Graph::Graph( int V) { this ->V = V; // all vertices are initialized with 0 height // and 0 excess flow for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) ver.push_back(Vertex(0, 0)); } void Graph::addEdge( int u, int v, int capacity) { // flow is initialized with 0 for all edge edge.push_back(Edge(0, capacity, u, v)); } void Graph::preflow( int s) { // Making h of source Vertex equal to no. of vertices // Height of other vertices is 0. ver[s].h = ver.size(); // for ( int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) { // If current edge goes from source if (edge[i].u == s) { // Flow is equal to capacity edge[i].flow = edge[i].capacity; // Initialize excess flow for adjacent v ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += edge[i].flow; // Add an edge from v to s in residual graph with // capacity equal to 0 edge.push_back(Edge(-edge[i].flow, 0, edge[i].v, s)); } } } // returns index of overflowing Vertex int overFlowVertex(vector<Vertex>& ver) { for ( int i = 1; i < ver.size() - 1; i++) if (ver[i].e_flow > 0) return i; // -1 if no overflowing Vertex return -1; } // Update reverse flow for flow added on ith Edge void Graph::updateReverseEdgeFlow( int i, int flow) { int u = edge[i].v, v = edge[i].u; for ( int j = 0; j < edge.size(); j++) { if (edge[j].v == v && edge[j].u == u) { edge[j].flow -= flow; return ; } } // adding reverse Edge in residual graph Edge e = Edge(0, flow, u, v); edge.push_back(e); } // To push flow from overflowing vertex u bool Graph::push( int u) { // Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent (of u) // to which flow can be pushed for ( int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) { // Checks u of current edge is same as given // overflowing vertex if (edge[i].u == u) { // if flow is equal to capacity then no push // is possible if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity) continue ; // Push is only possible if height of adjacent // is smaller than height of overflowing vertex if (ver[u].h > ver[edge[i].v].h) { // Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of // remaining flow on edge and excess flow. int flow = min(edge[i].capacity - edge[i].flow, ver[u].e_flow); // Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex ver[u].e_flow -= flow; // Increase excess flow for adjacent ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += flow; // Add residual flow (With capacity 0 and negative // flow) edge[i].flow += flow; updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow); return true ; } } } return false ; } // function to relabel vertex u void Graph::relabel( int u) { // Initialize minimum height of an adjacent int mh = INT_MAX; // Find the adjacent with minimum height for ( int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) { if (edge[i].u == u) { // if flow is equal to capacity then no // relabeling if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity) continue ; // Update minimum height if (ver[edge[i].v].h < mh) { mh = ver[edge[i].v].h; // updating height of u ver[u].h = mh + 1; } } } } // main function for printing maximum flow of graph int Graph::getMaxFlow( int s, int t) { preflow(s); // loop until none of the Vertex is in overflow while (overFlowVertex(ver) != -1) { int u = overFlowVertex(ver); if (!push(u)) relabel(u); } // ver.back() returns last Vertex, whose // e_flow will be final maximum flow return ver.back().e_flow; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { int V = 6; Graph g(V); // Creating above shown flow network g.addEdge(0, 1, 16); g.addEdge(0, 2, 13); g.addEdge(1, 2, 10); g.addEdge(2, 1, 4); g.addEdge(1, 3, 12); g.addEdge(2, 4, 14); g.addEdge(3, 2, 9); g.addEdge(3, 5, 20); g.addEdge(4, 3, 7); g.addEdge(4, 5, 4); // Initialize source and sink int s = 0, t = 5; cout << "Maximum flow is " << g.getMaxFlow(s, t); return 0; } |
输出:
Maximum flow is 23
本文中的代码由 悉达思·拉尔瓦尼 和 乌特卡什·特里维迪 . 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写评论


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



