我们得到了一个有向图。我们需要计算图是否有负循环。负循环是指整个循环的总和变为负的循环。
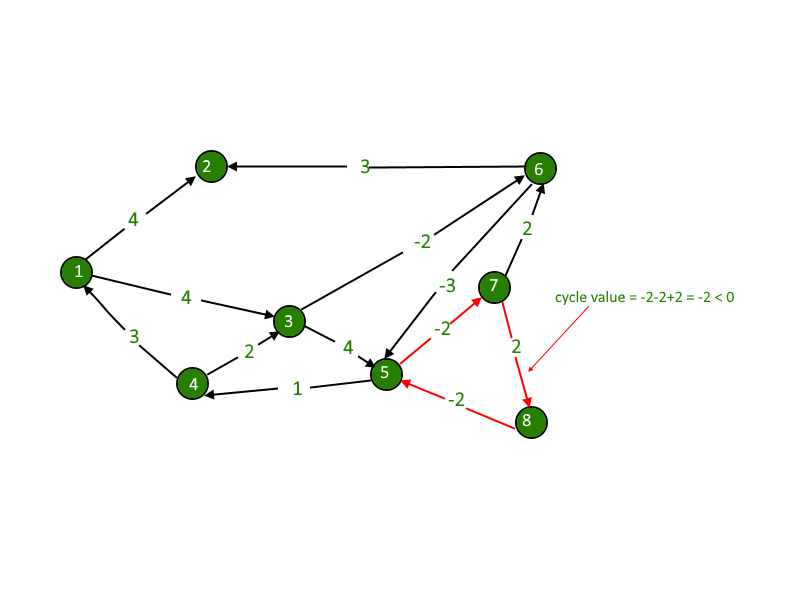
负权存在于图的各种应用中。例如,如果我们沿着这条路走,我们可能会获得一些优势,而不是为一条路支付成本。
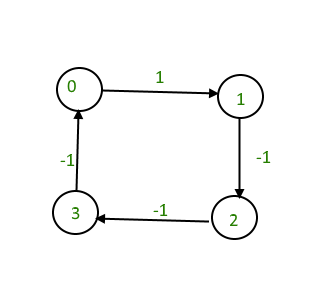
例如:
Input : 4 4
0 1 1
1 2 -1
2 3 -1
3 0 -1
Output : Yes
The graph contains a negative cycle.
这个想法是使用 贝尔曼-福特算法 .
下面是一个算法,用于确定给定源是否存在可到达的负权重循环。 1) 将从源到所有顶点的距离初始化为无限,将到源本身的距离初始化为0。创建一个大小为| V |的数组dist[],所有值都为无穷大,除了dist[src],其中src是源顶点。 2) 此步骤计算最短距离。执行以下|V |-1次,其中|V |是给定图形中的顶点数。 (a) 对每个u-v边执行以下操作。 b) 如果dist[v]>dist[u]+边缘uv的权重,则更新dist[v]。 c) 距离[v]=距离[u]+边缘uv的权重。 3) 此步骤报告图表中是否存在负权重循环。对每个u-v边执行以下操作 (a) 如果dist[v]>dist[u]+边缘uv的权重,则“图形具有负权重循环”
第3步的想法是,如果图中不包含负权重循环,第2步保证最短距离。如果我们在所有边上再迭代一次,得到任何顶点的较短路径,则存在负权重循环。
C++
// A C++ program to check if a graph contains negative // weight cycle using Bellman-Ford algorithm. This program // works only if all vertices are reachable from a source // vertex 0. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph struct Edge { int src, dest, weight; }; // a structure to represent a connected, directed and // weighted graph struct Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. struct Edge* edge; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges struct Graph* createGraph( int V, int E) { struct Graph* graph = new Graph; graph->V = V; graph->E = E; graph->edge = new Edge[graph->E]; return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle bool isNegCycleBellmanFord( struct Graph* graph, int src) { int V = graph->V; int E = graph->E; int dist[V]; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = INT_MAX; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for ( int j = 0; j < E; j++) { int u = graph->edge[j].src; int v = graph->edge[j].dest; int weight = graph->edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int u = graph->edge[i].src; int v = graph->edge[i].dest; int weight = graph->edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { /* Let us create the graph given in above example */ int V = 5; // Number of vertices in graph int E = 8; // Number of edges in graph struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph->edge[0].src = 0; graph->edge[0].dest = 1; graph->edge[0].weight = -1; // add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph->edge[1].src = 0; graph->edge[1].dest = 2; graph->edge[1].weight = 4; // add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph->edge[2].src = 1; graph->edge[2].dest = 2; graph->edge[2].weight = 3; // add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph->edge[3].src = 1; graph->edge[3].dest = 3; graph->edge[3].weight = 2; // add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph->edge[4].src = 1; graph->edge[4].dest = 4; graph->edge[4].weight = 2; // add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph->edge[5].src = 3; graph->edge[5].dest = 2; graph->edge[5].weight = 5; // add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph->edge[6].src = 3; graph->edge[6].dest = 1; graph->edge[6].weight = 1; // add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph->edge[7].src = 4; graph->edge[7].dest = 3; graph->edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0)) cout << "Yes" ; else cout << "No" ; return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to check if a graph contains negative // weight cycle using Bellman-Ford algorithm. This program // works only if all vertices are reachable from a source // vertex 0. import java.util.*; class GFG { // a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph static class Edge { int src, dest, weight; } // a structure to represent a connected, directed and // weighted graph static class Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. Edge edge[]; } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges static Graph createGraph( int V, int E) { Graph graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle static boolean isNegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src) { int V = graph.V; int E = graph.E; int [] dist = new int [V]; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; dist[src] = 0 ; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1 ; i <= V - 1 ; i++) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < E; j++) { int u = graph.edge[j].src; int v = graph.edge[j].dest; int weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0 ; i < E; i++) { int u = graph.edge[i].src; int v = graph.edge[i].dest; int weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 5 , E = 8 ; Graph graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 0 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].weight = - 1 ; // add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 1 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].weight = 4 ; // add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 2 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].weight = 3 ; // add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 3 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].weight = 2 ; // add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[ 4 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].dest = 4 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].weight = 2 ; // add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 5 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].weight = 5 ; // add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 6 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].weight = 1 ; // add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 7 ].src = 4 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].weight = - 3 ; if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0 )) System.out.println( "Yes" ); else System.out.println( "No" ); } } // This code is contributed by // sanjeev2552 |
Python3
# A Python3 program to check if a graph contains negative # weight cycle using Bellman-Ford algorithm. This program # works only if all vertices are reachable from a source # vertex 0. # a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph class Edge: def __init__( self ): self .src = 0 self .dest = 0 self .weight = 0 # a structure to represent a connected, directed and # weighted graph class Graph: def __init__( self ): # V. Number of vertices, E. Number of edges self .V = 0 self .E = 0 # graph is represented as an array of edges. self .edge = None # Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges def createGraph(V, E): graph = Graph() graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = [Edge() for i in range (graph.E)] return graph; # The main function that finds shortest distances # from src to all other vertices using Bellman- # Ford algorithm. The function also detects # negative weight cycle def isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, src): V = graph.V; E = graph.E; dist = [ 1000000 for i in range (V)]; dist[src] = 0 ; # Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. # A simple shortest path from src to any # other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 # edges for i in range ( 1 , V): for j in range (E): u = graph.edge[j].src; v = graph.edge[j].dest; weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] ! = 1000000 and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]): dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; # Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. # The above step guarantees shortest distances # if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. # If we get a shorter path, then there # is a cycle. for i in range (E): u = graph.edge[i].src; v = graph.edge[i].dest; weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] ! = 1000000 and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]): return True ; return False ; # Driver program to test above functions if __name__ = = '__main__' : # Let us create the graph given in above example V = 5 ; # Number of vertices in graph E = 8 ; # Number of edges in graph graph = createGraph(V, E); # add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 0 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].weight = - 1 ; # add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 1 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].weight = 4 ; # add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 2 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].weight = 3 ; # add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 3 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].weight = 2 ; # add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[ 4 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].dest = 4 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].weight = 2 ; # add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 5 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].weight = 5 ; # add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 6 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].weight = 1 ; # add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 7 ].src = 4 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].weight = - 3 ; if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0 )): print ( "Yes" ) else : print ( "No" ) # This code is contributed by pratham76 |
C#
// C# program to check if a graph contains negative // weight cycle using Bellman-Ford algorithm. This program // works only if all vertices are reachable from a source // vertex 0. using System; using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; class GFG { // a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph class Edge { public int src, dest, weight; } // a structure to represent a connected, directed and // weighted graph class Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges public int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. public Edge []edge; } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges static Graph createGraph( int V, int E) { Graph graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E]; for ( int i = 0; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle static bool isNegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src) { int V = graph.V; int E = graph.E; int [] dist = new int [V]; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = 1000000; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for ( int j = 0; j < E; j++) { int u = graph.edge[j].src; int v = graph.edge[j].dest; int weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != 1000000 && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int u = graph.edge[i].src; int v = graph.edge[i].dest; int weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != 1000000 && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Driver Code public static void Main( string [] args) { int V = 5, E = 8; Graph graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[0].src = 0; graph.edge[0].dest = 1; graph.edge[0].weight = -1; // add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[1].src = 0; graph.edge[1].dest = 2; graph.edge[1].weight = 4; // add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[2].src = 1; graph.edge[2].dest = 2; graph.edge[2].weight = 3; // add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[3].src = 1; graph.edge[3].dest = 3; graph.edge[3].weight = 2; // add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[4].src = 1; graph.edge[4].dest = 4; graph.edge[4].weight = 2; // add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[5].src = 3; graph.edge[5].dest = 2; graph.edge[5].weight = 5; // add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[6].src = 3; graph.edge[6].dest = 1; graph.edge[6].weight = 1; // add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[7].src = 4; graph.edge[7].dest = 3; graph.edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0)) Console.Write( "Yes" ); else Console.Write( "No" ); } } // This code is contributed by rutvik_56 |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to check if a graph contains negative // weight cycle using Bellman-Ford algorithm. This program // works only if all vertices are reachable from a source // vertex 0. // A structure to represent a weighted edge in graph class Edge { constructor() { let src, dest, weight; } } // A structure to represent a connected, directed and // weighted graph class Graph { constructor() { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges let V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. let edge = []; } } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges function createGraph(V,E) { let graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Array(graph.E); for (let i = 0; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle function isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, src) { let V = graph.V; let E = graph.E; let dist = new Array(V); // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = Number.MAX_VALUE; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for (let i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < E; j++) { let u = graph.edge[j].src; let v = graph.edge[j].dest; let weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != Number.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for (let i = 0; i < E; i++) { let u = graph.edge[i].src; let v = graph.edge[i].dest; let weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != Number.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Driver Code let V = 5, E = 8; let graph = createGraph(V, E); // Add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[0].src = 0; graph.edge[0].dest = 1; graph.edge[0].weight = -1; // Add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[1].src = 0; graph.edge[1].dest = 2; graph.edge[1].weight = 4; // add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[2].src = 1; graph.edge[2].dest = 2; graph.edge[2].weight = 3; // Add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[3].src = 1; graph.edge[3].dest = 3; graph.edge[3].weight = 2; // Add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[4].src = 1; graph.edge[4].dest = 4; graph.edge[4].weight = 2; // Add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[5].src = 3; graph.edge[5].dest = 2; graph.edge[5].weight = 5; // Add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[6].src = 3; graph.edge[6].dest = 1; graph.edge[6].weight = 1; // add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[7].src = 4; graph.edge[7].dest = 3; graph.edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, 0)) document.write( "Yes" ); else document.write( "No" ); // This code is contributed by unknown2108 </script> |
输出:
No
它是如何工作的? 如前所述 贝尔曼-福特算法 ,对于给定的源,首先计算路径中最多有一条边的最短距离。然后,它计算最多有两条边的最短路径,以此类推。在外循环的第i次迭代之后,计算出最多有i条边的最短路径。在任何简单路径上都可能有一个最大的|V |–1边,这就是为什么外部循环运行|V |–1次。如果有一个负权重循环,那么再进行一次迭代就会得到一条短路径。

如何处理断开连接的图形(如果无法从源访问循环)? 如果给定的图形断开连接,上述算法和程序可能无法工作。当所有顶点都可以从源顶点0访问时,该选项有效。 为了处理断开连接的图,我们可以对距离为无穷大的顶点重复这个过程。
C++
// A C++ program for Bellman-Ford's single source // shortest path algorithm. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph struct Edge { int src, dest, weight; }; // a structure to represent a connected, directed and // weighted graph struct Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges int V, E; // graph is represented as an array of edges. struct Edge* edge; }; // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges struct Graph* createGraph( int V, int E) { struct Graph* graph = new Graph; graph->V = V; graph->E = E; graph->edge = new Edge[graph->E]; return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle bool isNegCycleBellmanFord( struct Graph* graph, int src, int dist[]) { int V = graph->V; int E = graph->E; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = INT_MAX; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for ( int j = 0; j < E; j++) { int u = graph->edge[j].src; int v = graph->edge[j].dest; int weight = graph->edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int u = graph->edge[i].src; int v = graph->edge[i].dest; int weight = graph->edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Returns true if given graph has negative weight // cycle. bool isNegCycleDisconnected( struct Graph* graph) { int V = graph->V; // To keep track of visited vertices to avoid // recomputations. bool visited[V]; memset (visited, 0, sizeof (visited)); // This array is filled by Bellman-Ford int dist[V]; // Call Bellman-Ford for all those vertices // that are not visited for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false ) { // If cycle found if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, i, dist)) return true ; // Mark all vertices that are visited // in above call. for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) if (dist[i] != INT_MAX) visited[i] = true ; } } return false ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { /* Let us create the graph given in above example */ int V = 5; // Number of vertices in graph int E = 8; // Number of edges in graph struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E); // add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph->edge[0].src = 0; graph->edge[0].dest = 1; graph->edge[0].weight = -1; // add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph->edge[1].src = 0; graph->edge[1].dest = 2; graph->edge[1].weight = 4; // add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph->edge[2].src = 1; graph->edge[2].dest = 2; graph->edge[2].weight = 3; // add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph->edge[3].src = 1; graph->edge[3].dest = 3; graph->edge[3].weight = 2; // add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph->edge[4].src = 1; graph->edge[4].dest = 4; graph->edge[4].weight = 2; // add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph->edge[5].src = 3; graph->edge[5].dest = 2; graph->edge[5].weight = 5; // add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph->edge[6].src = 3; graph->edge[6].dest = 1; graph->edge[6].weight = 1; // add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph->edge[7].src = 4; graph->edge[7].dest = 3; graph->edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleDisconnected(graph)) cout << "Yes" ; else cout << "No" ; return 0; } |
JAVA
// A Java program for Bellman-Ford's single source // shortest path algorithm. import java.util.*; class GFG{ // A structure to represent a weighted // edge in graph static class Edge { int src, dest, weight; } // A structure to represent a connected, // directed and weighted graph static class Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, // E-> Number of edges int V, E; // Graph is represented as // an array of edges. Edge edge[]; } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges static Graph createGraph( int V, int E) { Graph graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E]; for ( int i = 0 ; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle static boolean isNegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src, int dist[]) { int V = graph.V; int E = graph.E; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE; dist[src] = 0 ; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1 ; i <= V - 1 ; i++) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < E; j++) { int u = graph.edge[j].src; int v = graph.edge[j].dest; int weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0 ; i < E; i++) { int u = graph.edge[i].src; int v = graph.edge[i].dest; int weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != Integer.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Returns true if given graph has negative weight // cycle. static boolean isNegCycleDisconnected(Graph graph) { int V = graph.V; // To keep track of visited vertices // to avoid recomputations. boolean visited[] = new boolean [V]; Arrays.fill(visited, false ); // This array is filled by Bellman-Ford int dist[] = new int [V]; // Call Bellman-Ford for all those vertices // that are not visited for ( int i = 0 ; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false ) { // If cycle found if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, i, dist)) return true ; // Mark all vertices that are visited // in above call. for ( int j = 0 ; j < V; j++) if (dist[j] != Integer.MAX_VALUE) visited[j] = true ; } } return false ; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int V = 5 , E = 8 ; Graph graph = createGraph(V, E); // Add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 0 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 0 ].weight = - 1 ; // Add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 1 ].src = 0 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 1 ].weight = 4 ; // Add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 2 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 2 ].weight = 3 ; // Add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 3 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 3 ].weight = 2 ; // Add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[ 4 ].src = 1 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].dest = 4 ; graph.edge[ 4 ].weight = 2 ; // Add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[ 5 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].dest = 2 ; graph.edge[ 5 ].weight = 5 ; // Add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[ 6 ].src = 3 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].dest = 1 ; graph.edge[ 6 ].weight = 1 ; // Add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[ 7 ].src = 4 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].dest = 3 ; graph.edge[ 7 ].weight = - 3 ; if (isNegCycleDisconnected(graph)) System.out.println( "Yes" ); else System.out.println( "No" ); } } // This code is contributed by adityapande88 |
Python3
# A Python3 program for Bellman-Ford's single source # shortest path algorithm. # The main function that finds shortest distances # from src to all other vertices using Bellman- # Ford algorithm. The function also detects # negative weight cycle def isNegCycleBellmanFord(src, dist): global graph, V, E # Step 1: Initialize distances from src # to all other vertices as INFINITE for i in range (V): dist[i] = 10 * * 18 dist[src] = 0 # Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. # A simple shortest path from src to any # other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 # edges for i in range ( 1 ,V): for j in range (E): u = graph[j][ 0 ] v = graph[j][ 1 ] weight = graph[j][ 2 ] if (dist[u] ! = 10 * * 18 and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]): dist[v] = dist[u] + weight # Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. # The above step guarantees shortest distances # if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. # If we get a shorter path, then there # is a cycle. for i in range (E): u = graph[i][ 0 ] v = graph[i][ 1 ] weight = graph[i][ 2 ] if (dist[u] ! = 10 * * 18 and dist[u] + weight < dist[v]): return True return False # Returns true if given graph has negative weight # cycle. def isNegCycleDisconnected(): global V, E, graph # To keep track of visited vertices to avoid # recomputations. visited = [ 0 ] * V # memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited)) # This array is filled by Bellman-Ford dist = [ 0 ] * V # Call Bellman-Ford for all those vertices # that are not visited for i in range (V): if (visited[i] = = 0 ): # If cycle found if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(i, dist)): return True # Mark all vertices that are visited # in above call. for i in range (V): if (dist[i] ! = 10 * * 18 ): visited[i] = True return False # Driver code if __name__ = = '__main__' : # /* Let us create the graph given in above example */ V = 5 # Number of vertices in graph E = 8 # Number of edges in graph graph = [[ 0 , 0 , 0 ] for i in range ( 8 )] # add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph[ 0 ][ 0 ] = 0 graph[ 0 ][ 1 ] = 1 graph[ 0 ][ 2 ] = - 1 # add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph[ 1 ][ 0 ] = 0 graph[ 1 ][ 1 ] = 2 graph[ 1 ][ 2 ] = 4 # add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph[ 2 ][ 0 ] = 1 graph[ 2 ][ 1 ] = 2 graph[ 2 ][ 2 ] = 3 # add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph[ 3 ][ 0 ] = 1 graph[ 3 ][ 1 ] = 3 graph[ 3 ][ 2 ] = 2 # add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph[ 4 ][ 0 ] = 1 graph[ 4 ][ 1 ] = 4 graph[ 4 ][ 2 ] = 2 # add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph[ 5 ][ 0 ] = 3 graph[ 5 ][ 1 ] = 2 graph[ 5 ][ 2 ] = 5 # add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph[ 6 ][ 0 ] = 3 graph[ 6 ][ 1 ] = 1 graph[ 6 ][ 2 ] = 1 # add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph[ 7 ][ 0 ] = 4 graph[ 7 ][ 1 ] = 3 graph[ 7 ][ 2 ] = - 3 if (isNegCycleDisconnected()): print ( "Yes" ) else : print ( "No" ) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 |
C#
// A C# program for Bellman-Ford's single source // shortest path algorithm. using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class GFG { // A structure to represent a weighted // edge in graph public class Edge { public int src, dest, weight; } // A structure to represent a connected, // directed and weighted graph public class Graph { // V-> Number of vertices, // E-> Number of edges public int V, E; // Graph is represented as // an array of edges. public Edge []edge; } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges static Graph createGraph( int V, int E) { Graph graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Edge[graph.E]; for ( int i = 0; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle static bool isNegCycleBellmanFord(Graph graph, int src, int []dist) { int V = graph.V; int E = graph.E; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = int .MaxValue; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for ( int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for ( int j = 0; j < E; j++) { int u = graph.edge[j].src; int v = graph.edge[j].dest; int weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != int .MaxValue && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for ( int i = 0; i < E; i++) { int u = graph.edge[i].src; int v = graph.edge[i].dest; int weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != int .MaxValue && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Returns true if given graph has negative weight // cycle. static bool isNegCycleDisconnected(Graph graph) { int V = graph.V; // To keep track of visited vertices // to avoid recomputations. bool []visited = new bool [V]; // This array is filled by Bellman-Ford int []dist = new int [V]; // Call Bellman-Ford for all those vertices // that are not visited for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false ) { // If cycle found if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, i, dist)) return true ; // Mark all vertices that are visited // in above call. for ( int j = 0; j < V; j++) if (dist[j] != int .MaxValue) visited[j] = true ; } } return false ; } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { int V = 5, E = 8; Graph graph = createGraph(V, E); // Add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[0].src = 0; graph.edge[0].dest = 1; graph.edge[0].weight = -1; // Add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[1].src = 0; graph.edge[1].dest = 2; graph.edge[1].weight = 4; // Add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[2].src = 1; graph.edge[2].dest = 2; graph.edge[2].weight = 3; // Add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[3].src = 1; graph.edge[3].dest = 3; graph.edge[3].weight = 2; // Add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[4].src = 1; graph.edge[4].dest = 4; graph.edge[4].weight = 2; // Add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[5].src = 3; graph.edge[5].dest = 2; graph.edge[5].weight = 5; // Add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[6].src = 3; graph.edge[6].dest = 1; graph.edge[6].weight = 1; // Add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[7].src = 4; graph.edge[7].dest = 3; graph.edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleDisconnected(graph)) Console.WriteLine( "Yes" ); else Console.WriteLine( "No" ); } } // This code is contributed by aashish1995 |
Javascript
<script> // A Javascript program for Bellman-Ford's single source // shortest path algorithm. // A structure to represent a weighted // edge in graph class Edge { constructor() { let src, dest, weight; } } // A structure to represent a connected, // directed and weighted graph class Graph { constructor() { // V-> Number of vertices, // E-> Number of edges let V, E; // Graph is represented as // an array of edges. let edge=[]; } } // Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges function createGraph(V,E) { let graph = new Graph(); graph.V = V; graph.E = E; graph.edge = new Array(graph.E); for (let i = 0; i < graph.E; i++) { graph.edge[i] = new Edge(); } return graph; } // The main function that finds shortest distances // from src to all other vertices using Bellman- // Ford algorithm. The function also detects // negative weight cycle function isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph,src,dist) { let V = graph.V; let E = graph.E; // Step 1: Initialize distances from src // to all other vertices as INFINITE for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) dist[i] = Number.MAX_VALUE; dist[src] = 0; // Step 2: Relax all edges |V| - 1 times. // A simple shortest path from src to any // other vertex can have at-most |V| - 1 // edges for (let i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++) { for (let j = 0; j < E; j++) { let u = graph.edge[j].src; let v = graph.edge[j].dest; let weight = graph.edge[j].weight; if (dist[u] != Number.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) dist[v] = dist[u] + weight; } } // Step 3: check for negative-weight cycles. // The above step guarantees shortest distances // if graph doesn't contain negative weight cycle. // If we get a shorter path, then there // is a cycle. for (let i = 0; i < E; i++) { let u = graph.edge[i].src; let v = graph.edge[i].dest; let weight = graph.edge[i].weight; if (dist[u] != Number.MAX_VALUE && dist[u] + weight < dist[v]) return true ; } return false ; } // Returns true if given graph has negative weight // cycle. function isNegCycleDisconnected(graph) { let V = graph.V; // To keep track of visited vertices // to avoid recomputations. let visited = new Array(V); for (let i=0;i<V;i++) { visited[i]= false ; } // This array is filled by Bellman-Ford let dist = new Array(V); // Call Bellman-Ford for all those vertices // that are not visited for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false ) { // If cycle found if (isNegCycleBellmanFord(graph, i, dist)) return true ; // Mark all vertices that are visited // in above call. for (let j = 0; j < V; j++) if (dist[j] != Number.MAX_VALUE) visited[j] = true ; } } return false ; } // Driver Code let V = 5, E = 8; let graph = createGraph(V, E); // Add edge 0-1 (or A-B in above figure) graph.edge[0].src = 0; graph.edge[0].dest = 1; graph.edge[0].weight = -1; // Add edge 0-2 (or A-C in above figure) graph.edge[1].src = 0; graph.edge[1].dest = 2; graph.edge[1].weight = 4; // Add edge 1-2 (or B-C in above figure) graph.edge[2].src = 1; graph.edge[2].dest = 2; graph.edge[2].weight = 3; // Add edge 1-3 (or B-D in above figure) graph.edge[3].src = 1; graph.edge[3].dest = 3; graph.edge[3].weight = 2; // Add edge 1-4 (or A-E in above figure) graph.edge[4].src = 1; graph.edge[4].dest = 4; graph.edge[4].weight = 2; // Add edge 3-2 (or D-C in above figure) graph.edge[5].src = 3; graph.edge[5].dest = 2; graph.edge[5].weight = 5; // Add edge 3-1 (or D-B in above figure) graph.edge[6].src = 3; graph.edge[6].dest = 1; graph.edge[6].weight = 1; // Add edge 4-3 (or E-D in above figure) graph.edge[7].src = 4; graph.edge[7].dest = 3; graph.edge[7].weight = -3; if (isNegCycleDisconnected(graph)) document.write( "Yes" ); else document.write( "No" ); // This code is contributed by patel2127 </script> |
输出:
No
本文由 卡尔蒂克 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 写极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄去评论-team@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



