定义二叉树的高度有两种约定 1) 从根节点到最深节点的最长路径上的节点数。 2) 从根节点到最深节点的最长路径上的边数。
null
在这篇文章中,遵循了第一个惯例。例如,下面这棵树的高度是3。
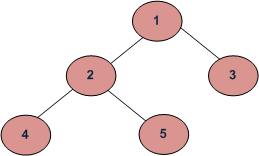
讨论了求二叉树高度的递推方法 在这里 .如何在没有递归的情况下找到高度?我们可以使用水平顺序遍历来查找高度,而无需递归。这个想法是一层一层地穿越。每当向下移动到某个标高时,将高度增加1(高度初始化为0)。计算每个级别的节点数,当下一级别的节点数为0时停止遍历。
下面是使用队列查找级别顺序遍历的详细算法。
Create a queue.Push root into the queue.height = 0nodeCount = 0 // Number of nodes in the current level.// If the number of nodes in the queue is 0, it implies that all the levels of the tree // have been parsed. So, return the height. Otherwise count the number of nodes in the current// level and push the children of all the nodes in the current level to the queue. Loop nodeCount = size of queue // If the number of nodes at this level is 0, return height if nodeCount is 0 return Height; else increase Height // Remove nodes of this level and add nodes of // next level while (nodeCount > 0) push its children to queue pop node from front decrease nodeCount // At this point, queue has nodes of next level
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
#include <iostream> #include <queue> using namespace std; // This approach counts the number of nodes from root to the // leaf to calculate the height of the tree. // Defining the structure of a Node. class Node { public : int data; Node* left; Node* right; }; // Helper function to create a newnode. // Input: Data for the newnode. // Return: Address of the newly created node. Node* createNode( int data) { Node* newnode = new Node(); newnode->data = data; newnode->left = NULL; newnode->right = NULL; return newnode; } // Function to calculate the height of given Binary Tree. // Input: Address of the root node of Binary Tree. // Return: Height of Binary Tree as a integer. This includes // the number of nodes from root to the leaf. int calculateHeight(Node* root) { queue<Node*> nodesInLevel; int height = 0; int nodeCount = 0; // Calculate number of nodes in a level. Node* currentNode; // Pointer to store the address of a // node in the current level. if (root == NULL) { return 0; } nodesInLevel.push(root); while (!nodesInLevel.empty()) { // This while loop runs for every level and // increases the height by 1 in each iteration. If // the queue is empty then it implies that the last // level of tree has been parsed. height++; // Create another while loop which will insert all // the child nodes of the current level in the // queue. nodeCount = nodesInLevel.size(); while (nodeCount--) { currentNode = nodesInLevel.front(); // Check if the current nodes has left child and // insert it in the queue. if (currentNode->left != NULL) { nodesInLevel.push(currentNode->left); } // Check if the current nodes has right child // and insert it in the queue. if (currentNode->right != NULL) { nodesInLevel.push(currentNode->right); } // Once the children of the current node are // inserted. Delete the current node. nodesInLevel.pop(); } } return height; } // Driver Function. int main() { // Creating a binary tree. Node* root = NULL; root = createNode(1); root->left = createNode(2); root->left->left = createNode(4); root->left->right = createNode(5); root->right = createNode(3); cout << "The height of the binary tree using iterative " "method is: " << calculateHeight(root) << "." ; return 0; } |
JAVA
// An iterative java program to find height of binary tree import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; // A binary tree node class Node { int data; Node left, right; Node( int item) { data = item; left = right; } } class BinaryTree { Node root; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree int treeHeight(Node node) { // Base Case if (node == null ) return 0 ; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.add(node); int height = 0 ; while ( 1 == 1 ) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates number of nodes // at current level. int nodeCount = q.size(); if (nodeCount == 0 ) return height; height++; // Dequeue all nodes of current level and Enqueue all // nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0 ) { Node newnode = q.peek(); q.remove(); if (newnode.left != null ) q.add(newnode.left); if (newnode.right != null ) q.add(newnode.right); nodeCount--; } } } // Driver program to test above functions public static void main(String args[]) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); // Let us create a binary tree shown in above diagram tree.root = new Node( 1 ); tree.root.left = new Node( 2 ); tree.root.right = new Node( 3 ); tree.root.left.left = new Node( 4 ); tree.root.left.right = new Node( 5 ); System.out.println( "Height of tree is " + tree.treeHeight(tree.root)); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal |
Python3
# Program to find height of tree by Iteration Method # A binary tree node class Node: # Constructor to create new node def __init__( self , data): self .data = data self .left = None self .right = None # Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree def treeHeight(root): # Base Case if root is None : return 0 # Create a empty queue for level order traversal q = [] # Enqueue Root and Initialize Height q.append(root) height = 0 while ( True ): # nodeCount(queue size) indicates number of nodes # at current level nodeCount = len (q) if nodeCount = = 0 : return height height + = 1 # Dequeue all nodes of current level and Enqueue # all nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0 ): node = q[ 0 ] q.pop( 0 ) if node.left is not None : q.append(node.left) if node.right is not None : q.append(node.right) nodeCount - = 1 # Driver program to test above function # Let us create binary tree shown in above diagram root = Node( 1 ) root.left = Node( 2 ) root.right = Node( 3 ) root.left.left = Node( 4 ) root.left.right = Node( 5 ) print ( "Height of tree is" , treeHeight(root)) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007) |
C#
// An iterative C# program to // find height of binary tree using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // A binary tree node class Node { public int data; public Node left, right; public Node( int item) { data = item; left = right; } } public class BinaryTree { Node root; // Iterative method to find // height of Binary Tree int treeHeight(Node node) { // Base Case if (node == null ) return 0; // Create an empty queue // for level order traversal Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>(); // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.Enqueue(node); int height = 0; while (1 == 1) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates // number of nodes at current level. int nodeCount = q.Count; if (nodeCount == 0) return height; height++; // Dequeue all nodes of current // level and Enqueue all // nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { Node newnode = q.Peek(); q.Dequeue(); if (newnode.left != null ) q.Enqueue(newnode.left); if (newnode.right != null ) q.Enqueue(newnode.right); nodeCount--; } } } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); // Let us create a binary // tree shown in above diagram tree.root = new Node(1); tree.root.left = new Node(2); tree.root.right = new Node(3); tree.root.left.left = new Node(4); tree.root.left.right = new Node(5); Console.WriteLine( "Height of tree is " + tree.treeHeight(tree.root)); } } // This code has been contributed by 29AjayKumar |
Javascript
<script> // An iterative javascript program to find height of binary tree // A binary tree node class Node { constructor(item) { this .data = item; this .left = this .right= null ; } } let root; // Iterative method to find height of Binary Tree function treeHeight(node) { // Base Case if (node == null ) return 0; // Create an empty queue for level order traversal let q = []; // Enqueue Root and initialize height q.push(node); let height = 0; while (1 == 1) { // nodeCount (queue size) indicates number of nodes // at current level. let nodeCount = q.length; if (nodeCount == 0) return height; height++; // Dequeue all nodes of current level and Enqueue all // nodes of next level while (nodeCount > 0) { let newnode = q.shift(); if (newnode.left != null ) q.push(newnode.left); if (newnode.right != null ) q.push(newnode.right); nodeCount--; } } } // Driver program to test above functions // Let us create a binary tree shown in above diagram root = new Node(1); root.left = new Node(2); root.right = new Node(3); root.left.left = new Node(4); root.left.right = new Node(5); document.write( "Height of tree is " + treeHeight(root)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script> |
输出:
The height of the binary tree using iterative method is: 3.
时间复杂性: O(n),其中n是给定二叉树中的节点数。
空间复杂性: O(n),其中n是给定二叉树中的节点数。
本文由 拉胡尔·库马尔 。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



