有向无环图(DAG)的拓扑排序是顶点的线性排序,使得对于每个有向边uv,顶点u在排序中位于v之前。如果图形不是DAG,则无法对其进行拓扑排序。 例如,下图的拓扑排序为“5 4 2 3 1 0”。一个图可以有多个拓扑排序。例如,下图的另一个拓扑排序是“45 2 3 1 0”。拓扑排序中的第一个顶点始终是阶数为0的顶点(一个没有进入边的顶点)。
null
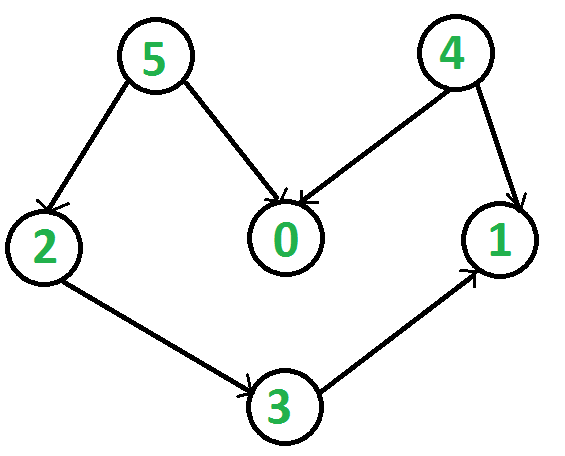
拓扑排序可以递归和非递归实现。首先,我们展示更清晰的递归版本,然后为非递归版本提供分析。
递归拓扑排序
Python3
#Python program to print topological sorting of a DAG from collections import defaultdict #Class to represent a graph class Graph: def __init__( self ,vertices): self .graph = defaultdict( list ) #dictionary containing adjacency List self .V = vertices #No. of vertices # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge( self ,u,v): self .graph[u].append(v) # A recursive function used by topologicalSort def topologicalSortUtil( self ,v,visited,stack): # Mark the current node as visited. visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to this vertex for i in self .graph[v]: if visited[i] = = False : self .topologicalSortUtil(i,visited,stack) # Push current vertex to stack which stores result stack.insert( 0 ,v) # The function to do Topological Sort. It uses recursive # topologicalSortUtil() def topologicalSort( self ): # Mark all the vertices as not visited visited = [ False ] * self .V stack = [] # Call the recursive helper function to store Topological # Sort starting from all vertices one by one for i in range ( self .V): if visited[i] = = False : self .topologicalSortUtil(i,visited,stack) # Print contents of stack print (stack) g = Graph( 6 ) g.addEdge( 5 , 2 ); g.addEdge( 5 , 0 ); g.addEdge( 4 , 0 ); g.addEdge( 4 , 1 ); g.addEdge( 2 , 3 ); g.addEdge( 3 , 1 ); print ( "Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph" ) g.topologicalSort() #This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav |
输出:
Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph5 4 2 3 1 0
非递归拓扑排序
算法:
解决拓扑排序的方法是在处理一个节点的所有子节点后再处理该节点。每次处理节点时,都会将其推入堆栈以保存最终结果。这种非递归的解决方案建立在DFS的相同概念之上,并进行了一些调整,这可以在上面和后面理解 本文 .然而,与递归解决方案不同,递归解决方案在所有相邻元素被推送到程序堆栈后保存堆栈中节点的顺序,该解决方案用工作堆栈替换程序堆栈。如果一个节点有一个未被访问的邻居,则当前节点和该邻居将被推送到工作堆栈中进行处理,直到没有更多可访问的邻居。 访问完所有节点后,剩下的是最终结果,该结果通过反向打印堆栈结果来找到。
Python3
#Python program to print topological sorting of a DAG from collections import defaultdict #Class to represent a graph class Graph: def __init__( self ,vertices): self .graph = defaultdict( list ) #dictionary containing adjacency List self .V = vertices #No. of vertices # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge( self ,u,v): self .graph[u].append(v) # neighbors lazy generator given key def neighbor_gen( self ,v): for k in self .graph[v]: yield k # non recursive topological sort def nonRecursiveTopologicalSortUtil( self , v, visited,stack): # working stack contains key and the corresponding current generator working_stack = [(v, self .neighbor_gen(v))] while len (working_stack) > 0 : # get last element in stack v, gen = working_stack[ - 1 ] visited[v] = True # delete it from stack working_stack.pop() # run through neighbor generator until its empty continue_flag = True while continue_flag: next_neighbor = next (gen, None ) # if generator has returned all neighbors if next_neighbor is None : continue_flag = False # Save current key into the result stack stack.append(v) continue # if new neighbor push current key and neighbor into stack if not (visited[next_neighbor]): working_stack.append((v,gen)) working_stack.append((next_neighbor, self .neighbor_gen(next_neighbor))) continue_flag = False # The function to do Topological Sort. def nonRecursiveTopologicalSort( self ): # Mark all the vertices as not visited visited = [ False ] * self .V # result stack stack = [] # Call the helper function to store Topological # Sort starting from all vertices one by one for i in range ( self .V): if not (visited[i]): self .nonRecursiveTopologicalSortUtil(i, visited,stack) # Print contents of the stack in reverse print (stack[:: - 1 ]) g = Graph( 6 ) g.addEdge( 5 , 2 ); g.addEdge( 5 , 0 ); g.addEdge( 4 , 0 ); g.addEdge( 4 , 1 ); g.addEdge( 2 , 3 ); g.addEdge( 3 , 1 ); print ( "The following is a Topological Sort of the given graph" ) g.nonRecursiveTopologicalSort() # The following code was based of Neelam Yadav's code and is modified by Suhail Alnahari |
输出:
Following is a Topological Sort of the given graph5 4 2 3 1 0
复杂性分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(V+E): 上面的算法只是带有一个工作堆栈和一个结果堆栈的DFS。与递归解决方案不同,递归深度在这里不是问题。
- 辅助空间:O(V): 使用的两个堆栈需要额外的空间。
请参阅完整的文章 拓扑排序 更多细节。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



