两个数的GCD是将两个数相除的最大数。求GCD的一个简单方法是将两个数分解并乘以公共素数因子。
null
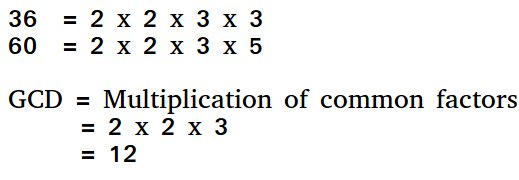
GCD的基本欧几里德算法 该算法基于以下事实。
- 如果我们从一个较大的数字中减去一个较小的数字(我们减少了一个较大的数字),GCD不会改变。因此,如果我们不断重复减去两个中较大的一个,我们最终得到的是GCD。
- 现在不是减法,如果我们除以较小的数字,当我们找到余数0时,算法停止。
下面是使用欧几里德算法计算gcd的递归函数。
CPP
// C++ program to demonstrate // Basic Euclidean Algorithm #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function to return // gcd of a and b int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // Driver Code int main() { int a = 10, b = 15; cout << "GCD(" << a << ", " << b << ") = " << gcd(a, b) << endl; a = 35, b = 10; cout << "GCD(" << a << ", " << b << ") = " << gcd(a, b) << endl; a = 31, b = 2; cout << "GCD(" << a << ", " << b << ") = " << gcd(a, b) << endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed // by Nimit Garg |
C
// C program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm #include <stdio.h> // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b%a, a); } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int a = 10, b = 15; printf ( "GCD(%d, %d) = %dn" , a, b, gcd(a, b)); a = 35, b = 10; printf ( "GCD(%d, %d) = %dn" , a, b, gcd(a, b)); a = 31, b = 2; printf ( "GCD(%d, %d) = %dn" , a, b, gcd(a, b)); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to demonstrate working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; class GFG { // extended Euclidean Algorithm public static int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0 ) return b; return gcd(b%a, a); } // Driver Program public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10 , b = 15 , g; g = gcd(a, b); System.out.println( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b+ ") = " + g); a = 35 ; b = 10 ; g = gcd(a, b); System.out.println( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b+ ") = " + g); a = 31 ; b = 2 ; g = gcd(a, b); System.out.println( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b+ ") = " + g); } } // Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG <(0_o)> |
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate Basic Euclidean Algorithm # Function to return gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if a = = 0 : return b return gcd(b % a, a) a = 10 b = 15 print ( "gcd(" , a , "," , b, ") = " , gcd(a, b)) a = 35 b = 10 print ( "gcd(" , a , "," , b, ") = " , gcd(a, b)) a = 31 b = 2 print ( "gcd(" , a , "," , b, ") = " , gcd(a, b)) # Code Contributed By Mohit Gupta_OMG <(0_o)> |
C#
using System; class GFG { public static int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int a = 10, b = 15, g; g = gcd(a, b); Console.WriteLine( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b + ") = " + g); a = 35; b = 10; g = gcd(a, b); Console.WriteLine( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b + ") = " + g); a = 31; b = 2; g = gcd(a, b); Console.WriteLine( "GCD(" + a + " , " + b + ") = " + g); } } // This code is contributed by ajit |
PHP
<?php // PHP program to demonstrate // Basic Euclidean Algorithm // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd( $a , $b ) { if ( $a == 0) return $b ; return gcd( $b % $a , $a ); } // Driver Code $a = 10; $b = 15; echo "GCD(" , $a , "," , $b , ") = " , gcd( $a , $b ); echo "" ; $a = 35; $b = 10; echo "GCD(" , $a , "," , $b , ") = " , gcd( $a , $b ); echo "" ; $a = 31; $b = 2; echo "GCD(" , $a , "," , $b , ") = " , gcd( $a , $b ); // This code is contributed by m_kit ?> |
Javascript
<script> // JavaScript program to demonstrate // Basic Euclidean Algorithm // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd( a, b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // Driver Code let a = 10, b = 15; document.write( "GCD(" + a + ", " + b + ") = " + gcd(a, b) + "<br/>" ); a = 35, b = 10; document.write( "GCD(" + a + ", " + b + ") = " + gcd(a, b) + "<br/>" ); a = 31, b = 2; document.write( "GCD(" + a + ", " + b + ") = " + gcd(a, b) + "<br/>" ); // This code contributed by aashish1995 </script> |
输出:
GCD(10, 15) = 5GCD(35, 10) = 5GCD(31, 2) = 1
时间复杂性: O(对数最大值(a,b)) 扩展欧几里德算法: 扩展的欧几里德算法还可以找到整数系数x和y,以便:
ax + by = gcd(a, b)
例如:
Input: a = 30, b = 20Output: gcd = 10 x = 1, y = -1(Note that 30*1 + 20*(-1) = 10)Input: a = 35, b = 15Output: gcd = 5 x = 1, y = -2(Note that 35*1 + 15*(-2) = 5)
扩展的欧几里德算法使用递归调用gcd(b%a,a)计算的结果更新gcd(a,b)的结果。让递归调用计算的x和y的值为x 1. 还有y 1. .x和y使用以下表达式进行更新。
x = y1 - ⌊b/a⌋ * x1y = x1
下面是基于上述公式的实现。
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate working of // extended Euclidean Algorithm #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Function for extended Euclidean Algorithm int gcdExtended( int a, int b, int *x, int *y) { // Base Case if (a == 0) { *x = 0; *y = 1; return b; } int x1, y1; // To store results of recursive call int gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1); // Update x and y using results of // recursive call *x = y1 - (b/a) * x1; *y = x1; return gcd; } // Driver Code int main() { int x, y, a = 35, b = 15; int g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y); cout << "GCD(" << a << ", " << b << ") = " << g << endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed by TusharSabhani |
C
// C program to demonstrate working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm #include <stdio.h> // C function for extended Euclidean Algorithm int gcdExtended( int a, int b, int *x, int *y) { // Base Case if (a == 0) { *x = 0; *y = 1; return b; } int x1, y1; // To store results of recursive call int gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, &x1, &y1); // Update x and y using results of recursive // call *x = y1 - (b/a) * x1; *y = x1; return gcd; } // Driver Program int main() { int x, y; int a = 35, b = 15; int g = gcdExtended(a, b, &x, &y); printf ( "gcd(%d, %d) = %d" , a, b, g); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to demonstrate working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; class GFG { // extended Euclidean Algorithm public static int gcdExtended( int a, int b, int x, int y) { // Base Case if (a == 0 ) { x = 0 ; y = 1 ; return b; } int x1= 1 , y1= 1 ; // To store results of recursive call int gcd = gcdExtended(b%a, a, x1, y1); // Update x and y using results of recursive // call x = y1 - (b/a) * x1; y = x1; return gcd; } // Driver Program public static void main(String[] args) { int x= 1 , y= 1 ; int a = 35 , b = 15 ; int g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y); System.out.print( "gcd(" + a + " , " + b+ ") = " + g); } } // Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG <(0-o)> |
Python3
# Python program to demonstrate working of extended # Euclidean Algorithm # function for extended Euclidean Algorithm def gcdExtended(a, b): # Base Case if a = = 0 : return b, 0 , 1 gcd, x1, y1 = gcdExtended(b % a, a) # Update x and y using results of recursive # call x = y1 - (b / / a) * x1 y = x1 return gcd, x, y # Driver code a, b = 35 , 15 g, x, y = gcdExtended(a, b) print ( "gcd(" , a , "," , b, ") = " , g) |
C#
// C# program to demonstrate working // of extended Euclidean Algorithm using System; class GFG { // extended Euclidean Algorithm public static int gcdExtended( int a, int b, int x, int y) { // Base Case if (a == 0) { x = 0; y = 1; return b; } // To store results of // recursive call int x1 = 1, y1 = 1; int gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x1, y1); // Update x and y using // results of recursive call x = y1 - (b / a) * x1; y = x1; return gcd; } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int x = 1, y = 1; int a = 35, b = 15; int g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y); Console.WriteLine( "gcd(" + a + " , " + b + ") = " + g); } } // This code is contributed by m_kit |
PHP
<?php // PHP program to demonstrate // working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm // PHP function for // extended Euclidean // Algorithm function gcdExtended( $a , $b , $x , $y ) { // Base Case if ( $a == 0) { $x = 0; $y = 1; return $b ; } // To store results // of recursive call $gcd = gcdExtended( $b % $a , $a , $x , $y ); // Update x and y using // results of recursive // call $x = $y - floor ( $b / $a ) * $x ; $y = $x ; return $gcd ; } // Driver Code $x = 0; $y = 0; $a = 35; $b = 15; $g = gcdExtended( $a , $b , $x , $y ); echo "gcd(" , $a ; echo ", " , $b , ")" ; echo " = " , $g ; // This code is contributed by ajit ?> |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to demonstrate // working of extended // Euclidean Algorithm // Javascript function for // extended Euclidean // Algorithm function gcdExtended(a, b, x, y) { // Base Case if (a == 0) { x = 0; y = 1; return b; } // To store results // of recursive call let gcd = gcdExtended(b % a, a, x, y); // Update x and y using // results of recursive // call x = y - (b / a) * x; y = x; return gcd; } // Driver Code let x = 0; let y = 0; let a = 35; let b = 15; let g = gcdExtended(a, b, x, y); document.write( "gcd(" + a); document.write( ", " + b + ")" ); document.write( " = " + g); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal </script> |
输出:
gcd(35, 15) = 5
扩展算法是如何工作的?
As seen above, x and y are results for inputs a and b, a.x + b.y = gcd ----(1) And x1 and y1 are results for inputs b%a and a (b%a).x1 + a.y1 = gcd When we put b%a = (b - (⌊b/a⌋).a) in above, we get following. Note that ⌊b/a⌋ is floor(b/a) (b - (⌊b/a⌋).a).x1 + a.y1 = gcdAbove equation can also be written as below b.x1 + a.(y1 - (⌊b/a⌋).x1) = gcd ---(2)After comparing coefficients of 'a' and 'b' in (1) and (2), we get following x = y1 - ⌊b/a⌋ * x1 y = x1
扩展算法如何有用? 当a和b是互质(或gcd为1)时,扩展的欧几里德算法特别有用。因为x是“a模b”的模乘逆,y是“b模a”的模乘逆。特别是模乘逆的计算是RSA公钥加密方法中的一个重要步骤。 参考资料: http://e-maxx.ru/algo/extended_euclid_algorithm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euclidean_algorithm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extended_Euclidean_algorithm 本文由 安克尔 。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



