null
分配
- 均匀分布: 它产生随机整数值i,其均匀分布在闭合区间[a,b]上,由以下概率质量函数描述:

- 运算符(): 它生成根据概率函数分布的随机数。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最大下限,这是均匀分布的分布参数“a”。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最小上界,这是均匀分布的分布参数“b”。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便在后续使用时,结果不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator()// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Constructing a trivial random generator engineunsigned s = 2;// The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator (s);uniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1,10);cout <<"Some random numbers between 1 and 10";for(inti = 0; i < 10; ++i)cout << distribution(generator) ;cout << endl;return0;}输出:
Some random numbers between 1 and 10: 1 3 6 10 1 5 1 4 4 9
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){//the random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the uniform distributionuniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1, 1000);// First random number is generatedcout << distribution(generator) << endl;//Resets the distributiondistribution.reset();// Second random number is//generated independent of previous numbercout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
1 132
- 均匀实分布: 产生浮点值的是随机数分布,由以下概率密度函数描述:

- 运算符(): 它返回一个跟随分布参数的新随机数。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最大下限,这是均匀实分布的分布参数“a”。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最小上界,这是均匀实分布的分布参数“b”。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便在后续使用时,结果不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator()// in uniform_int_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Constructing a trivial random generator engineunsigned s = 2;// The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator (s);uniform_int_distribution<int> distribution(1,10);cout <<"Random numbers between 1 and 10";for(inti = 0; i< 10; ++i)cout << distribution(generator) ;cout << endl;return0;}输出:
some random numbers between 0.0 and 10.0: 0.150031 9.77072 3.36669 7.06447 5.11455 8.43061 1.93792 7.78965 8.31532 5.14354
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset// in uniform_real_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){default_random_engine generator;uniform_real_distribution<double> distribution(0.0,100.0);// It prints two independent values:// First random number is generatedcout << distribution(generator) << endl;//Resets the distributiondistribution.reset();// Second random number is//generated independent of previous numbercout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
13.1538 45.865
- 伯努利分布: 正是随机数分布根据伯努利分布产生布尔值,由以下概率质量函数给出:

- 运算符(): 它返回一个新的随机数。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最大下限,对于bernoulli_分布,该下限为false。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()返回的值范围的最小上界,这对于伯努利分布是正确的。
// C++ program to illustrate// the bernoulli_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){constinttemp=500;//The random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;//Initialising the bernoulli distributionbernoulli_distribution distribution(0.7);// count number of truesintcount=0;for(inti = 0; i < temp; ++i){// checking for true conditionif(distribution(generator))count++;}cout <<"bernoulli_distribution (0.7) x 500:"<< endl;cout <<"true: "<< count << endl;cout <<"false: "<< temp-count << endl;return0;}输出:
bernoulli_distribution (0.7) x 500: true: 360 false: 140
// C++ program to// illustrate the use of reset#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;//Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the bernoulli distributionbernoulli_distribution distribution;// print two independent values:cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// use of reset// Generates second output without// the effect of first outputdistribution.reset();cout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
1 1
- 二项分布: 正是随机数分布根据二项式离散分布产生整数,该分布由概率质量函数给出:

- 运算符(): 它会生成一个新的随机数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上界,对于二项式分布,它是分布参数t。
- 敏: 它返回成员运算符()给出的范围的最大下界,对于二项式分布,该下界始终为零。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random//generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising binomial distributionbinomial_distribution<int> distribution (15, 0.4);cout <<"some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}输出:
some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): 7 6 7 8 4 6 7 6 9 3 5 6 4 6 7
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random//generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising binomial distributionbinomial_distribution<int> distribution (15, 0.4);cout <<"some binomial results (t=15, p=0.4): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}输出:
57 52
- 几何分布: 它是一种随机数分布,根据几何离散分布产生整数,由以下概率质量函数给出:

- 运算符(): 它返回一个跟随分布参数的新随机数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上限。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()给出的最小值。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate//the use of geometric_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <string>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// construct a trivial random// generator engine from a time-based seed:intseed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialises the geometric distributiongeometric_distribution<int> distribution (1.0 / 5);cout <<"Plus sign is 5 spaces away from the next :"<< endl;for(inti = 0; i < 10 ; ++i){intnumber = distribution(generator);cout << string (number,' ') <<"+";}return0;}输出:
each plus sign is 5 spaces away from the next : ++ + + + ++ + ++// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the geometric distributiongeometric_distribution<int> distribution(0.3);// Prints two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
0 1
- 负二项分布: 它是一种随机数分布,根据负二项离散分布(也称为Pascal分布)生成整数,由以下概率质量函数给出:
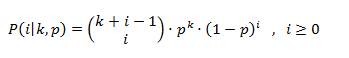
- 运算符(): 它返回一个新的随机数,该随机数跟随分布参数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上限。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()给出的最小值,对于负二项分布,该值始终为零。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of operator() in// negative_binomial_distribution#include <iostream>#include <chrono>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// construct a trivial random// generator engine from a time-based seed:unsigned seed = chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();default_random_engine generator (seed);// Initialising negative binomial distributionnegative_binomial_distribution<int> distribution (6,0.7);cout <<"Negative binomial results (t=6, p=0.7): ";for(inti = 0; i < 15; ++i){// Use of operatorcout << distribution(generator) <<" ";}cout << endl;return0;}输出:
Negative binomial results (t=6, p=0.7): 2 6 3 1 4 1 4 1 2 0 7 3 4 4 4
// C++ program to illustrate// the use of reset in// negative_binomial_distribution::#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the negative binomial distributionnegative_binomial_distribution<int> distribution(20, 0.5);// print two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates the second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
23 30
- 离散分布: 它是一种随机数分布,根据离散分布生成整数值。
- 运算符(): 它返回一个跟随分布参数的新随机数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上限。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最大下限。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of operator() in// discrete_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;intmain(){// number of experimentsintn = 10000;// maximum number of stars to distributeintm = 100;// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;//Initialising discrete distributiondiscrete_distribution<int> distribution { 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1, 1, 2, 2 };intp[10] = {};// use of operator()for(inti = 0; i < n; i++){intnumber = distribution(generator);p[number]++;}cout <<"a discrete_distribution:"<< endl;for(inti = 0; i < 10; ++i){cout << i <<": "<< string(p[i]*m/n,'*') << endl;}return0;}输出:
a discrete_distribution: 0: ************ 1: ************* 2: ***** 3: ****** 4: ************ 5: ************ 6: ****** 7: ****** 8: ************ 9: ************
// C++ program to illustrate//the use of reset in//discrete_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising the discrete distributiondiscrete_distribution<int> distribution {20,20,30,40};// print two independent values:// Generates the first valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates the secong valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
0 2
- 分段常数分布: 它是一种随机数分布,产生的浮点值均匀分布在一系列连续的子区间上,由以下概率密度函数给出:

- 运算符(): 它返回一个跟随分布参数的新随机数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上限。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最大下限。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of reset in// piecewise_constant_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialisind piecewise_constant_distributionpiecewise_constant_distribution<double> distribution( 4, 0.0, 10.0, [](doublex){returnx;} );// print two independent values:// Generates the first value// Use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// Generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
3.4205 6.6692
- 分段线性分布: 它是一种随机数分布,产生分布在连续子区间序列上的浮点值。
- 运算符(): 它返回一个跟随分布参数的新随机数。
- 最大值: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最小上限。
- 敏: 它返回运算符()给出的范围的最大下限。
- 重置: 它重置分布,以便对象的后续使用不依赖于它已经生成的值。
// C++ program to illustrate the// use of reset in// piecewise_linear_distribution#include <iostream>#include <random>usingnamespacestd;// Driver programintmain(){// Random number generatordefault_random_engine generator;// Initialising piecewise_linear_distributionpiecewise_linear_distribution<double>distribution ( 5, 0.0, 10.0, [](doublex){returnx+1.0;} );// print two independent values:// generates first value// use of operator()cout << distribution(generator) << endl;// Use of resetdistribution.reset();// generates second valuecout << distribution(generator) << endl;return0;}输出:
2.48143 6.07656
本文由 沙姆巴维·辛格 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 贡献极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄到contribute@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。
如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END





![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



