给定两个数N和M。找出阶乘N可以表示为两个或多个连续数之和的方法数。以M为单位打印结果。 例如:
null
Input : N = 3, M = 7Output : 1Explanation: 3! can be expressed in one way, i.e. 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. Hence 1 % 7 = 1Input : N = 4, M = 7Output : 1Explanation: 4! can be expressed in one way, i.e. 7 + 8 + 9 = 24Hence 1 % 7 = 1
A. 简单解决方案 首先是 计算阶乘 ,然后使用 计数将一个数表示为连续数之和的方法 .此解决方案会导致溢出。 下面是一个例子 更好的解决方案 以避免溢出。 让我们考虑r个连续数之和表示为: (a+1)+(a+2)+(a+3)+……+(a+r),简化为(r*(r+2*a+1))/2 因此,(a+1)+(a+2)+(a+3)+……+(a+r)=(r*(r+2*a+1))/2。由于上述表达式等于阶乘N,我们将其写成 2*N!=r*(r+2*a+1) 我们不计算所有对(r,a),而是计算所有对(r,r+2*a+1)。现在,我们正在计算XY=2*N的所有有序对(X,Y)!其中X ![]() 以下是上述方法的实施情况。
以下是上述方法的实施情况。
C++
// CPP program to count number of // ways we can express a factorial // as sum of consecutive numbers #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define MAX 50002 vector< int > primes; // sieve of Eratosthenes to compute // the prime numbers void sieve() { bool isPrime[MAX]; memset (isPrime, true , sizeof (isPrime)); for ( int p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) { if (isPrime[p] == true ) { for ( int i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p) isPrime[i] = false ; } } // Store all prime numbers for ( int p = 2; p < MAX; p++) if (isPrime[p]) primes.push_back(p); } // function to calculate the largest // power of a prime in a number long long int power( long long int x, long long int y) { long long int count = 0; long long int z = y; while (x >= z) { count += (x / z); z *= y; } return count; } // Modular multiplication to avoid // the overflow of multiplication // Please see below for details long long int modMult( long long int a, long long int b, long long int mod) { long long int res = 0; a = a % mod; while (b > 0) { if (b % 2 == 1) res = (res + a) % mod; a = (a * 2) % mod; b /= 2; } return res % mod; } // Returns count of ways to express n! // as sum of consecutives. long long int countWays( long long int n, long long int m) { long long int ans = 1; // We skip 2 (First prime) as we need to // consider only odd primes for ( int i = 1; i < primes.size(); i++) { // compute the largest power of prime long long int powers = power(n, primes[i]); // if the power of current prime number // is zero in N!, power of primes greater // than current prime number will also // be zero, so break out from the loop if (powers == 0) break ; // multiply the result at every step ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m; } // subtract 1 to exclude the case of 1 // being an odd divisor if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0) return (ans - 1 + m) % m; else return (ans - 1) % m; } // Driver Code int main() { sieve(); long long int n = 4, m = 7; cout << countWays(n, m); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to count number of // ways we can express a factorial // as sum of consecutive numbers import java.util.*; class GFG { static int MAX = 50002 ; static ArrayList<Integer> primes = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // sieve of Eratosthenes to compute // the prime numbers public static void sieve() { boolean isPrime[] = new boolean [MAX]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < MAX; i++) isPrime[i] = true ; for ( int p = 2 ; p * p < MAX; p++) { if (isPrime[p] == true ) { for ( int i = p * 2 ; i < MAX; i += p) isPrime[i] = false ; } } // Store all prime numbers for ( int p = 2 ; p < MAX; p++) if (isPrime[p] == true ) primes.add(p); } // function to calculate the largest // power of a prime in a number public static int power( int x, int y) { int count = 0 ; int z = y; while (x >= z) { count += (x / z); z *= y; } return count; } // Modular multiplication to avoid // the overflow of multiplication // Please see below for details public static int modMult( int a, int b, int mod) { int res = 0 ; a = a % mod; while (b > 0 ) { if (b % 2 == 1 ) res = (res + a) % mod; a = (a * 2 ) % mod; b /= 2 ; } return res % mod; } // Returns count of ways to express n! // as sum of consecutives. public static int countWays( int n, int m) { int ans = 1 ; // We skip 2 (First prime) as we need to // consider only odd primes for ( int i = 1 ; i < primes.size(); i++) { // compute the largest power of prime int powers = power(n, primes.get(i)); // if the power of current prime number // is zero in N!, power of primes greater // than current prime number will also // be zero, so break out from the loop if (powers == 0 ) break ; // multiply the result at every step ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1 , m) % m; } // subtract 1 to exclude the case of 1 // being an odd divisor if (((ans - 1 ) % m) < 0 ) return (ans - 1 + m) % m; else return (ans - 1 ) % m; } //Driver function public static void main (String[] args) { sieve(); int n = 4 , m = 7 ; System.out.println(countWays(n,m)); } } // This code is contributed by akash1295. |
Python 3
# Python 3 program to count number of # ways we can express a factorial # as sum of consecutive numbers MAX = 50002 ; primes = [] # sieve of Eratosthenes to compute # the prime numbers def sieve(): isPrime = [ True ] * ( MAX ) p = 2 while p * p < MAX : if (isPrime[p] = = True ): for i in range ( p * 2 , MAX , p): isPrime[i] = False p + = 1 # Store all prime numbers for p in range ( 2 , MAX ): if (isPrime[p]): primes.append(p) # function to calculate the largest # power of a prime in a number def power( x, y): count = 0 z = y while (x > = z): count + = (x / / z) z * = y return count # Modular multiplication to avoid # the overflow of multiplication # Please see below for details def modMult(a, b,mod): res = 0 a = a % mod while (b > 0 ): if (b % 2 = = 1 ): res = (res + a) % mod a = (a * 2 ) % mod b / / = 2 return res % mod # Returns count of ways to express n! # as sum of consecutives. def countWays(n,m): ans = 1 # We skip 2 (First prime) as we need to # consider only odd primes for i in range ( 1 , len (primes)): # compute the largest power of prime powers = power(n, primes[i]) # if the power of current prime number # is zero in N!, power of primes greater # than current prime number will also # be zero, so break out from the loop if (powers = = 0 ): break # multiply the result at every step ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1 , m) % m # subtract 1 to exclude the case of 1 # being an odd divisor if (((ans - 1 ) % m) < 0 ): return (ans - 1 + m) % m else : return (ans - 1 ) % m # Driver Code if __name__ = = "__main__" : sieve() n = 4 m = 7 print (countWays(n, m)) # This code is contributed by ChitraNayal |
C#
// C# program to count number of // ways we can express a factorial // as sum of consecutive numbers using System ; using System.Collections; class GFG { static int MAX = 50002; static ArrayList primes = new ArrayList (); // sieve of Eratosthenes to compute // the prime numbers public static void sieve() { bool []isPrime = new bool [MAX]; for ( int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) isPrime[i] = true ; for ( int p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) { if (isPrime[p] == true ) { for ( int i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p) isPrime[i] = false ; } } // Store all prime numbers for ( int p = 2; p < MAX; p++) if (isPrime[p] == true ) primes.Add(p); } // function to calculate the largest // power of a prime in a number public static int power_prime( int x, int y) { int count = 0; int z = y; while (x >= z) { count += (x / z); z *= y; } return count; } // Modular multiplication to avoid // the overflow of multiplication // Please see below for details public static int modMult( int a, int b, int mod) { int res = 0; a = a % mod; while (b > 0) { if (b % 2 == 1) res = (res + a) % mod; a = (a * 2) % mod; b /= 2; } return res % mod; } // Returns count of ways to express n! // as sum of consecutives. public static int countWays( int n, int m) { int ans = 1; // We skip 2 (First prime) as we need to // consider only odd primes for ( int i = 1; i < primes.Count; i++) { // compute the largest power of prime int powers = power_prime(n, Convert.ToInt32(primes[i])); // if the power of current prime number // is zero in N!, power of primes greater // than current prime number will also // be zero, so break out from the loop if (powers == 0) break ; // multiply the result at every step ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m; } // subtract 1 to exclude the case of 1 // being an odd divisor if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0) return (ans - 1 + m) % m; else return (ans - 1) % m; } //Driver function public static void Main () { sieve(); int n = 4, m = 7; Console.WriteLine(countWays(n,m)); } } // This code is contributed by Ryuga |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to count number of // ways we can express a factorial // as sum of consecutive numbers let MAX = 50002; let primes = []; // sieve of Eratosthenes to compute // the prime numbers function sieve() { let isPrime = new Array(MAX); for (let i = 0; i < MAX; i++) isPrime[i] = true ; for (let p = 2; p * p < MAX; p++) { if (isPrime[p] == true ) { for (let i = p * 2; i < MAX; i += p) isPrime[i] = false ; } } // Store all prime numbers for (let p = 2; p < MAX; p++) if (isPrime[p] == true ) primes.push(p); } // function to calculate the largest // power of a prime in a number function power(x,y) { let count = 0; let z = y; while (x >= z) { count += Math.floor(x / z); z *= y; } return count; } // Modular multiplication to avoid // the overflow of multiplication // Please see below for details function modMult(a,b,mod) { let res = 0; a = a % mod; while (b > 0) { if (b % 2 == 1) res = (res + a) % mod; a = (a * 2) % mod; b = Math.floor(b/2); } return res % mod; } // Returns count of ways to express n! // as sum of consecutives. function countWays(n,m) { let ans = 1; // We skip 2 (First prime) as we need to // consider only odd primes for (let i = 1; i < primes.length; i++) { // compute the largest power of prime let powers = power(n, primes[i]); // if the power of current prime number // is zero in N!, power of primes greater // than current prime number will also // be zero, so break out from the loop if (powers == 0) break ; // multiply the result at every step ans = modMult(ans, powers + 1, m) % m; } // subtract 1 to exclude the case of 1 // being an odd divisor if (((ans - 1) % m) < 0) return (ans - 1 + m) % m; else return (ans - 1) % m; } //Driver function sieve(); let n = 4, m = 7; document.write(countWays(n,m)); // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 </script> |
输出:
1
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END
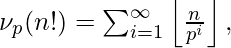


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



