给定字符串s,以迭代方式打印给定字符串的所有可能子序列。我们已经讨论过了 递归方法打印字符串的所有子序列 .
例如:
Input : abcOutput : a, b, c, ab, ac, bc, abcInput : aabOutput : a, b, aa, ab, aab
方法1: 在这里,我们讨论更简单、更简单的迭代方法,它类似于 动力装置 .我们使用 二进制表示法 长度为1到2^的–1。
输入=“abc” 二进制表示考虑1到(2 ^ 3-1),即1到7。 从二进制表示法的左(MSB)到右(LSB)开始,将输入字符串中对应于二进制表示法中位值1的字符附加到最终子序列字符串sub。
例子: 001=>abc。只有c对应于位1。所以,子序列=c。 101=>abc。a和c对应于位1。所以,子序列=ac。 二进制表示法(1)=001=>c 二进制_表示(2)=010=>b 二进制表示法(3)=011=>bc 二进制表示法(4)=100=>a 二进制表示法(5)=101=>ac 二进制_表示(6)=110=>ab 二进制表示法(7)=111=>abc
以下是上述方法的实施情况:
C++
// C++ program to print all Subsequences // of a string in iterative manner #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // function to find subsequence string subsequence(string s, int binary, int len) { string sub = "" ; for ( int j = 0; j < len; j++) // check if jth bit in binary is 1 if (binary & (1 << j)) // if jth bit is 1, include it // in subsequence sub += s[j]; return sub; } // function to print all subsequences void possibleSubsequences(string s){ // map to store subsequence // lexicographically by length map< int , set<string> > sorted_subsequence; int len = s.size(); // Total number of non-empty subsequence // in string is 2^len-1 int limit = pow (2, len); // i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for ( int i = 1; i <= limit - 1; i++) { // subsequence for binary pattern i string sub = subsequence(s, i, len); // storing sub in map sorted_subsequence[sub.length()].insert(sub); } for ( auto it : sorted_subsequence) { // it.first is length of Subsequence // it.second is set<string> cout << "Subsequences of length = " << it.first << " are:" << endl; for ( auto ii : it.second) // ii is iterator of type set<string> cout << ii << " " ; cout << endl; } } // driver function int main() { string s = "aabc" ; possibleSubsequences(s); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to print all Subsequences // of a String in iterative manner import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Map; import java.util.SortedMap; import java.util.TreeMap; class Graph{ // Function to find subsequence static String subsequence(String s, int binary, int len) { String sub = "" ; for ( int j = 0 ; j < len; j++) // Check if jth bit in binary is 1 if ((binary & ( 1 << j)) != 0 ) // If jth bit is 1, include it // in subsequence sub += s.charAt(j); return sub; } // Function to print all subsequences static void possibleSubsequences(String s) { // Map to store subsequence // lexicographically by length SortedMap<Integer, HashSet<String>> sorted_subsequence = new TreeMap<Integer, HashSet<String>>(); int len = s.length(); // Total number of non-empty subsequence // in String is 2^len-1 int limit = ( int ) Math.pow( 2 , len); // i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for ( int i = 1 ; i <= limit - 1 ; i++) { // Subsequence for binary pattern i String sub = subsequence(s, i, len); // Storing sub in map if (!sorted_subsequence.containsKey(sub.length())) sorted_subsequence.put( sub.length(), new HashSet<>()); sorted_subsequence.get( sub.length()).add(sub); } for (Map.Entry<Integer, HashSet<String>> it : sorted_subsequence.entrySet()) { // it.first is length of Subsequence // it.second is set<String> System.out.println( "Subsequences of length = " + it.getKey() + " are:" ); for (String ii : it.getValue()) // ii is iterator of type set<String> System.out.print(ii + " " ); System.out.println(); } } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { String s = "aabc" ; possibleSubsequences(s); } } // This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 |
Python3
# Python3 program to print all Subsequences # of a string in iterative manner # function to find subsequence def subsequence(s, binary, length): sub = "" for j in range (length): # check if jth bit in binary is 1 if (binary & ( 1 << j)): # if jth bit is 1, include it # in subsequence sub + = s[j] return sub # function to print all subsequences def possibleSubsequences(s): # map to store subsequence # lexicographically by length sorted_subsequence = {} length = len (s) # Total number of non-empty subsequence # in string is 2^len-1 limit = 2 * * length # i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for i in range ( 1 , limit): # subsequence for binary pattern i sub = subsequence(s, i, length) # storing sub in map if len (sub) in sorted_subsequence.keys(): sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)] = tuple ( list (sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)]) + [sub]) else : sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)] = [sub] for it in sorted_subsequence: # it.first is length of Subsequence # it.second is set<string> print ( "Subsequences of length =" , it, "are:" ) for ii in sorted ( set (sorted_subsequence[it])): # ii is iterator of type set<string> print (ii, end = ' ' ) print () # Driver Code s = "aabc" possibleSubsequences(s) # This code is contributed by ankush_953 |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to print all Subsequences // of a string in iterative manner // function to find subsequence function subsequence(s, binary, len) { let sub = "" ; for (let j = 0; j < len; j++) // Check if jth bit in binary is 1 if (binary & (1 << j)) // If jth bit is 1, include it // in subsequence sub += s[j]; return sub; } // Function to print all subsequences function possibleSubsequences(s) { // map to store subsequence // lexicographically by length let sorted_subsequence = new Map(); let len = s.length; // Total number of non-empty subsequence // in string is 2^len-1 let limit = Math.pow(2, len); // i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for (let i = 1; i <= limit - 1; i++) { // Subsequence for binary pattern i let sub = subsequence(s, i, len); // Storing sub in map if (!sorted_subsequence.has(sub.length)) sorted_subsequence.set(sub.length, new Set()); sorted_subsequence.get(sub.length).add(sub); } for (let it of sorted_subsequence) { // it.first is length of Subsequence // it.second is set<string> document.write( "Subsequences of length = " + it[0] + " are:" + "<br>" ); for (let ii of it[1]) // ii is iterator of type set<string> document.write(ii + " " ); document.write( "<br>" ); } } // Driver code let s = "aabc" ; possibleSubsequences(s); // This code is contributed by gfgking </script> |
输出:
Subsequences of length = 1 are:a b c Subsequences of length = 2 are:aa ab ac bc Subsequences of length = 3 are:aab aac abc Subsequences of length = 4 are:aabc
时间复杂性: ![]() ,其中n是查找子序列的字符串长度,l是二进制字符串的长度。
,其中n是查找子序列的字符串长度,l是二进制字符串的长度。
方法2: 这种方法是获取最右边的设置位的位置,并在将给定字符串中的相应字符添加到子序列后重置该位,然后重复相同的操作,直到相应的二进制模式没有设置位为止。
如果输入为s=“abc” 二进制表示考虑1到(2 ^ 3-1),即1到7。 001=>abc。只有c对应于位1。所以,子序列=c 101=>abc。a和c对应于位1。所以,子序列=ac。 让我们使用5的二进制表示,即101。 最右边的位在位置1,在sub=c的开头追加字符,重置位置1=>100 最右边的位位于位置3,在sub=ac的开头追加字符,重置位置3=>000 因为现在我们没有设置位了,所以我们停止计算子序列。
例子: 二进制表示法(1)=001=>c 二进制_表示(2)=010=>b 二进制表示法(3)=011=>bc 二进制表示法(4)=100=>a 二进制表示法(5)=101=>ac 二进制_表示(6)=110=>ab 二进制表示法(7)=111=>abc
以下是上述方法的实施情况:
C++
// C++ code all Subsequences of a // string in iterative manner #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // function to find subsequence string subsequence(string s, int binary) { string sub = "" ; int pos; // loop while binary is greater than 0 while (binary>0) { // get the position of rightmost set bit pos=log2(binary&-binary)+1; // append at beginning as we are // going from LSB to MSB sub=s[pos-1]+sub; // resets bit at pos in binary binary= (binary & ~(1 << (pos-1))); } reverse(sub.begin(),sub.end()); return sub; } // function to print all subsequences void possibleSubsequences(string s){ // map to store subsequence // lexicographically by length map< int , set<string> > sorted_subsequence; int len = s.size(); // Total number of non-empty subsequence // in string is 2^len-1 int limit = pow (2, len); // i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for ( int i = 1; i <= limit - 1; i++) { // subsequence for binary pattern i string sub = subsequence(s, i); // storing sub in map sorted_subsequence[sub.length()].insert(sub); } for ( auto it : sorted_subsequence) { // it.first is length of Subsequence // it.second is set<string> cout << "Subsequences of length = " << it.first << " are:" << endl; for ( auto ii : it.second) // ii is iterator of type set<string> cout << ii << " " ; cout << endl; } } // driver function int main() { string s = "aabc" ; possibleSubsequences(s); return 0; } |
Python3
# Python3 program to print all Subsequences # of a string in an iterative manner from math import log2, floor # function to find subsequence def subsequence(s, binary): sub = "" # loop while binary is greater than while (binary > 0 ): # get the position of rightmost set bit pos = floor(log2(binary& - binary) + 1 ) # append at beginning as we are # going from LSB to MSB sub = s[pos - 1 ] + sub # resets bit at pos in binary binary = (binary & ~( 1 << (pos - 1 ))) sub = sub[:: - 1 ] return sub # function to print all subsequences def possibleSubsequences(s): # map to store subsequence # lexicographically by length sorted_subsequence = {} length = len (s) # Total number of non-empty subsequence # in string is 2^len-1 limit = 2 * * length # i=0, corresponds to empty subsequence for i in range ( 1 , limit): # subsequence for binary pattern i sub = subsequence(s, i) # storing sub in map if len (sub) in sorted_subsequence.keys(): sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)] = tuple ( list (sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)]) + [sub]) else : sorted_subsequence[ len (sub)] = [sub] for it in sorted_subsequence: # it.first is length of Subsequence # it.second is set<string> print ( "Subsequences of length =" , it, "are:" ) for ii in sorted ( set (sorted_subsequence[it])): # ii is iterator of type set<string> print (ii, end = ' ' ) print () # Driver Code s = "aabc" possibleSubsequences(s) # This code is contributed by ankush_953 |
输出:
Subsequences of length = 1 are:a b c Subsequences of length = 2 are:aa ab ac bc Subsequences of length = 3 are:aab aac abc Subsequences of length = 4 are:aabc
时间复杂性: ![]() ,其中n是查找子序列的字符串长度,b是二进制字符串中的设置位数。
,其中n是查找子序列的字符串长度,b是二进制字符串中的设置位数。
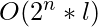


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



