在现实生活中,当我们需要做一些决定时,我们会根据这些决定来决定下一步该做什么。在编程中也会出现类似的情况,我们需要做出一些决定,并根据这些决定执行下一段代码。例如,在C中,如果发生x,则执行y,否则执行z。也可以有多个条件,如在C中,如果发生x,则执行p,否则如果发生y,则执行q,否则执行r。C中的这个条件是导入多个条件的多种方式之一。
![图片[1]-C/C++中的决策(IF,if……,嵌套if,如果是)-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/uploads/geeks/20191202/geeks_CPP-Decision-Making.png)
编程语言中的决策语句决定程序执行的方向。在C或C++中可用的决策语句是:
C/C中的if语句++
if语句是最简单的决策语句。它用于决定是否执行某个语句或语句块,即如果某个条件为真,则执行语句块,否则不执行。 语法 :
if(condition) { // Statements to execute if // condition is true}
给 条件 之后的评估将是正确的或错误的。C if语句接受布尔值——如果该值为真,则它将执行它下面的语句块,否则不会。如果我们在if(条件)之后不提供卷曲括号'{‘和’}’,那么默认情况下,如果语句将考虑第一个紧跟在下面的语句在它的块内。 实例 :
if(condition) statement1; statement2;// Here if the condition is true, if block // will consider only statement1 to be inside // its block.
流程图
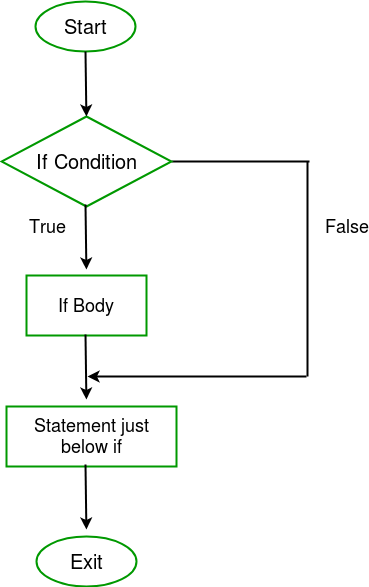
C
// C program to illustrate If statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i = 10; if (i > 15) { printf ( "10 is less than 15" ); } printf ( "I am Not in if" ); } |
C++
// C++ program to illustrate If statement #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 10; if (i > 15) { cout<< "10 is less than 15" ; } cout<< "I am Not in if" ; } |
I am Not in if
因为if语句中存在的条件是错误的。因此,if语句下面的块不会被执行。
如果C/C中有其他内容++
这个 如果 语句本身告诉我们,如果一个条件为真,它将执行一组语句,如果条件为假,它将不会执行。但是如果条件为假,我们想做些别的事情呢。C来了 其他的 陈述我们可以使用 其他的 声明 如果 语句在条件为false时执行代码块。 语法 :
if (condition){ // Executes this block if // condition is true}else{ // Executes this block if // condition is false}
流程图 :

例子:
C
// C program to illustrate If statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i = 20; if (i < 15){ printf ( "i is smaller than 15" ); } else { printf ( "i is greater than 15" ); } return 0; } |
C++
// C++ program to illustrate if-else statement #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 20; if (i < 15) cout<< "i is smaller than 15" ; else cout<< "i is greater than 15" ; return 0; } |
i is greater than 15
下面的代码块 其他的 语句作为 如果 声明是假的。
C/C中的嵌套if++
C中的嵌套if是另一个if语句的目标if语句。嵌套if语句是指另一个if语句中的if语句。是的,C和C++都允许嵌套if语句中的语句,也就是说,我们可以将if语句放在另一个if语句中。 语法:
if (condition1) { // Executes when condition1 is true if (condition2) { // Executes when condition2 is true }}
流程图
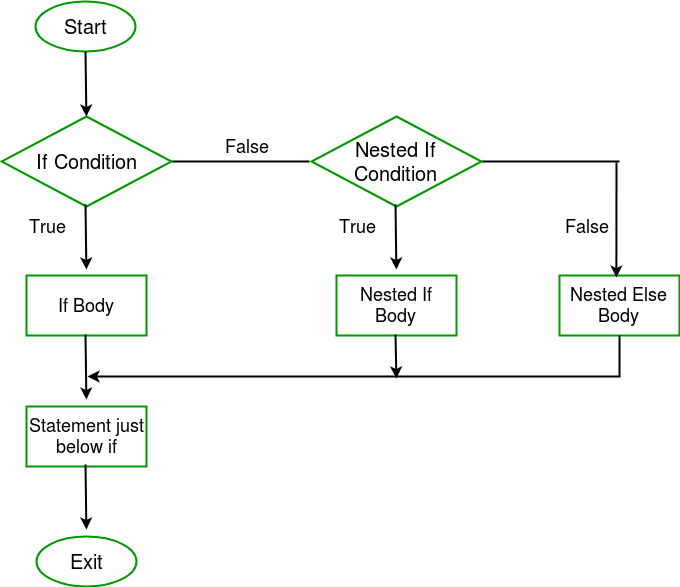
例子:
C
// C program to illustrate nested-if statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i = 10; if (i == 10) { // First if statement if (i < 15) printf ( "i is smaller than 15" ); // Nested - if statement // Will only be executed if statement above // is true if (i < 12) printf ( "i is smaller than 12 too" ); else printf ( "i is greater than 15" ); } return 0; } |
C++
// C++ program to illustrate nested-if statement #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 10; if (i == 10) { // First if statement if (i < 15) cout<< "i is smaller than 15" ; // Nested - if statement // Will only be executed if statement above // is true if (i < 12) cout<< "i is smaller than 12 too" ; else cout<< "i is greater than 15" ; } return 0; } |
i is smaller than 15i is smaller than 12 too
C/C中的if else if梯形图++
在这里,用户可以在多个选项中进行选择。C if语句是自上而下执行的。一旦控制if的条件之一为真,就会执行与该if关联的语句,并绕过C else if梯形图的其余部分。如果所有条件都不成立,那么将执行最终的else语句。 语法:
if (condition) statement;else if (condition) statement;..else statement;
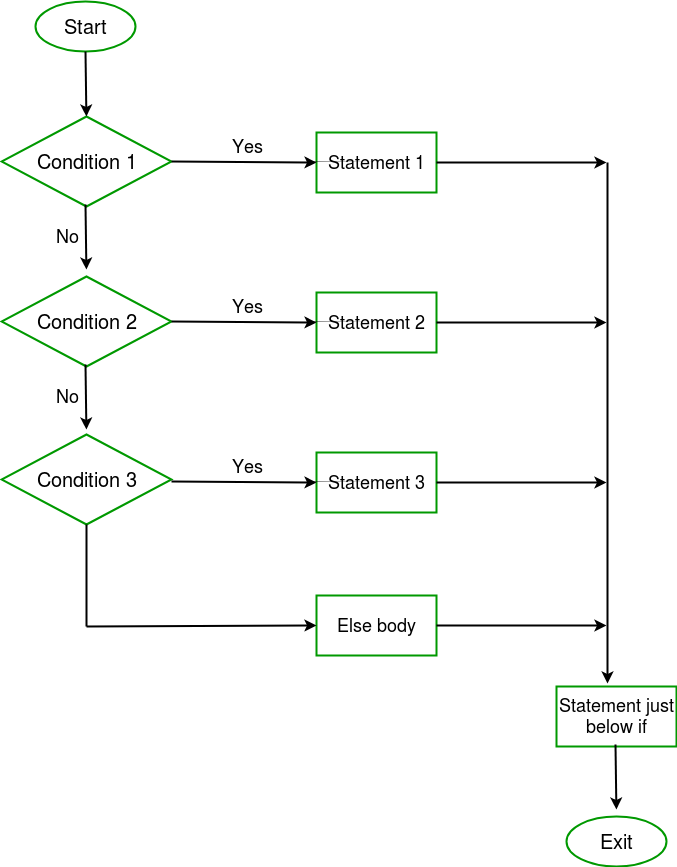
例子:
C
// C program to illustrate nested-if statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { int i = 20; if (i == 10) printf ( "i is 10" ); else if (i == 15) printf ( "i is 15" ); else if (i == 20) printf ( "i is 20" ); else printf ( "i is not present" ); } |
C++
// C++ program to illustrate if-else-if ladder #include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int i = 20; if (i == 10) cout<< "i is 10" ; else if (i == 15) cout<< "i is 15" ; else if (i == 20) cout<< "i is 20" ; else cout<< "i is not present" ; } |
i is 20
C/C中的跳转语句++
这些语句在C orC++中用于在程序中的所有函数中实现无条件的控制流。它们支持四种类型的跳转语句:
- C休息: 此循环控制语句用于终止循环。一旦在循环中遇到break语句,循环迭代就在那里停止,控制从循环立即返回到循环后的第一条语句。 语法:
break;
- 基本上,break语句用于我们不确定循环的实际迭代次数,或者我们希望根据某些条件终止循环的情况。
![图片[6]-C/C++中的决策(IF,if……,嵌套if,如果是)-yiteyi-C++库](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/break.png)
- 例子:
C
// C program to illustrate // Linear Search #include <stdio.h> void findElement( int arr[], int size, int key) { // loop to traverse array and search for key for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { printf ( "Element found at position: %d" , (i + 1)); break ; } } } int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; // no of elements int n = 6; // key to be searched int key = 3; // Calling function to find the key findElement(arr, n, key); return 0; } |
C++
// CPP program to illustrate // Linear Search #include <iostream> using namespace std; void findElement( int arr[], int size, int key) { // loop to traverse array and search for key for ( int i = 0; i < size; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { cout << "Element found at position: " << (i + 1); break ; } } } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 }; int n = 6; // no of elements int key = 3; // key to be searched // Calling function to find the key findElement(arr, n, key); return 0; } |
Element found at position: 3
- C 继续 : 这个循环控制语句与 中断声明 这个 持续 声明与break的声明相反 陈述 ,而不是终止循环,它强制执行循环的下一次迭代。 顾名思义,continue语句强制循环继续或执行下一个迭代。当continue语句在循环中执行时,continue语句后面的循环中的代码将被跳过,循环的下一次迭代将开始。 语法:
continue;
![图片[7]-C/C++中的决策(IF,if……,嵌套if,如果是)-yiteyi-C++库](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/uploads/continue.png)
- 例子:
C
// C program to explain the use // of continue statement #include <stdio.h> int main() { // loop from 1 to 10 for ( int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { // If i is equals to 6, // continue to next iteration // without printing if (i == 6) continue ; else // otherwise print the value of i printf ( "%d " , i); } return 0; } |
C++
// C++ program to explain the use // of continue statement #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { // loop from 1 to 10 for ( int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) { // If i is equals to 6, // continue to next iteration // without printing if (i == 6) continue ; else // otherwise print the value of i cout << i << " " ; } return 0; } |
1 2 3 4 5 7 8 9 10
如果在C/C++中的If-else中创建一个变量,那么它将仅位于If/else块的本地。可以在if/else块中使用全局变量。如果在If/else中创建的变量的名称与任何全局变量相同,则“局部变量”将被赋予优先级。
C++
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ int gfg=0; // local variable for main cout<< "Before if-else block " <<gfg<<endl; if (1){ int gfg = 100; // new local variable of if block cout<< "if block " <<gfg<<endl; } cout<< "After if block " <<gfg<<endl; return 0; } /* Before if-else block 0 if block 100 After if block 0 */ |
C
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int gfg=0; // local variable for main printf ( "Before if-else block %d" ,gfg); if (1){ int gfg = 100; // new local variable of if block printf ( "if block %d" ,gfg); } printf ( "After if block %d" ,gfg); return 0; } |
- C后藤: C/C++中的goto语句也称为无条件跳转语句,可用于在函数中从一点跳转到另一点。 语法 :
Syntax1 | Syntax2----------------------------goto label; | label: . | .. | .. | .label: | goto label;
- 在上述语法中,第一行告诉编译器转到或跳转到标记为标签的语句。这里label是一个用户定义的标识符,用于指示目标语句。紧跟在“label:”后面的语句是destination语句。“label:”也可以出现在“goto label;”之前上述语法中的语句。
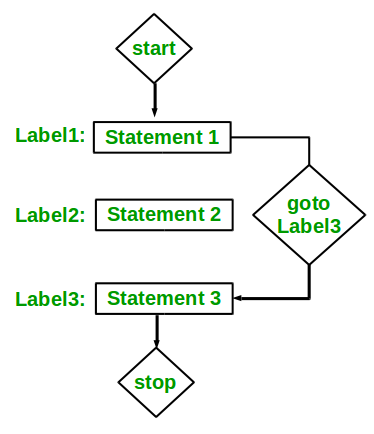
- 下面是一些如何使用goto语句的示例: 例如:
C
// C program to print numbers // from 1 to 10 using goto statement #include <stdio.h> // function to print numbers from 1 to 10 void printNumbers() { int n = 1; label: printf ( "%d " ,n); n++; if (n <= 10) goto label; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { printNumbers(); return 0; } |
C++
// C++ program to print numbers // from 1 to 10 using goto statement #include <iostream> using namespace std; // function to print numbers from 1 to 10 void printNumbers() { int n = 1; label: cout << n << " " ; n++; if (n <= 10) goto label; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { printNumbers(); return 0; } |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
- C返回: C或C++中的返回将执行的流程从调用的函数返回到函数。此语句不强制要求使用任何条件语句。语句一执行,程序流立即停止,并返回调用它的控件。对于void函数,return语句可能返回也可能不返回任何内容,但对于非void函数,必须返回返回值is。 语法:
return[expression];
- 例子:
C
// C code to illustrate return // statement #include <stdio.h> // non-void return type // function to calculate sum int SUM( int a, int b) { int s1 = a + b; return s1; } // returns void // function to print void Print( int s2) { printf ( "The sum is %d" , s2); return ; } int main() { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 10; int sum_of = SUM(num1, num2); Print(sum_of); return 0; } |
C++
// C++ code to illustrate return // statement #include <iostream> using namespace std; // non-void return type // function to calculate sum int SUM( int a, int b) { int s1 = a + b; return s1; } // returns void // function to print void Print( int s2) { cout << "The sum is " << s2; return ; } int main() { int num1 = 10; int num2 = 10; int sum_of = SUM(num1, num2); Print(sum_of); return 0; } |
The sum is 20
?列表=PLQM7ALHXFYSGG6GSRME2IN4K8FPH5QVB


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



