我们建议阅读以下两篇文章,作为这篇文章的先决条件。 1. 贪婪算法|集7(Dijkstra最短路径算法) 2. 图及其表示 我们讨论过 图的邻接矩阵表示的Dijkstra算法及其实现 .矩阵表示的时间复杂度为O(V^2)。本文讨论了邻接表表示的O(ELogV)算法。 如前一篇文章所述,在Dijkstra的算法中,保留了两个集合,一个集合包含SPT(最短路径树)中已包含的顶点列表,另一个集合包含尚未包含的顶点。使用邻接列表表示法,可以在O(V+E)时间内使用 BFS 。其思想是使用 BFS 并使用最小堆存储尚未包含在SPT中的顶点(或尚未确定最短距离的顶点)。Min Heap用作优先级队列,以从尚未包含的顶点集中获取最小距离顶点。对于最小堆,提取最小值和减少键值等操作的时间复杂度为O(LogV)。 以下是详细的步骤。 1) 创建一个大小为V的最小堆,其中V是给定图形中的顶点数。最小堆的每个节点都包含顶点数和顶点的距离值。 2) 以源顶点为根初始化最小堆(分配给源顶点的距离值为0)。指定给所有其他顶点的距离值为INF(无限)。 3) 当Min Heap不为空时,执行以下操作 ….. (a) 从Min Heap中提取具有最小距离值节点的顶点。将提取的顶点设为u。 ….. b) 对于u的每个相邻顶点v,检查v是否在最小堆中。如果v在最小堆中,且距离值大于u-v的权重加上u的距离值,则更新v的距离值。 让我们用下面的例子来理解。设给定的源顶点为0
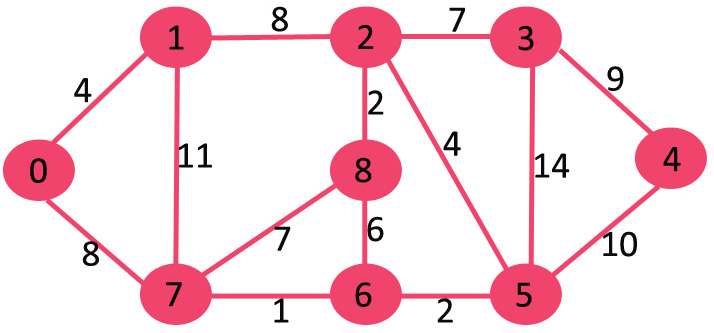
最初,源顶点的距离值为0,所有其他顶点的距离值为INF(无限)。因此,从最小堆中提取源顶点,并更新与0(1和7)相邻的顶点的距离值。最小堆包含除顶点0之外的所有顶点。 绿色的顶点是最终确定最小距离且不在最小堆中的顶点

由于顶点1的距离值在最小堆中的所有节点中都是最小的,因此会从最小堆中提取该距离值,并更新与1相邻的顶点的距离值(如果a顶点在最小堆中且通过1的距离小于之前的距离,则更新距离)。最小堆包含除顶点0和1之外的所有顶点。

从最小堆中拾取具有最小距离值的顶点。顶点7已拾取。所以min heap现在包含除0、1和7之外的所有顶点。更新7的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点6和8的距离值变得有限(分别为15和9)。

拾取与最小堆之间距离最小的顶点。顶点6已拾取。所以min heap现在包含除0、1、7和6之外的所有顶点。更新6的相邻顶点的距离值。顶点5和8的距离值将更新。

重复上述步骤,直到最小堆不为空。最后,我们得到以下最短路径树。

C++
// C / C++ program for Dijkstra's // shortest path algorithm for adjacency // list representation of graph #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <limits.h> // A structure to represent a // node in adjacency list struct AdjListNode { int dest; int weight; struct AdjListNode* next; }; // A structure to represent // an adjacency list struct AdjList { // Pointer to head node of list struct AdjListNode *head; }; // A structure to represent a graph. // A graph is an array of adjacency lists. // Size of array will be V (number of // vertices in graph) struct Graph { int V; struct AdjList* array; }; // A utility function to create // a new adjacency list node struct AdjListNode* newAdjListNode( int dest, int weight) { struct AdjListNode* newNode = ( struct AdjListNode*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct AdjListNode)); newNode->dest = dest; newNode->weight = weight; newNode->next = NULL; return newNode; } // A utility function that creates // a graph of V vertices struct Graph* createGraph( int V) { struct Graph* graph = ( struct Graph*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Graph)); graph->V = V; // Create an array of adjacency lists. // Size of array will be V graph->array = ( struct AdjList*) malloc (V * sizeof ( struct AdjList)); // Initialize each adjacency list // as empty by making head as NULL for ( int i = 0; i < V; ++i) graph->array[i].head = NULL; return graph; } // Adds an edge to an undirected graph void addEdge( struct Graph* graph, int src, int dest, int weight) { // Add an edge from src to dest. // A new node is added to the adjacency // list of src. The node is // added at the beginning struct AdjListNode* newNode = newAdjListNode(dest, weight); newNode->next = graph->array[src].head; graph->array[src].head = newNode; // Since graph is undirected, // add an edge from dest to src also newNode = newAdjListNode(src, weight); newNode->next = graph->array[dest].head; graph->array[dest].head = newNode; } // Structure to represent a min heap node struct MinHeapNode { int v; int dist; }; // Structure to represent a min heap struct MinHeap { // Number of heap nodes present currently int size; // Capacity of min heap int capacity; // This is needed for decreaseKey() int *pos; struct MinHeapNode **array; }; // A utility function to create a // new Min Heap Node struct MinHeapNode* newMinHeapNode( int v, int dist) { struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode = ( struct MinHeapNode*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct MinHeapNode)); minHeapNode->v = v; minHeapNode->dist = dist; return minHeapNode; } // A utility function to create a Min Heap struct MinHeap* createMinHeap( int capacity) { struct MinHeap* minHeap = ( struct MinHeap*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct MinHeap)); minHeap->pos = ( int *) malloc ( capacity * sizeof ( int )); minHeap->size = 0; minHeap->capacity = capacity; minHeap->array = ( struct MinHeapNode**) malloc (capacity * sizeof ( struct MinHeapNode*)); return minHeap; } // A utility function to swap two // nodes of min heap. // Needed for min heapify void swapMinHeapNode( struct MinHeapNode** a, struct MinHeapNode** b) { struct MinHeapNode* t = *a; *a = *b; *b = t; } // A standard function to // heapify at given idx // This function also updates // position of nodes when they are swapped. // Position is needed for decreaseKey() void minHeapify( struct MinHeap* minHeap, int idx) { int smallest, left, right; smallest = idx; left = 2 * idx + 1; right = 2 * idx + 2; if (left < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[left]->dist < minHeap->array[smallest]->dist ) smallest = left; if (right < minHeap->size && minHeap->array[right]->dist < minHeap->array[smallest]->dist ) smallest = right; if (smallest != idx) { // The nodes to be swapped in min heap MinHeapNode *smallestNode = minHeap->array[smallest]; MinHeapNode *idxNode = minHeap->array[idx]; // Swap positions minHeap->pos[smallestNode->v] = idx; minHeap->pos[idxNode->v] = smallest; // Swap nodes swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[smallest], &minHeap->array[idx]); minHeapify(minHeap, smallest); } } // A utility function to check if // the given minHeap is ampty or not int isEmpty( struct MinHeap* minHeap) { return minHeap->size == 0; } // Standard function to extract // minimum node from heap struct MinHeapNode* extractMin( struct MinHeap* minHeap) { if (isEmpty(minHeap)) return NULL; // Store the root node struct MinHeapNode* root = minHeap->array[0]; // Replace root node with last node struct MinHeapNode* lastNode = minHeap->array[minHeap->size - 1]; minHeap->array[0] = lastNode; // Update position of last node minHeap->pos[root->v] = minHeap->size-1; minHeap->pos[lastNode->v] = 0; // Reduce heap size and heapify root --minHeap->size; minHeapify(minHeap, 0); return root; } // Function to decreasy dist value // of a given vertex v. This function // uses pos[] of min heap to get the // current index of node in min heap void decreaseKey( struct MinHeap* minHeap, int v, int dist) { // Get the index of v in heap array int i = minHeap->pos[v]; // Get the node and update its dist value minHeap->array[i]->dist = dist; // Travel up while the complete // tree is not hepified. // This is a O(Logn) loop while (i && minHeap->array[i]->dist < minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]->dist) { // Swap this node with its parent minHeap->pos[minHeap->array[i]->v] = (i-1)/2; minHeap->pos[minHeap->array[ (i-1)/2]->v] = i; swapMinHeapNode(&minHeap->array[i], &minHeap->array[(i - 1) / 2]); // move to parent index i = (i - 1) / 2; } } // A utility function to check if a given vertex // 'v' is in min heap or not bool isInMinHeap( struct MinHeap *minHeap, int v) { if (minHeap->pos[v] < minHeap->size) return true ; return false ; } // A utility function used to print the solution void printArr( int dist[], int n) { printf ( "Vertex Distance from Source" ); for ( int i = 0; i < n; ++i) printf ( "%d %d" , i, dist[i]); } // The main function that calculates // distances of shortest paths from src to all // vertices. It is a O(ELogV) function void dijkstra( struct Graph* graph, int src) { // Get the number of vertices in graph int V = graph->V; // dist values used to pick // minimum weight edge in cut int dist[V]; // minHeap represents set E struct MinHeap* minHeap = createMinHeap(V); // Initialize min heap with all // vertices. dist value of all vertices for ( int v = 0; v < V; ++v) { dist[v] = INT_MAX; minHeap->array[v] = newMinHeapNode(v, dist[v]); minHeap->pos[v] = v; } // Make dist value of src vertex // as 0 so that it is extracted first minHeap->array[src] = newMinHeapNode(src, dist[src]); minHeap->pos[src] = src; dist[src] = 0; decreaseKey(minHeap, src, dist[src]); // Initially size of min heap is equal to V minHeap->size = V; // In the followin loop, // min heap contains all nodes // whose shortest distance // is not yet finalized. while (!isEmpty(minHeap)) { // Extract the vertex with // minimum distance value struct MinHeapNode* minHeapNode = extractMin(minHeap); // Store the extracted vertex number int u = minHeapNode->v; // Traverse through all adjacent // vertices of u (the extracted // vertex) and update // their distance values struct AdjListNode* pCrawl = graph->array[u].head; while (pCrawl != NULL) { int v = pCrawl->dest; // If shortest distance to v is // not finalized yet, and distance to v // through u is less than its // previously calculated distance if (isInMinHeap(minHeap, v) && dist[u] != INT_MAX && pCrawl->weight + dist[u] < dist[v]) { dist[v] = dist[u] + pCrawl->weight; // update distance // value in min heap also decreaseKey(minHeap, v, dist[v]); } pCrawl = pCrawl->next; } } // print the calculated shortest distances printArr(dist, V); } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { // create the graph given in above fugure int V = 9; struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V); addEdge(graph, 0, 1, 4); addEdge(graph, 0, 7, 8); addEdge(graph, 1, 2, 8); addEdge(graph, 1, 7, 11); addEdge(graph, 2, 3, 7); addEdge(graph, 2, 8, 2); addEdge(graph, 2, 5, 4); addEdge(graph, 3, 4, 9); addEdge(graph, 3, 5, 14); addEdge(graph, 4, 5, 10); addEdge(graph, 5, 6, 2); addEdge(graph, 6, 7, 1); addEdge(graph, 6, 8, 6); addEdge(graph, 7, 8, 7); dijkstra(graph, 0); return 0; } |
Python3
# A Python program for Dijkstra's shortest # path algorithm for adjacency # list representation of graph from collections import defaultdict import sys class Heap(): def __init__( self ): self .array = [] self .size = 0 self .pos = [] def newMinHeapNode( self , v, dist): minHeapNode = [v, dist] return minHeapNode # A utility function to swap two nodes # of min heap. Needed for min heapify def swapMinHeapNode( self , a, b): t = self .array[a] self .array[a] = self .array[b] self .array[b] = t # A standard function to heapify at given idx # This function also updates position of nodes # when they are swapped.Position is needed # for decreaseKey() def minHeapify( self , idx): smallest = idx left = 2 * idx + 1 right = 2 * idx + 2 if (left < self .size and self .array[left][ 1 ] < self .array[smallest][ 1 ]): smallest = left if (right < self .size and self .array[right][ 1 ] < self .array[smallest][ 1 ]): smallest = right # The nodes to be swapped in min # heap if idx is not smallest if smallest ! = idx: # Swap positions self .pos[ self .array[smallest][ 0 ]] = idx self .pos[ self .array[idx][ 0 ]] = smallest # Swap nodes self .swapMinHeapNode(smallest, idx) self .minHeapify(smallest) # Standard function to extract minimum # node from heap def extractMin( self ): # Return NULL wif heap is empty if self .isEmpty() = = True : return # Store the root node root = self .array[ 0 ] # Replace root node with last node lastNode = self .array[ self .size - 1 ] self .array[ 0 ] = lastNode # Update position of last node self .pos[lastNode[ 0 ]] = 0 self .pos[root[ 0 ]] = self .size - 1 # Reduce heap size and heapify root self .size - = 1 self .minHeapify( 0 ) return root def isEmpty( self ): return True if self .size = = 0 else False def decreaseKey( self , v, dist): # Get the index of v in heap array i = self .pos[v] # Get the node and update its dist value self .array[i][ 1 ] = dist # Travel up while the complete tree is # not hepified. This is a O(Logn) loop while (i > 0 and self .array[i][ 1 ] < self .array[(i - 1 ) / / 2 ][ 1 ]): # Swap this node with its parent self .pos[ self .array[i][ 0 ] ] = (i - 1 ) / / 2 self .pos[ self .array[(i - 1 ) / / 2 ][ 0 ] ] = i self .swapMinHeapNode(i, (i - 1 ) / / 2 ) # move to parent index i = (i - 1 ) / / 2 ; # A utility function to check if a given # vertex 'v' is in min heap or not def isInMinHeap( self , v): if self .pos[v] < self .size: return True return False def printArr(dist, n): print ( "Vertex Distance from source" ) for i in range (n): print ( "%d %d" % (i,dist[i])) class Graph(): def __init__( self , V): self .V = V self .graph = defaultdict( list ) # Adds an edge to an undirected graph def addEdge( self , src, dest, weight): # Add an edge from src to dest. A new node # is added to the adjacency list of src. The # node is added at the beginning. The first # element of the node has the destination # and the second elements has the weight newNode = [dest, weight] self .graph[src].insert( 0 , newNode) # Since graph is undirected, add an edge # from dest to src also newNode = [src, weight] self .graph[dest].insert( 0 , newNode) # The main function that calculates distances # of shortest paths from src to all vertices. # It is a O(ELogV) function def dijkstra( self , src): V = self .V # Get the number of vertices in graph dist = [] # dist values used to pick minimum # weight edge in cut # minHeap represents set E minHeap = Heap() # Initialize min heap with all vertices. # dist value of all vertices for v in range (V): dist.append( 1e7 ) minHeap.array.append( minHeap. newMinHeapNode(v, dist[v])) minHeap.pos.append(v) # Make dist value of src vertex as 0 so # that it is extracted first minHeap.pos[src] = src dist[src] = 0 minHeap.decreaseKey(src, dist[src]) # Initially size of min heap is equal to V minHeap.size = V; # In the following loop, # min heap contains all nodes # whose shortest distance is not yet finalized. while minHeap.isEmpty() = = False : # Extract the vertex # with minimum distance value newHeapNode = minHeap.extractMin() u = newHeapNode[ 0 ] # Traverse through all adjacent vertices of # u (the extracted vertex) and update their # distance values for pCrawl in self .graph[u]: v = pCrawl[ 0 ] # If shortest distance to v is not finalized # yet, and distance to v through u is less # than its previously calculated distance if (minHeap.isInMinHeap(v) and dist[u] ! = 1e7 and pCrawl[ 1 ] + dist[u] < dist[v]): dist[v] = pCrawl[ 1 ] + dist[u] # update distance value # in min heap also minHeap.decreaseKey(v, dist[v]) printArr(dist,V) # Driver program to test the above functions graph = Graph( 9 ) graph.addEdge( 0 , 1 , 4 ) graph.addEdge( 0 , 7 , 8 ) graph.addEdge( 1 , 2 , 8 ) graph.addEdge( 1 , 7 , 11 ) graph.addEdge( 2 , 3 , 7 ) graph.addEdge( 2 , 8 , 2 ) graph.addEdge( 2 , 5 , 4 ) graph.addEdge( 3 , 4 , 9 ) graph.addEdge( 3 , 5 , 14 ) graph.addEdge( 4 , 5 , 10 ) graph.addEdge( 5 , 6 , 2 ) graph.addEdge( 6 , 7 , 1 ) graph.addEdge( 6 , 8 , 6 ) graph.addEdge( 7 , 8 , 7 ) graph.dijkstra( 0 ) # This code is contributed by Divyanshu Mehta |
JAVA
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { static class AdjListNode { int vertex, weight; AdjListNode( int v, int w) { vertex = v; weight = w; } int getVertex() { return vertex; } int getWeight() { return weight; } } // Function to find the shortest distance of all the // vertices from the source vertex S. public static int [] dijkstra( int V, ArrayList<ArrayList<AdjListNode> > graph, int source) { int [] distance = new int [V]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) distance[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; distance = 0 ; PriorityQueue<AdjListNode> pq = new PriorityQueue<>( (v1, v2) -> v1.getWeight() - v2.getWeight()); pq.add( new AdjListNode(source, 0 )); while (pq.size() > 0 ) { AdjListNode current = pq.poll(); for (AdjListNode n : graph.get(current.getVertex())) { if (distance[current.getVertex()] + n.getWeight() < distance[n.getVertex()]) { distance[n.getVertex()] = n.getWeight() + distance[current.getVertex()]; pq.add( new AdjListNode( n.getVertex(), distance[n.getVertex()])); } } } // If you want to calculate distance from source to // a particular target, you can return // distance[target] return distance; } public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 9 ; ArrayList<ArrayList<AdjListNode> > graph = new ArrayList<>(); for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) { graph.add( new ArrayList<>()); } int source = 0 ; graph.get( 0 ).add( new AdjListNode( 1 , 4 )); graph.get( 0 ).add( new AdjListNode( 7 , 8 )); graph.get( 1 ).add( new AdjListNode( 2 , 8 )); graph.get( 1 ).add( new AdjListNode( 7 , 11 )); graph.get( 1 ).add( new AdjListNode( 0 , 7 )); graph.get( 2 ).add( new AdjListNode( 1 , 8 )); graph.get( 2 ).add( new AdjListNode( 3 , 7 )); graph.get( 2 ).add( new AdjListNode( 8 , 2 )); graph.get( 2 ).add( new AdjListNode( 5 , 4 )); graph.get( 3 ).add( new AdjListNode( 2 , 7 )); graph.get( 3 ).add( new AdjListNode( 4 , 9 )); graph.get( 3 ).add( new AdjListNode( 5 , 14 )); graph.get( 4 ).add( new AdjListNode( 3 , 9 )); graph.get( 4 ).add( new AdjListNode( 5 , 10 )); graph.get( 5 ).add( new AdjListNode( 4 , 10 )); graph.get( 5 ).add( new AdjListNode( 6 , 2 )); graph.get( 6 ).add( new AdjListNode( 5 , 2 )); graph.get( 6 ).add( new AdjListNode( 7 , 1 )); graph.get( 6 ).add( new AdjListNode( 8 , 6 )); graph.get( 7 ).add( new AdjListNode( 0 , 8 )); graph.get( 7 ).add( new AdjListNode( 1 , 11 )); graph.get( 7 ).add( new AdjListNode( 6 , 1 )); graph.get( 7 ).add( new AdjListNode( 8 , 7 )); graph.get( 8 ).add( new AdjListNode( 2 , 2 )); graph.get( 8 ).add( new AdjListNode( 6 , 6 )); graph.get( 8 ).add( new AdjListNode( 7 , 1 )); int [] distance = dijkstra(V, graph, source); // Printing the Output System.out.println( "Vertex " + " Distance from Source" ); for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) { System.out.println(i + " " + distance[i]); } } } |
输出:
Vertex Distance from Source0 01 42 123 194 215 116 97 88 14
时间复杂性: 上述代码/算法的时间复杂度看起来是O(V^2),因为有两个嵌套的while循环。如果我们仔细观察,我们可以观察到内部循环中的语句执行O(V+E)次(类似于BFS)。内部循环有decreaseKey()操作,需要O(LogV)时间。所以总的时间复杂度是O(E+V)*O(LogV),也就是O((E+V)*LogV)=O(ELogV) 注意,上面的代码使用二进制堆实现优先级队列。使用Fibonacci堆可以将时间复杂度降低到O(E+VLogV)。原因是,斐波那契堆减少密钥操作需要O(1)时间,而二进制堆需要O(Logn)时间。 笔记:
- 代码计算最短距离,但不计算路径信息。我们可以创建一个父数组,在距离更新时更新父数组(如 prim的实现 )并使用它显示从源到不同顶点的最短路径。
- 该代码用于无向图,同样的dijekstra函数也可用于有向图。
- 该代码查找从源到所有顶点的最短距离。如果我们只对从源到单个目标的最短距离感兴趣,我们可以在拾取的最小距离顶点等于目标时打破for循环(算法步骤3.a)。
- Dijkstra算法不适用于具有负权边的图。对于具有负权边的图, 贝尔曼-福特算法 可以使用,我们将很快作为一个单独的帖子进行讨论。 Dijkstra最短路径算法中的打印路径 基于STL集合的Dijkstra最短路径算法
参考资料: Clifford Stein、Thomas H.Cormen、Charles E.Leiserson、Ronald L。 Sanjoy Dasgupta、Christos Papadimitriou、Umesh Vazirani的算法
如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



