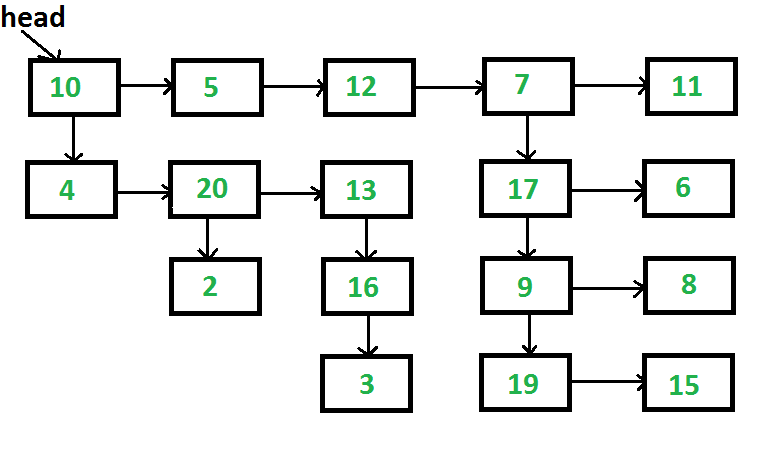
给定一个链表,其中除下一个指针外,每个节点都有一个子指针,该子指针可能指向也可能不指向单独的列表。这些子列表可能有自己的一个或多个子列表,以此类推,以生成一个多级数据结构,如下图所示。您将获得列表第一级的标题。展平列表,使所有节点都显示在一个级别的链接列表中。您需要将列表展平,使第一级的所有节点都应位于第一级,然后是第二级的节点,依此类推。 每个节点都是具有以下定义的C结构。
null
C
struct List { int data; struct List *next; struct List *child; }; |
JAVA
static class List { public int data; public List next; public List child; }; // This code is contributed by pratham76 |
Python3
# A linked list node has data, # next pointer and child pointer class Node: def __init__( self , data): self .data = data self . next = None self .child = None # This code contributed by umadevi9616 |
C#
static class List { public int data; public List next; public List child; }; // This code is contributed by rutvik_56 |
Javascript
<script> class List { constructor(){ this .data = 0; this .next = null ; this .child = null ; } } // This code contributed by aashish1995 </script> |
以上列表应转换为10->5->12->7->11->4->20->13->17->6->2->16->9->8->3->19->15
问题清楚地表明,我们需要一层一层地扁平化。解决方案的想法是,我们从第一级开始,逐个处理所有节点,如果一个节点有一个子节点,那么我们将子节点附加到列表的末尾,否则我们什么都不做。处理第一级后,所有下一级节点都将追加到第一级之后。附加的节点也遵循相同的过程。
1) Take "cur" pointer, which will point to head of the first level of the list2) Take "tail" pointer, which will point to end of the first level of the list3) Repeat the below procedure while "curr" is not NULL. I) if current node has a child then a) append this new child list to the "tail" tail->next = cur->child b) find the last node of new child list and update "tail" tmp = cur->child; while (tmp->next != NULL) tmp = tmp->next; tail = tmp; II) move to the next node. i.e. cur = cur->next
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ Program to flatten list with // next and child pointers #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Macro to find number of elements in array #define SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0])) // A linked list node has data, // next pointer and child pointer class Node { public : int data; Node *next; Node *child; }; // A utility function to create a linked list // with n nodes. The data of nodes is taken // from arr[]. All child pointers are set as NULL Node *createList( int *arr, int n) { Node *head = NULL; Node *p; int i; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (head == NULL) head = p = new Node(); else { p->next = new Node(); p = p->next; } p->data = arr[i]; p->next = p->child = NULL; } return head; } // A utility function to print // all nodes of a linked list void printList(Node *head) { while (head != NULL) { cout << head->data << " " ; head = head->next; } cout<<endl; } // This function creates the input // list. The created list is same // as shown in the above figure Node *createList( void ) { int arr1[] = {10, 5, 12, 7, 11}; int arr2[] = {4, 20, 13}; int arr3[] = {17, 6}; int arr4[] = {9, 8}; int arr5[] = {19, 15}; int arr6[] = {2}; int arr7[] = {16}; int arr8[] = {3}; /* create 8 linked lists */ Node *head1 = createList(arr1, SIZE(arr1)); Node *head2 = createList(arr2, SIZE(arr2)); Node *head3 = createList(arr3, SIZE(arr3)); Node *head4 = createList(arr4, SIZE(arr4)); Node *head5 = createList(arr5, SIZE(arr5)); Node *head6 = createList(arr6, SIZE(arr6)); Node *head7 = createList(arr7, SIZE(arr7)); Node *head8 = createList(arr8, SIZE(arr8)); /* modify child pointers to create the list shown above */ head1->child = head2; head1->next->next->next->child = head3; head3->child = head4; head4->child = head5; head2->next->child = head6; head2->next->next->child = head7; head7->child = head8; /* Return head pointer of first linked list. Note that all nodes are reachable from head1 */ return head1; } /* The main function that flattens a multilevel linked list */ void flattenList(Node *head) { /*Base case*/ if (head == NULL) return ; Node *tmp; /* Find tail node of first level linked list */ Node *tail = head; while (tail->next != NULL) tail = tail->next; // One by one traverse through all nodes of first level // linked list till we reach the tail node Node *cur = head; while (cur != tail) { // If current node has a child if (cur->child) { // then append the child at the end of current list tail->next = cur->child; // and update the tail to new last node tmp = cur->child; while (tmp->next) tmp = tmp->next; tail = tmp; } // Change current node cur = cur->next; } } // Driver code int main( void ) { Node *head = NULL; head = createList(); flattenList(head); printList(head); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
// Program to flatten list with next and child pointers #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // Macro to find number of elements in array #define SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0])) // A linked list node has data, next pointer and child pointer struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; struct Node *child; }; // A utility function to create a linked list with n nodes. The data // of nodes is taken from arr[]. All child pointers are set as NULL struct Node *createList( int *arr, int n) { struct Node *head = NULL; struct Node *p; int i; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (head == NULL) head = p = ( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof (*p)); else { p->next = ( struct Node *) malloc ( sizeof (*p)); p = p->next; } p->data = arr[i]; p->next = p->child = NULL; } return head; } // A utility function to print all nodes of a linked list void printList( struct Node *head) { while (head != NULL) { printf ( "%d " , head->data); head = head->next; } printf ( "" ); } // This function creates the input list. The created list is same // as shown in the above figure struct Node *createList( void ) { int arr1[] = {10, 5, 12, 7, 11}; int arr2[] = {4, 20, 13}; int arr3[] = {17, 6}; int arr4[] = {9, 8}; int arr5[] = {19, 15}; int arr6[] = {2}; int arr7[] = {16}; int arr8[] = {3}; /* create 8 linked lists */ struct Node *head1 = createList(arr1, SIZE(arr1)); struct Node *head2 = createList(arr2, SIZE(arr2)); struct Node *head3 = createList(arr3, SIZE(arr3)); struct Node *head4 = createList(arr4, SIZE(arr4)); struct Node *head5 = createList(arr5, SIZE(arr5)); struct Node *head6 = createList(arr6, SIZE(arr6)); struct Node *head7 = createList(arr7, SIZE(arr7)); struct Node *head8 = createList(arr8, SIZE(arr8)); /* modify child pointers to create the list shown above */ head1->child = head2; head1->next->next->next->child = head3; head3->child = head4; head4->child = head5; head2->next->child = head6; head2->next->next->child = head7; head7->child = head8; /* Return head pointer of first linked list. Note that all nodes are reachable from head1 */ return head1; } /* The main function that flattens a multilevel linked list */ void flattenList( struct Node *head) { /*Base case*/ if (head == NULL) return ; struct Node *tmp; /* Find tail node of first level linked list */ struct Node *tail = head; while (tail->next != NULL) tail = tail->next; // One by one traverse through all nodes of first level // linked list till we reach the tail node struct Node *cur = head; while (cur != tail) { // If current node has a child if (cur->child) { // then append the child at the end of current list tail->next = cur->child; // and update the tail to new last node tmp = cur->child; while (tmp->next) tmp = tmp->next; tail = tmp; } // Change current node cur = cur->next; } } // A driver program to test above functions int main( void ) { struct Node *head = NULL; head = createList(); flattenList(head); printList(head); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to flatten linked list with next and child pointers class LinkedList { static Node head; class Node { int data; Node next, child; Node( int d) { data = d; next = child = null ; } } // A utility function to create a linked list with n nodes. The data // of nodes is taken from arr[]. All child pointers are set as NULL Node createList( int arr[], int n) { Node node = null ; Node p = null ; int i; for (i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { if (node == null ) { node = p = new Node(arr[i]); } else { p.next = new Node(arr[i]); p = p.next; } p.next = p.child = null ; } return node; } // A utility function to print all nodes of a linked list void printList(Node node) { while (node != null ) { System.out.print(node.data + " " ); node = node.next; } System.out.println( "" ); } Node createList() { int arr1[] = new int []{ 10 , 5 , 12 , 7 , 11 }; int arr2[] = new int []{ 4 , 20 , 13 }; int arr3[] = new int []{ 17 , 6 }; int arr4[] = new int []{ 9 , 8 }; int arr5[] = new int []{ 19 , 15 }; int arr6[] = new int []{ 2 }; int arr7[] = new int []{ 16 }; int arr8[] = new int []{ 3 }; /* create 8 linked lists */ Node head1 = createList(arr1, arr1.length); Node head2 = createList(arr2, arr2.length); Node head3 = createList(arr3, arr3.length); Node head4 = createList(arr4, arr4.length); Node head5 = createList(arr5, arr5.length); Node head6 = createList(arr6, arr6.length); Node head7 = createList(arr7, arr7.length); Node head8 = createList(arr8, arr8.length); /* modify child pointers to create the list shown above */ head1.child = head2; head1.next.next.next.child = head3; head3.child = head4; head4.child = head5; head2.next.child = head6; head2.next.next.child = head7; head7.child = head8; /* Return head pointer of first linked list. Note that all nodes are reachable from head1 */ return head1; } /* The main function that flattens a multilevel linked list */ void flattenList(Node node) { /*Base case*/ if (node == null ) { return ; } Node tmp = null ; /* Find tail node of first level linked list */ Node tail = node; while (tail.next != null ) { tail = tail.next; } // One by one traverse through all nodes of first level // linked list till we reach the tail node Node cur = node; while (cur != tail) { // If current node has a child if (cur.child != null ) { // then append the child at the end of current list tail.next = cur.child; // and update the tail to new last node tmp = cur.child; while (tmp.next != null ) { tmp = tmp.next; } tail = tmp; } // Change current node cur = cur.next; } } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); head = list.createList(); list.flattenList(head); list.printList(head); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal |
Python3
# Python3 Program to flatten list with # next and child pointers # A linked list node has data, # next pointer and child pointer class Node: def __init__( self , data): self .data = data self . next = None self .child = None # Return Node def newNode(data): return Node(data) # The main function that flattens # a multilevel linked list def flattenlist(head): # Base case if not head: return # Find tail node of first level linked list temp = head while (temp. next ! = None ): temp = temp. next currNode = head # One by one traverse through all nodes # of first level linked list # till we reach the tail node while (currNode ! = temp): # If current node has a child if (currNode.child): # then append the child # at the end of current list temp. next = currNode.child # and update the tail to new last node tmp = currNode.child while (tmp. next ): tmp = tmp. next temp = tmp # Change current node currNode = currNode. next # A utility function to print # all nodes of a linked list def printList(head): if not head: return while (head): print ( "{}" . format (head.data), end = " " ) head = head. next # Driver code if __name__ = = '__main__' : # Child list of 13 child13 = newNode( 16 ) child13.child = newNode( 3 ) # Child List of 10 head1 = newNode( 4 ) head1. next = newNode( 20 ) head1. next .child = newNode( 2 ) #Child of 20 head1. next . next = newNode( 13 ) head1. next . next .child = child13 # Child of 9 child9 = newNode( 19 ) child9. next = newNode( 15 ) # Child List of 17 child17 = newNode( 9 ) child17. next = newNode( 8 ) child17.child = child9 # Child List of 7 head2 = newNode( 17 ) head2. next = newNode( 6 ) head2.child = child17 # Main List head = newNode( 10 ) head.child = head1 head. next = newNode( 5 ) head. next . next = newNode( 12 ) head. next . next . next = newNode( 7 ) head. next . next . next .child = head2 head. next . next . next . next = newNode( 11 ) flattenlist(head) print ( "Flattened list is: " , end = "") printList(head) # This code is contributed by 0_hero |
C#
// C# program to flatten linked list // with next and child pointers using System; public class LinkedList { static Node head; class Node { public int data; public Node next, child; public Node( int d) { data = d; next = child = null ; } } // A utility function to create // a linked list with n nodes. The data // of nodes is taken from arr[]. // All child pointers are set as NULL Node createList( int []arr, int n) { Node node = null ; Node p = null ; int i; for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { if (node == null ) { node = p = new Node(arr[i]); } else { p.next = new Node(arr[i]); p = p.next; } p.next = p.child = null ; } return node; } // A utility function to print // all nodes of a linked list void printList(Node node) { while (node != null ) { Console.Write(node.data + " " ); node = node.next; } Console.WriteLine( "" ); } Node createList() { int []arr1 = new int []{10, 5, 12, 7, 11}; int []arr2 = new int []{4, 20, 13}; int []arr3 = new int []{17, 6}; int []arr4 = new int []{9, 8}; int []arr5 = new int []{19, 15}; int []arr6 = new int []{2}; int []arr7 = new int []{16}; int []arr8 = new int []{3}; /* create 8 linked lists */ Node head1 = createList(arr1, arr1.Length); Node head2 = createList(arr2, arr2.Length); Node head3 = createList(arr3, arr3.Length); Node head4 = createList(arr4, arr4.Length); Node head5 = createList(arr5, arr5.Length); Node head6 = createList(arr6, arr6.Length); Node head7 = createList(arr7, arr7.Length); Node head8 = createList(arr8, arr8.Length); /* modify child pointers to create the list shown above */ head1.child = head2; head1.next.next.next.child = head3; head3.child = head4; head4.child = head5; head2.next.child = head6; head2.next.next.child = head7; head7.child = head8; /* Return head pointer of first linked list. Note that all nodes are reachable from head1 */ return head1; } /* The main function that flattens a multilevel linked list */ void flattenList(Node node) { /*Base case*/ if (node == null ) { return ; } Node tmp = null ; /* Find tail node of first level linked list */ Node tail = node; while (tail.next != null ) { tail = tail.next; } // One by one traverse through // all nodes of first level // linked list till we reach the tail node Node cur = node; while (cur != tail) { // If current node has a child if (cur.child != null ) { // then append the child at // the end of current list tail.next = cur.child; // and update the tail to new last node tmp = cur.child; while (tmp.next != null ) { tmp = tmp.next; } tail = tmp; } // Change current node cur = cur.next; } } // Driver code public static void Main() { LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); head = list.createList(); list.flattenList(head); list.printList(head); } } /* This code is contributed PrinciRaj1992 */ |
输出:
10 5 12 7 11 4 20 13 17 6 2 16 9 8 3 19 15
时间复杂性: 由于每个节点最多访问两次,时间复杂度为O(n),其中n是给定链表中的节点数。
本文由 纳伦德拉·康拉尔卡 。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



