给定N个元素的数组和形式为lrx的Q查询。对于每个查询,必须输出元素X是否存在于索引L和R(包括)之间的数组中。 先决条件: 莫氏算法 例如:
Input : N = 5 arr = [1, 1, 5, 4, 5] Q = 3 1 3 2 2 5 1 3 5 5 Output : No Yes YesExplanation :For the first query, 2 does not exist between the indices 1 and 3.For the second query, 1 exists between the indices 2 and 5.For the third query, 5 exists between the indices 3 and 5.
天真的方法: 简单的方法是为每个查询遍历从L到R的元素,线性搜索X。在最坏的情况下,从L到R可能有N个元素,因此每个查询的最坏情况时间复杂度为O(N)。因此,对于所有的Q查询,时间复杂度都是O(Q*N)。 使用联合查找方法: 此方法只检查所有连续相等值中的一个元素。如果X不等于这些值,那么算法将跳过所有其他相等的元素,并继续遍历下一个不同的元素。显然,只有当大量连续相等元素时,该算法才有用。 算法:
- 将所有连续的相等元素合并到一个组中。
- 处理查询时,从R开始。让index=R。
- 将[索引]与X进行比较。如果它们相等,则打印“是” 从穿越范围的其他部分中解脱出来。否则,全部跳过 属于[索引]组的连续元素。指数 变为小于该组根的索引的1。
- 继续上述步骤,直到找到X或 索引变为小于L。
- 如果索引变为小于L,则打印“否”。
下面是上述想法的实施。
C++
// Program to determine if the element // exists for different range queries #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Structure to represent a query range struct Query { int L, R, X; }; const int maxn = 100; int root[maxn]; // Find the root of the group containing // the element at index x int find( int x) { return x == root[x] ? x : root[x] = find(root[x]); } // merge the two groups containing elements // at indices x and y into one group int uni( int x, int y) { int p = find(x), q = find(y); if (p != q) { root[p] = root[q]; } } void initialize( int a[], int n, Query q[], int m) { // make n subsets with every // element as its root for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) root[i] = i; // consecutive elements equal in value are // merged into one single group for ( int i = 1; i < n; i++) if (a[i] == a[i - 1]) uni(i, i - 1); } // Driver code int main() { int a[] = { 1, 1, 5, 4, 5 }; int n = sizeof (a) / sizeof (a[0]); Query q[] = { { 0, 2, 2 }, { 1, 4, 1 }, { 2, 4, 5 } }; int m = sizeof (q) / sizeof (q[0]); initialize(a, n, q, m); for ( int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int flag = 0; int l = q[i].L, r = q[i].R, x = q[i].X; int p = r; while (p >= l) { // check if the current element in // consideration is equal to x or not // if it is equal, then x exists in the range if (a[p] == x) { flag = 1; break ; } p = find(p) - 1; } // Print if x exists or not if (flag != 0) cout << x << " exists between [" << l << ", " << r << "] " << endl; else cout << x << " does not exist between [" << l << ", " << r << "] " << endl; } } |
JAVA
// Java program to determine if the element // exists for different range queries import java.util.*; class GFG { // Structure to represent a query range static class Query { int L, R, X; public Query( int L, int R, int X) { this .L = L; this .R = R; this .X = X; } }; static int maxn = 100 ; static int []root = new int [maxn]; // Find the root of the group containing // the element at index x static int find( int x) { if (x == root[x]) return x; else return root[x] = find(root[x]); } // merge the two groups containing elements // at indices x and y into one group static void uni( int x, int y) { int p = find(x), q = find(y); if (p != q) { root[p] = root[q]; } } static void initialize( int a[], int n, Query q[], int m) { // make n subsets with every // element as its root for ( int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) root[i] = i; // consecutive elements equal in value are // merged into one single group for ( int i = 1 ; i < n; i++) if (a[i] == a[i - 1 ]) uni(i, i - 1 ); } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { int a[] = { 1 , 1 , 5 , 4 , 5 }; int n = a.length; Query q[] = { new Query( 0 , 2 , 2 ), new Query( 1 , 4 , 1 ), new Query( 2 , 4 , 5 ) }; int m = q.length; initialize(a, n, q, m); for ( int i = 0 ; i < m; i++) { int flag = 0 ; int l = q[i].L, r = q[i].R, x = q[i].X; int p = r; while (p >= l) { // check if the current element in // consideration is equal to x or not // if it is equal, then x exists in the range if (a[p] == x) { flag = 1 ; break ; } p = find(p) - 1 ; } // Print if x exists or not if (flag != 0 ) System.out.println(x + " exists between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " ); else System.out.println(x + " does not exist between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " ); } } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar |
Python3
# Python3 program to determine if the element # exists for different range queries # Structure to represent a query range class Query: def __init__( self , L, R, X): self .L = L self .R = R self .X = X maxn = 100 root = [ 0 ] * maxn # Find the root of the group containing # the element at index x def find(x): if x = = root[x]: return x else : root[x] = find(root[x]) return root[x] # merge the two groups containing elements # at indices x and y into one group def uni(x, y): p = find(x) q = find(y) if p ! = q: root[p] = root[q] def initialize(a, n, q, m): # make n subsets with every # element as its root for i in range (n): root[i] = i # consecutive elements equal in value are # merged into one single group for i in range ( 1 , n): if a[i] = = a[i - 1 ]: uni(i, i - 1 ) # Driver Code if __name__ = = "__main__" : a = [ 1 , 1 , 5 , 4 , 5 ] n = len (a) q = [Query( 0 , 2 , 2 ), Query( 1 , 4 , 1 ), Query( 2 , 4 , 5 )] m = len (q) initialize(a, n, q, m) for i in range (m): flag = False l = q[i].L r = q[i].R x = q[i].X p = r while p > = l: # check if the current element in # consideration is equal to x or not # if it is equal, then x exists in the range if a[p] = = x: flag = True break p = find(p) - 1 # Print if x exists or not if flag: print ( "%d exists between [%d, %d]" % (x, l, r)) else : print ( "%d does not exists between [%d, %d]" % (x, l, r)) # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552 |
C#
// C# program to determine if the element // exists for different range queries using System; class GFG { // Structure to represent a query range public class Query { public int L, R, X; public Query( int L, int R, int X) { this .L = L; this .R = R; this .X = X; } }; static int maxn = 100; static int []root = new int [maxn]; // Find the root of the group containing // the element at index x static int find( int x) { if (x == root[x]) return x; else return root[x] = find(root[x]); } // merge the two groups containing elements // at indices x and y into one group static void uni( int x, int y) { int p = find(x), q = find(y); if (p != q) { root[p] = root[q]; } } static void initialize( int []a, int n, Query []q, int m) { // make n subsets with every // element as its root for ( int i = 0; i < n; i++) root[i] = i; // consecutive elements equal in value are // merged into one single group for ( int i = 1; i < n; i++) if (a[i] == a[i - 1]) uni(i, i - 1); } // Driver code public static void Main(String []args) { int []a = { 1, 1, 5, 4, 5 }; int n = a.Length; Query []q = { new Query(0, 2, 2), new Query(1, 4, 1), new Query(2, 4, 5)}; int m = q.Length; initialize(a, n, q, m); for ( int i = 0; i < m; i++) { int flag = 0; int l = q[i].L, r = q[i].R, x = q[i].X; int p = r; while (p >= l) { // check if the current element in // consideration is equal to x or not // if it is equal, then x exists in the range if (a[p] == x) { flag = 1; break ; } p = find(p) - 1; } // Print if x exists or not if (flag != 0) Console.WriteLine(x + " exists between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " ); else Console.WriteLine(x + " does not exist between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " ); } } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to determine if the element // exists for different range queries // Structure to represent a query range class Query { constructor(L, R, X) { this .L = L; this .R = R; this .X = X; } }; let maxn = 100; let root = new Array(maxn); // Find the root of the group containing // the element at index x function find(x) { if (x == root[x]) return x; else return root[x] = find(root[x]); } // merge the two groups containing elements // at indices x and y into one group function uni(x, y) { let p = find(x), q = find(y); if (p != q) { root[p] = root[q]; } } function initialize(a, n, q, m) { // make n subsets with every // element as its root for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) root[i] = i; // consecutive elements equal in value are // merged into one single group for (let i = 1; i < n; i++) if (a[i] == a[i - 1]) uni(i, i - 1); } // Driver code let a = [ 1, 1, 5, 4, 5 ]; let n = a.length; let q = [ new Query(0, 2, 2 ), new Query( 1, 4, 1 ), new Query( 2, 4, 5 ) ]; let m = q.length; initialize(a, n, q, m); for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) { let flag = 0; let l = q[i].L, r = q[i].R, x = q[i].X; let p = r; while (p >= l) { // check if the current element in // consideration is equal to x or not // if it is equal, then x exists in the range if (a[p] == x) { flag = 1; break ; } p = find(p) - 1; } // Print if x exists or not if (flag != 0) document.write(x + " exists between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " + "<br>" ); else document.write(x + " does not exist between [" + l + ", " + r + "] " + "<br>" ); } // This code is contributed by gfgking </script> |
2 does not exist between [0, 2] 1 exists between [1, 4] 5 exists between [2, 4]
高效方法(使用莫氏算法): 莫的算法是平方根分解的最佳应用之一。 它的基本思想是使用前一个查询的答案来计算当前查询的答案。这是可能的,因为Mo算法的构造方式是,如果F([L,R])已知,那么F([L+1,R])、F([L-1,R])、F([L,R+1])、F([L,R+1])和F([L,R-1])都可以在O(F)时间内轻松计算。 按照询问的顺序回答问题,则时间复杂度不会提高到需要的程度。为了大大降低时间复杂度,将查询划分为块,然后进行排序。对查询进行排序的确切算法如下:
- 表示块大小=sqrt(N)
- 具有相同L/BLOCK_大小的所有查询都放在同一个块中
- 在一个块中,查询根据其R值进行排序
- 因此,sort函数比较两个查询Q1和Q2,如下所示: 如果出现以下情况,第一季度必须在第二季度之前: 1. L1/块大小
对查询进行排序后,下一步是计算第一个查询的答案,然后回答其余的查询。要确定特定元素是否存在,请检查该范围内元素的频率。非零频率确认该范围内存在该元素。 为了存储元素的频率,以下代码中使用了STL映射。 在给出的示例中,对查询数组排序后的第一个查询是{0,2,2}。散列[0,2]中元素的频率,然后从映射中检查元素2的频率。因为2出现0次,所以打印“否”。 在处理下一个查询(本例中为{1,4,1})时,减少范围[0,1]中元素的频率,并增加范围[3,4]中元素的频率。这一步给出了[1,4]中元素的频率,从地图上可以很容易地看出1存在于这个范围内。 时间复杂性: 预处理部分,即对查询进行排序,需要O(m logm)时间。 R的索引变量最多会发生变化 ![]() 在整个运行过程中,L的时间最多会改变其值
在整个运行过程中,L的时间最多会改变其值 ![]() 时报。因此,处理所有查询需要花费大量时间
时报。因此,处理所有查询需要花费大量时间 ![]() +
+ ![]() =
= ![]() 时间 下面是C++实现上述思想:
时间 下面是C++实现上述思想:
CPP
// CPP code to determine if the element // exists for different range queries #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Variable to represent block size. // This is made global, so compare() // of sort can use it. int block; // Structure to represent a query range struct Query { int L, R, X; }; // Function used to sort all queries so // that all queries of same block are // arranged together and within a block, // queries are sorted in increasing order // of R values. bool compare(Query x, Query y) { // Different blocks, sort by block. if (x.L / block != y.L / block) return x.L / block < y.L / block; // Same block, sort by R value return x.R < y.R; } // Determines if the element is present for all // query ranges. m is number of queries // n is size of array a[]. void queryResults( int a[], int n, Query q[], int m) { // Find block size block = ( int ) sqrt (n); // Sort all queries so that queries of same // blocks are arranged together. sort(q, q + m, compare); // Initialize current L, current R int currL = 0, currR = 0; // To store the frequencies of // elements of the given range map< int , int > mp; // Traverse through all queries for ( int i = 0; i < m; i++) { // L and R values of current range int L = q[i].L, R = q[i].R, X = q[i].X; // Decrement frequencies of extra elements // of previous range. For example if previous // range is [0, 3] and current range is [2, 5], // then the frequencies of a[0] and a[1] are decremented while (currL < L) { mp[a[currL]]--; currL++; } // Increment frequencies of elements of current Range while (currL > L) { mp[a[currL - 1]]++; currL--; } while (currR <= R) { mp[a[currR]]++; currR++; } // Decrement frequencies of elements of previous // range. For example when previous range is [0, 10] // and current range is [3, 8], then frequencies of // a[9] and a[10] are decremented while (currR > R + 1) { mp[a[currR - 1]]--; currR--; } // Print if X exists or not if (mp[X] != 0) cout << X << " exists between [" << L << ", " << R << "] " << endl; else cout << X << " does not exist between [" << L << ", " << R << "] " << endl; } } // Driver program int main() { int a[] = { 1, 1, 5, 4, 5 }; int n = sizeof (a) / sizeof (a[0]); Query q[] = { { 0, 2, 2 }, { 1, 4, 1 }, { 2, 4, 5 } }; int m = sizeof (q) / sizeof (q[0]); queryResults(a, n, q, m); return 0; } |
2 does not exist between [0, 2] 1 exists between [1, 4] 5 exists between [2, 4]
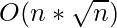


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



