我们引入了链接列表 以前的职位 .我们还创建了一个包含3个节点的简单链表,并讨论了链表遍历。 本文中讨论的所有程序都考虑链表的以下表示形式。
C++
// A linked list node class Node { public : int data; Node *next; }; // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
// A linked list node struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; |
JAVA
// Linked List Class class LinkedList { Node head; // head of list /* Node Class */ class Node { int data; Node next; // Constructor to create a new node Node( int d) {data = d; next = null ; } } } |
Python3
# Node class class Node: # Function to initialize the node object def __init__( self , data): self .data = data # Assign data self . next = None # Initialize next as null # Linked List class class LinkedList: # Function to initialize the Linked List object def __init__( self ): self .head = None |
C#
/* Linked list Node*/ public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node( int d) {data = d; next = null ; } } |
Javascript
<script> // Linked List Class var head; // head of list /* Node Class */ class Node { // Constructor to create a new node constructor(d) { this .data = d; this .next = null ; } } // This code is contributed by todaysgaurav </script> |
本文讨论了在链表中插入新节点的方法。可以通过三种方式添加节点 1) 在链接列表的前面 2) 在给定节点之后。 3) 在链接列表的末尾。
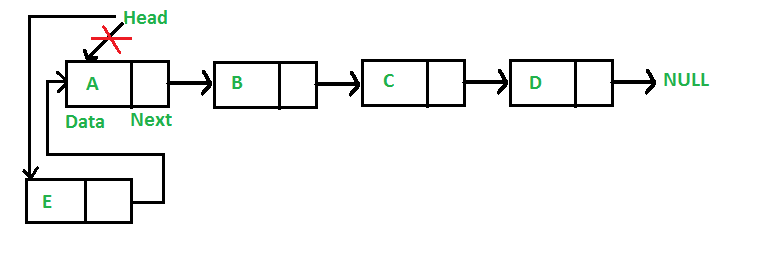
在前面添加一个节点:(4步流程) 新节点总是添加到给定链表的头之前。新添加的节点成为链表的新头。例如,如果给定的链表是10->15->20->25,并且我们在前面添加了一个项目5,那么链表就变成了5->10->15->20->25。让我们调用在列表前面添加的函数push()。push()必须接收指向头指针的指针,因为push必须将头指针更改为指向新节点(请参阅) 这 )
以下是在前端添加节点的4个步骤。
C++
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */ void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ Node* new_node = new Node(); /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. Make next of new node as head */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* 4. move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */ void push( struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. Make next of new node as head */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* 4. move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } |
JAVA
/* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new Node at front of the list. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void push( int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } |
Python3
# This function is in LinkedList class # Function to insert a new node at the beginning def push( self , new_data): # 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new Node as head new_node. next = self .head # 4. Move the head to point to new Node self .head = new_node |
C#
/* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */ public void push( int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } |
Javascript
<script> /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new Node at front of the list. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function push(new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } // This code contributed by Rajput-Ji </script> |
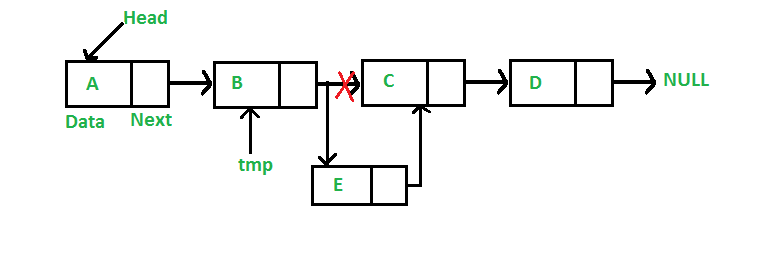
push()的时间复杂度为O(1),因为它做的是恒定的工作量。 在给定节点后添加一个节点:(5步流程) 我们得到一个指向某个节点的指针,新节点插入到给定节点之后。
C++
// Given a node prev_node, insert a // new node after the given // prev_node void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data) { // 1. Check if the given prev_node is NULL if (prev_node == NULL) { cout << "The given previous node cannot be NULL" ; return ; } // 2. Allocate new node Node* new_node = new Node(); // 3. Put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // 4. Make next of new node as // next of prev_node new_node->next = prev_node->next; // 5. move the next of prev_node // as new_node prev_node->next = new_node; } // This code is contributed by anmolgautam818, // arkajyotibasak |
C
/* Given a node prev_node, insert a new node after the given prev_node */ void insertAfter( struct Node* prev_node, int new_data) { /*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */ if (prev_node == NULL) { printf ( "the given previous node cannot be NULL" ); return ; } /* 2. allocate new node */ struct Node* new_node = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); /* 3. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */ new_node->next = prev_node->next; /* 5. move the next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node->next = new_node; } |
JAVA
/* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { System.out.println( "The given previous node cannot be null" ); return ; } /* 2. Allocate the Node & 3. Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } |
Python3
# This function is in LinkedList class. # Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ def insertAfter( self , prev_node, new_data): # 1. check if the given prev_node exists if prev_node is None : print ( "The given previous node must inLinkedList." ) return # 2. Create new node & # 3. Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node new_node. next = prev_node. next # 5. make next of prev_node as new_node prev_node. next = new_node |
C#
/* Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { Console.WriteLine( "The given previous node" + " cannot be null" ); return ; } /* 2 & 3: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } |
Javascript
<script> /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function insertAfter(prev_node , new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { document.write( "The given previous node cannot be null" ); return ; } /* 2. Allocate the Node & 3. Put in the data*/ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } // This code is contributed by aashish1995 </script> |
insertAfter()的时间复杂度为O(1),因为它做的是恒定的工作量。
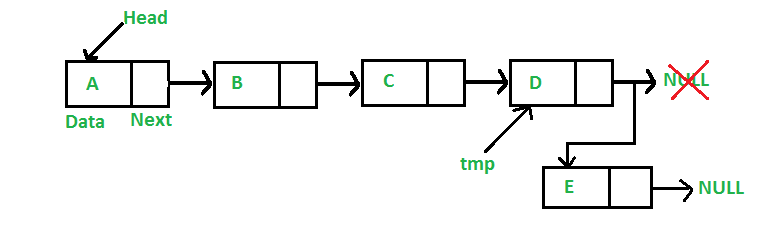
在末尾添加一个节点:(6步流程) 新节点始终添加在给定链表的最后一个节点之后。例如,如果给定的链表是5->10->15->20->25,并且我们在末尾添加了一个项目30,那么链表将变成5->10->15->20->25->30。 由于链表通常由其头部表示,因此我们必须遍历链表直到结束,然后将从下一个到最后一个节点更改为新节点。
下面是在末尾添加节点的6个步骤。
C++
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head // of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { // 1. allocate node Node* new_node = new Node(); // Used in step 5 Node *last = *head_ref; // 2. Put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // 3. This new node is going to be // the last node, so make next of // it as NULL new_node->next = NULL; // 4. If the Linked List is empty, // then make the new node as head if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return ; } // 5. Else traverse till the last node while (last->next != NULL) { last = last->next; } // 6. Change the next of last node last->next = new_node; return ; } // This code is contributed by anmolgautam818, arkajyotibasak |
C
/* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */ void append( struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); struct Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/ /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as NULL*/ new_node->next = NULL; /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return ; } /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ while (last->next != NULL) last = last->next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last->next = new_node; return ; } |
JAVA
/* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append( int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } |
Python3
# This function is defined in Linked List class # Appends a new node at the end. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above def append( self , new_data): # 1. Create a new node # 2. Put in the data # 3. Set next as None new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the # new node as head if self .head is None : self .head = new_node return # 5. Else traverse till the last node last = self .head while (last. next ): last = last. next # 6. Change the next of last node last. next = new_node |
C#
/* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append( int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } |
Javascript
<script> /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function append(new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ var last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } // This code contributed by aashish1995 </script> |
append的时间复杂度为O(n),其中n是链表中的节点数。由于从头到尾都有一个循环,所以函数不工作。 这种方法也可以通过保持一个指向链表尾部的额外指针来优化,以在O(1)中工作/
下面是一个完整的程序,它使用上述所有方法创建一个链表。
C++
// A complete working C++ program to demonstrate // all insertion methods on Linked List #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // A linked list node class Node { public : int data; Node *next; }; /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */ void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ Node* new_node = new Node(); /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. Make next of new node as head */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* 4. move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } /* Given a node prev_node, insert a new node after the given prev_node */ void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data) { /*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */ if (prev_node == NULL) { cout<< "The given previous node cannot be NULL" ; return ; } /* 2. allocate new node */ Node* new_node = new Node(); /* 3. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */ new_node->next = prev_node->next; /* 5. move the next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node->next = new_node; } /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */ void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ Node* new_node = new Node(); Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/ /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as NULL*/ new_node->next = NULL; /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return ; } /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ while (last->next != NULL) { last = last->next; } /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last->next = new_node; return ; } // This function prints contents of // linked list starting from head void printList(Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { cout<< " " <<node->data; node = node->next; } } /* Driver code*/ int main() { /* Start with the empty list */ Node* head = NULL; // Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NULL append(&head, 6); // Insert 7 at the beginning. // So linked list becomes 7->6->NULL push(&head, 7); // Insert 1 at the beginning. // So linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL push(&head, 1); // Insert 4 at the end. So // linked list becomes 1->7->6->4->NULL append(&head, 4); // Insert 8, after 7. So linked // list becomes 1->7->8->6->4->NULL insertAfter(head->next, 8); cout<< "Created Linked list is: " ; printList(head); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra, arkajyotibasak |
C
// A complete working C program to demonstrate all insertion methods // on Linked List #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> // A linked list node struct Node { int data; struct Node *next; }; /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */ void push( struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. Make next of new node as head */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* 4. move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } /* Given a node prev_node, insert a new node after the given prev_node */ void insertAfter( struct Node* prev_node, int new_data) { /*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */ if (prev_node == NULL) { printf ( "the given previous node cannot be NULL" ); return ; } /* 2. allocate new node */ struct Node* new_node =( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); /* 3. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */ new_node->next = prev_node->next; /* 5. move the next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node->next = new_node; } /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */ void append( struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); struct Node *last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/ /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as NULL*/ new_node->next = NULL; /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return ; } /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ while (last->next != NULL) last = last->next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last->next = new_node; return ; } // This function prints contents of linked list starting from head void printList( struct Node *node) { while (node != NULL) { printf ( " %d " , node->data); node = node->next; } } /* Driver program to test above functions*/ int main() { /* Start with the empty list */ struct Node* head = NULL; // Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NULL append(&head, 6); // Insert 7 at the beginning. So linked list becomes 7->6->NULL push(&head, 7); // Insert 1 at the beginning. So linked list becomes 1->7->6->NULL push(&head, 1); // Insert 4 at the end. So linked list becomes 1->7->6->4->NULL append(&head, 4); // Insert 8, after 7. So linked list becomes 1->7->8->6->4->NULL insertAfter(head->next, 8); printf ( " Created Linked list is: " ); printList(head); return 0; } |
JAVA
// A complete working Java program to demonstrate all insertion methods // on linked list class LinkedList { Node head; // head of list /* Linked list Node*/ class Node { int data; Node next; Node( int d) {data = d; next = null ; } } /* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */ public void push( int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } /* Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { System.out.println( "The given previous node cannot be null" ); return ; } /* 2 & 3: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append( int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } /* This function prints contents of linked list starting from the given node */ public void printList() { Node tnode = head; while (tnode != null ) { System.out.print(tnode.data+ " " ); tnode = tnode.next; } } /* Driver program to test above functions. Ideally this function should be in a separate user class. It is kept here to keep code compact */ public static void main(String[] args) { /* Start with the empty list */ LinkedList llist = new LinkedList(); // Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NUllist llist.append( 6 ); // Insert 7 at the beginning. So linked list becomes // 7->6->NUllist llist.push( 7 ); // Insert 1 at the beginning. So linked list becomes // 1->7->6->NUllist llist.push( 1 ); // Insert 4 at the end. So linked list becomes // 1->7->6->4->NUllist llist.append( 4 ); // Insert 8, after 7. So linked list becomes // 1->7->8->6->4->NUllist llist.insertAfter(llist.head.next, 8 ); System.out.println( "Created Linked list is: " ); llist.printList(); } } // This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra |
Python3
# A complete working Python program to demonstrate all # insertion methods of linked list # Node class class Node: # Function to initialise the node object def __init__( self , data): self .data = data # Assign data self . next = None # Initialize next as null # Linked List class contains a Node object class LinkedList: # Function to initialize head def __init__( self ): self .head = None # Function to insert a new node at the beginning def push( self , new_data): # 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new Node as head new_node. next = self .head # 4. Move the head to point to new Node self .head = new_node # This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a # new node after the given prev_node. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ def insertAfter( self , prev_node, new_data): # 1. check if the given prev_node exists if prev_node is None : print ( "The given previous node must inLinkedList." ) return # 2. create new node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node new_node. next = prev_node. next # 5. make next of prev_node as new_node prev_node. next = new_node # This function is defined in Linked List class # Appends a new node at the end. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ def append( self , new_data): # 1. Create a new node # 2. Put in the data # 3. Set next as None new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the # new node as head if self .head is None : self .head = new_node return # 5. Else traverse till the last node last = self .head while (last. next ): last = last. next # 6. Change the next of last node last. next = new_node # Utility function to print the linked list def printList( self ): temp = self .head while (temp): print (temp.data,end = " " ) temp = temp. next # Code execution starts here if __name__ = = '__main__' : # Start with the empty list llist = LinkedList() # Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->None llist.append( 6 ) # Insert 7 at the beginning. So linked list becomes 7->6->None llist.push( 7 ); # Insert 1 at the beginning. So linked list becomes 1->7->6->None llist.push( 1 ); # Insert 4 at the end. So linked list becomes 1->7->6->4->None llist.append( 4 ) # Insert 8, after 7. So linked list becomes 1 -> 7-> 8-> 6-> 4-> None llist.insertAfter(llist.head. next , 8 ) print ( 'Created linked list is: ' ) llist.printList() # This code is contributed by Manikantan Narasimhan |
C#
// A complete working C# program to demonstrate // all insertion methods on linked list using System; class GFG { public Node head; // head of list /* Linked list Node*/ public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node( int d) {data = d; next = null ;} } /* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */ public void push( int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } /* Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { Console.WriteLine( "The given previous" + " node cannot be null" ); return ; } /* 2 & 3: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append( int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } /* This function prints contents of linked list starting from the given node */ public void printList() { Node tnode = head; while (tnode != null ) { Console.Write(tnode.data + " " ); tnode = tnode.next; } } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { /* Start with the empty list */ GFG llist = new GFG(); // Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NUllist llist.append(6); // Insert 7 at the beginning. // So linked list becomes 7->6->NUllist llist.push(7); // Insert 1 at the beginning. // So linked list becomes 1->7->6->NUllist llist.push(1); // Insert 4 at the end. So linked list becomes // 1->7->6->4->NUllist llist.append(4); // Insert 8, after 7. So linked list becomes // 1->7->8->6->4->NUllist llist.insertAfter(llist.head.next, 8); Console.Write( "Created Linked list is: " ); llist.printList(); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji |
Javascript
<script> // A complete working javascript program // to demonstrate all insertion methods // on linked list var head; // head of list /* Linked list Node */ class Node { constructor(val) { this .data = val; this .next = null ; } } /* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */ function push(new_data) { /* * 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data */ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } /* Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. */ function insertAfter(prev_node , new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null ) { document.write( "The given previous node cannot be null" ); return ; } /* * 2 & 3: Allocate the Node & Put in the data */ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } /* * Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class * shown above */ function append(new_data) { /* * 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* * 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null ) { head = new Node(new_data); return ; } /* * 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null ; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ var last = head; while (last.next != null ) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return ; } /* * This function prints contents of linked list starting from the given node */ function printList() { var tnode = head; while (tnode != null ) { document.write(tnode.data + " " ); tnode = tnode.next; } } /* * Driver program to test above functions. Ideally this function should be in a * separate user class. It is kept here to keep code compact */ /* Start with the empty list */ // Insert 6. So linked list becomes 6->NUllist append(6); // Insert 7 at the beginning. So linked list becomes // 7->6->NUllist push(7); // Insert 1 at the beginning. So linked list becomes // 1->7->6->NUllist push(1); // Insert 4 at the end. So linked list becomes // 1->7->6->4->NUllist append(4); // Insert 8, after 7. So linked list becomes // 1->7->8->6->4->NUllist insertAfter(head.next, 8); document.write( "Created Linked list is: " ); printList(); // This code contributed by gauravrajput1 </script> |
输出:
Created Linked list is: 1 7 8 6 4
你可以试试 在链表上练习MCQ问题 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



