A. 不相交集数据结构 是一种数据结构,用于跟踪被划分为多个不相交(非重叠)子集的一组元素。A. 联合查找算法 是一种算法,可对此类数据结构执行两种有用的操作:
查找: 确定特定元素所在的子集。这可用于确定两个元素是否在同一个子集中。
工会: 将两个子集合并为一个子集。首先我们要检查这两个子集是否属于同一个集合。如果没有,那么我们就不能执行联合。
在这篇文章中,我们将讨论不相交集数据结构的应用。应用程序用于检查给定的图形是否包含循环。
联合查找算法 可用于检查无向图是否包含循环。请注意,我们已经讨论了 循环检测算法 .这是另一种基于 联合发现 。此方法假定图形不包含任何自循环。
我们可以跟踪一维数组中的子集,我们称之为父[]。 让我们考虑下面的图表:
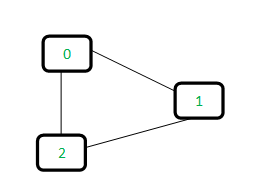
对于每条边,使用边的两个顶点创建子集。如果两个顶点在同一个子集中,则会找到一个循环。
最初,父数组的所有插槽都初始化为-1(意味着每个子集中只有一个项)。
0 1 2-1 -1 -1
现在逐个处理所有边。 边缘0-1: 找到顶点0和1所在的子集。因为它们在不同的子集中,所以我们取它们的并集。要获取并集,请将节点0设为节点1的父节点,反之亦然。
0 1 2 <----- 1 is made parent of 0 (1 is now representative of subset {0, 1})1 -1 -1
边缘1-2: 1在子集1中,2在子集2中。以联合为例。
0 1 2 <----- 2 is made parent of 1 (2 is now representative of subset {0, 1, 2})1 2 -1
边缘0-2: 0在子集2中,2也在子集2中。因此,包括这条边就形成了一个循环。 0的子集如何与2相同? 0->1->2//1是0的父级,2是1的父级
基于上述解释,以下是实现:
C++
// A union-find algorithm to detect cycle in a graph #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // a structure to represent an edge in graph class Edge { public : int src, dest; }; // a structure to represent a graph class Graph { public : // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges Edge* edge; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges Graph* createGraph( int V, int E) { Graph* graph = new Graph(); graph->V = V; graph->E = E; graph->edge = new Edge[graph->E * sizeof (Edge)]; return graph; } // A utility function to find the subset of an element i int find( int parent[], int i) { if (parent[i] == -1) return i; return find(parent, parent[i]); } // A utility function to do union of two subsets void Union( int parent[], int x, int y) { parent[x] = y; } // The main function to check whether a given graph contains // cycle or not int isCycle(Graph* graph) { // Allocate memory for creating V subsets int * parent = new int [graph->V * sizeof ( int )]; // Initialize all subsets as single element sets memset (parent, -1, sizeof ( int ) * graph->V); // Iterate through all edges of graph, find subset of // both vertices of every edge, if both subsets are // same, then there is cycle in graph. for ( int i = 0; i < graph->E; ++i) { int x = find(parent, graph->edge[i].src); int y = find(parent, graph->edge[i].dest); if (x == y) return 1; Union(parent, x, y); } return 0; } // Driver code int main() { /* Let us create the following graph 0 | | 1---2 */ int V = 3, E = 3; Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 graph->edge[0].src = 0; graph->edge[0].dest = 1; // add edge 1-2 graph->edge[1].src = 1; graph->edge[1].dest = 2; // add edge 0-2 graph->edge[2].src = 0; graph->edge[2].dest = 2; if (isCycle(graph)) cout << "graph contains cycle" ; else cout << "graph doesn't contain cycle" ; return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
// A union-find algorithm to detect cycle in a graph #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> // a structure to represent an edge in graph struct Edge { int src, dest; }; // a structure to represent a graph struct Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges struct Edge* edge; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges struct Graph* createGraph( int V, int E) { struct Graph* graph = ( struct Graph*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Graph) ); graph->V = V; graph->E = E; graph->edge = ( struct Edge*) malloc ( graph->E * sizeof ( struct Edge ) ); return graph; } // A utility function to find the subset of an element i int find( int parent[], int i) { if (parent[i] == -1) return i; return find(parent, parent[i]); } // A utility function to do union of two subsets void Union( int parent[], int x, int y) { parent[x] = y; } // The main function to check whether a given graph contains // cycle or not int isCycle( struct Graph* graph ) { // Allocate memory for creating V subsets int *parent = ( int *) malloc ( graph->V * sizeof ( int ) ); // Initialize all subsets as single element sets memset (parent, -1, sizeof ( int ) * graph->V); // Iterate through all edges of graph, find subset of both // vertices of every edge, if both subsets are same, then // there is cycle in graph. for ( int i = 0; i < graph->E; ++i) { int x = find(parent, graph->edge[i].src); int y = find(parent, graph->edge[i].dest); if (x == y) return 1; Union(parent, x, y); } return 0; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { /* Let us create the following graph 0 | | 1---2 */ int V = 3, E = 3; struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 graph->edge[0].src = 0; graph->edge[0].dest = 1; // add edge 1-2 graph->edge[1].src = 1; graph->edge[1].dest = 2; // add edge 0-2 graph->edge[2].src = 0; graph->edge[2].dest = 2; if (isCycle(graph)) printf ( "graph contains cycle" ); else printf ( "graph doesn't contain cycle" ); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java Program for union-find algorithm to detect cycle in a graph import java.util.*; import java.lang.*; import java.io.*; class Graph { int V, E; // V-> no. of vertices & E->no.of edges Edge edge[]; // /collection of all edges class Edge { int src, dest; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges Graph( int v, int e) { V = v; E = e; edge = new Edge[E]; for ( int i= 0 ; i<e; ++i) edge[i] = new Edge(); } // A utility function to find the subset of an element i int find( int parent[], int i) { if (parent[i] == - 1 ) return i; return find(parent, parent[i]); } // A utility function to do union of two subsets void Union( int parent[], int x, int y) { parent[x] = y; } // The main function to check whether a given graph // contains cycle or not int isCycle( Graph graph) { // Allocate memory for creating V subsets int parent[] = new int [graph.V]; // Initialize all subsets as single element sets for ( int i= 0 ; i<graph.V; ++i) parent[i]=- 1 ; // Iterate through all edges of graph, find subset of both // vertices of every edge, if both subsets are same, then // there is cycle in graph. for ( int i = 0 ; i < graph.E; ++i) { int x = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].src); int y = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].dest); if (x == y) return 1 ; graph.Union(parent, x, y); } return 0 ; } // Driver Method public static void main (String[] args) { /* Let us create the following graph 0 | | 1---2 */ int V = 3 , E = 3 ; Graph graph = new Graph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 graph.edge[ 0 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].dest = 1 ; // add edge 1-2 graph.edge[ 1 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].dest = 2 ; // add edge 0-2 graph.edge[ 2 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].dest = 2 ; if (graph.isCycle(graph)== 1 ) System.out.println( "graph contains cycle" ); else System.out.println( "graph doesn't contain cycle" ); } } |
Python3
# Python Program for union-find algorithm to detect cycle in a undirected graph # we have one egde for any two vertex i.e 1-2 is either 1-2 or 2-1 but not both from collections import defaultdict #This class represents a undirected graph using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__( self ,vertices): self .V = vertices #No. of vertices self .graph = defaultdict( list ) # default dictionary to store graph # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge( self ,u,v): self .graph[u].append(v) # A utility function to find the subset of an element i def find_parent( self , parent,i): if parent[i] = = - 1 : return i if parent[i]! = - 1 : return self .find_parent(parent,parent[i]) # A utility function to do union of two subsets def union( self ,parent,x,y): parent[x] = y # The main function to check whether a given graph # contains cycle or not def isCyclic( self ): # Allocate memory for creating V subsets and # Initialize all subsets as single element sets parent = [ - 1 ] * ( self .V) # Iterate through all edges of graph, find subset of both # vertices of every edge, if both subsets are same, then # there is cycle in graph. for i in self .graph: for j in self .graph[i]: x = self .find_parent(parent, i) y = self .find_parent(parent, j) if x = = y: return True self .union(parent,x,y) # Create a graph given in the above diagram g = Graph( 3 ) g.addEdge( 0 , 1 ) g.addEdge( 1 , 2 ) g.addEdge( 2 , 0 ) if g.isCyclic(): print ( "Graph contains cycle" ) else : print ( "Graph does not contain cycle " ) #This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav |
C#
// C# Program for union-find // algorithm to detect cycle // in a graph using System; class Graph{ // V-> no. of vertices & // E->no.of edges public int V, E; // collection of all edges public Edge []edge; class Edge { public int src, dest; }; // Creates a graph with V // vertices and E edges public Graph( int v, int e) { V = v; E = e; edge = new Edge[E]; for ( int i = 0; i < e; ++i) edge[i] = new Edge(); } // A utility function to find // the subset of an element i int find( int []parent, int i) { if (parent[i] == -1) return i; return find(parent, parent[i]); } // A utility function to do // union of two subsets void Union( int []parent, int x, int y) { parent[x] = y; } // The main function to check // whether a given graph // contains cycle or not int isCycle(Graph graph) { // Allocate memory for // creating V subsets int []parent = new int [graph.V]; // Initialize all subsets as // single element sets for ( int i = 0; i < graph.V; ++i) parent[i] =- 1; // Iterate through all edges of graph, // find subset of both vertices of every // edge, if both subsets are same, then // there is cycle in graph. for ( int i = 0; i < graph.E; ++i) { int x = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].src); int y = graph.find(parent, graph.edge[i].dest); if (x == y) return 1; graph.Union(parent, x, y); } return 0; } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { /* Let us create the following graph 0 | | 1---2 */ int V = 3, E = 3; Graph graph = new Graph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 graph.edge[0].src = 0; graph.edge[0].dest = 1; // add edge 1-2 graph.edge[1].src = 1; graph.edge[1].dest = 2; // add edge 0-2 graph.edge[2].src = 0; graph.edge[2].dest = 2; if (graph.isCycle(graph) == 1) Console.WriteLine( "graph contains cycle" ); else Console.WriteLine( "graph doesn't contain cycle" ); } } // This code is contributed by Princi Singh |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program for union-find // algorithm to detect cycle // in a graph // V-> no. of vertices & // E->no.of edges var V, E; // Collection of all edges var edge; class Edge { constructor() { this .src = 0; this .dest = 0; } }; // Creates a graph with V // vertices and E edges function initialize(v,e) { V = v; E = e; edge = Array.from(Array(E), () => Array()); } // A utility function to find // the subset of an element i function find(parent, i) { if (parent[i] == -1) return i; return find(parent, parent[i]); } // A utility function to do // union of two subsets function Union(parent, x, y) { parent[x] = y; } // The main function to check // whether a given graph // contains cycle or not function isCycle() { // Allocate memory for // creating V subsets var parent = Array(V).fill(0); // Initialize all subsets as // single element sets for ( var i = 0; i < V; ++i) parent[i] =- 1; // Iterate through all edges of graph, // find subset of both vertices of every // edge, if both subsets are same, then // there is cycle in graph. for ( var i = 0; i < E; ++i) { var x = find(parent, edge[i].src); var y = find(parent, edge[i].dest); if (x == y) return 1; Union(parent, x, y); } return 0; } // Driver code /* Let us create the following graph 0 | | 1---2 */ var V = 3, E = 3; initialize(V, E); // Add edge 0-1 edge[0].src = 0; edge[0].dest = 1; // Add edge 1-2 edge[1].src = 1; edge[1].dest = 2; // Add edge 0-2 edge[2].src = 0; edge[2].dest = 2; if (isCycle() == 1) document.write( "graph contains cycle" ); else document.write( "graph doesn't contain cycle" ); // This code is contributed by rutvik_56 </script> |
输出:
graph contains cycle
请注意 工会() 和 查找() 是天真的,在最坏的情况下需要O(n)时间。这些方法可以通过使用 按等级或高度联合 .我们很快就会讨论 按等级联合 在另一个帖子里。 https://youtu.be/mHz-mx-8lJ8?list=PLqM7alHXFySEaZgcg7uRYJFBnYMLti-新罕布什尔州
相关文章: 并集查找算法|集2(按秩并集和路径压缩) 不相交集数据结构(Java实现) 贪婪算法|集2(Kruskal最小生成树算法) 作业排序问题|集2(使用不相交集) 本文由 阿希什·巴恩瓦尔 并由Geeksforgeks团队审核。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



