给定一个N×N矩阵(M)填充1,0,2,3。找到从源移动到目标(接收器)所需的最小移动次数。而只遍历空白单元格。你可以上下左右移动。 细胞的价值 1. 意思是来源。 细胞的价值 2. 意思是目的地。 细胞的价值 3. 表示空白单元格。 细胞的价值 0 意思是空白墙。
null
笔记 :只有一个源和一个目标。它们可能是从源到目标(接收器)的多条路径。矩阵中的每一个移动我们都认为是“1”。
例如:
Input : M[3][3] = {{ 0 , 3 , 2 }, { 3 , 3 , 0 }, { 1 , 3 , 0 }};Output : 4 Input : M[4][4] = {{ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 }, { 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 }, { 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 }, { 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 }};Output : 4
被问到: Adobe访谈 .
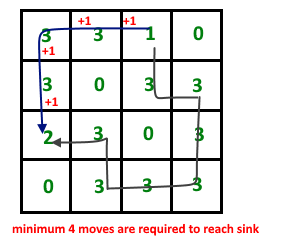
其思想是使用水平图(宽度优先遍历)。将每个单元视为一个节点,两个相邻单元之间的每个边界是一个边。所以节点的总数是N*N。
- 1.创建一个有N*N个节点(顶点)的空图。
- 2.将所有节点推到图形中。
- 3.记下源顶点和汇顶点。
- 4.现在应用水平图概念(我们使用BFS实现)。我们从源顶点找到每个节点的级别。之后,我们返回’Level[d]’(d是目的地)。(这是从源到汇的最小移动)
下面是上述想法的实施。
C++
// C++ program to find the minimum numbers // of moves needed to move from source to // destination . #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define N 4 class Graph { int V ; list < int > *adj; public : Graph( int V ) { this ->V = V ; adj = new list< int >[V]; } void addEdge( int s , int d ) ; int BFS ( int s , int d) ; }; // add edge to graph void Graph :: addEdge ( int s , int d ) { adj[s].push_back(d); adj[d].push_back(s); } // Level BFS function to find minimum path // from source to sink int Graph :: BFS( int s, int d) { // Base case if (s == d) return 0; // make initial distance of all vertex -1 // from source int *level = new int [V]; for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) level[i] = -1 ; // Create a queue for BFS list< int > queue; // Mark the source node level[s] = '0' level[s] = 0 ; queue.push_back(s); // it will be used to get all adjacent // vertices of a vertex list< int >::iterator i; while (!queue.empty()) { // Dequeue a vertex from queue s = queue.front(); queue.pop_front(); // Get all adjacent vertices of the // dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has // not been visited ( level[i] < '0') , // then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1 // and enqueue it for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) { // Else, continue to do BFS if (level[*i] < 0 || level[*i] > level[s] + 1 ) { level[*i] = level[s] + 1 ; queue.push_back(*i); } } } // return minimum moves from source to sink return level[d] ; } bool isSafe( int i, int j, int M[][N]) { if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N ) || M[i][j] == 0) return false ; return true ; } // Returns minimum numbers of moves from a source (a // cell with value 1) to a destination (a cell with // value 2) int MinimumPath( int M[][N]) { int s , d ; // source and destination int V = N*N+2; Graph g(V); // create graph with n*n node // each cell consider as node int k = 1 ; // Number of current vertex for ( int i =0 ; i < N ; i++) { for ( int j = 0 ; j < N; j++) { if (M[i][j] != 0) { // connect all 4 adjacent cell to // current cell if ( isSafe ( i , j+1 , M ) ) g.addEdge ( k , k+1 ); if ( isSafe ( i , j-1 , M ) ) g.addEdge ( k , k-1 ); if (j< N-1 && isSafe ( i+1 , j , M ) ) g.addEdge ( k , k+N ); if ( i > 0 && isSafe ( i-1 , j , M ) ) g.addEdge ( k , k-N ); } // source index if ( M[i][j] == 1 ) s = k ; // destination index if (M[i][j] == 2) d = k; k++; } } // find minimum moves return g.BFS (s, d) ; } // driver program to check above function int main() { int M[N][N] = {{ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 }, { 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 }, { 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 }, { 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 } }; cout << MinimumPath(M) << endl; return 0; } |
Python3
# Python3 program to find the minimum numbers # of moves needed to move from source to # destination . class Graph: def __init__( self , V): self .V = V self .adj = [[] for i in range (V)] # add edge to graph def addEdge ( self , s , d ): self .adj[s].append(d) self .adj[d].append(s) # Level BFS function to find minimum # path from source to sink def BFS( self , s, d): # Base case if (s = = d): return 0 # make initial distance of all # vertex -1 from source level = [ - 1 ] * self .V # Create a queue for BFS queue = [] # Mark the source node level[s] = '0' level[s] = 0 queue.append(s) # it will be used to get all adjacent # vertices of a vertex while ( len (queue) ! = 0 ): # Dequeue a vertex from queue s = queue.pop() # Get all adjacent vertices of the # dequeued vertex s. If a adjacent has # not been visited ( level[i] < '0') , # then update level[i] == parent_level[s] + 1 # and enqueue it i = 0 while i < len ( self .adj[s]): # Else, continue to do BFS if (level[ self .adj[s][i]] < 0 or level[ self .adj[s][i]] > level[s] + 1 ): level[ self .adj[s][i]] = level[s] + 1 queue.append( self .adj[s][i]) i + = 1 # return minimum moves from source # to sink return level[d] def isSafe(i, j, M): global N if ((i < 0 or i > = N) or (j < 0 or j > = N ) or M[i][j] = = 0 ): return False return True # Returns minimum numbers of moves from a # source (a cell with value 1) to a destination # (a cell with value 2) def MinimumPath(M): global N s , d = None , None # source and destination V = N * N + 2 g = Graph(V) # create graph with n*n node # each cell consider as node k = 1 # Number of current vertex for i in range (N): for j in range (N): if (M[i][j] ! = 0 ): # connect all 4 adjacent cell to # current cell if (isSafe (i , j + 1 , M)): g.addEdge (k , k + 1 ) if (isSafe (i , j - 1 , M)): g.addEdge (k , k - 1 ) if (j < N - 1 and isSafe (i + 1 , j , M)): g.addEdge (k , k + N) if (i > 0 and isSafe (i - 1 , j , M)): g.addEdge (k , k - N) # source index if (M[i][j] = = 1 ): s = k # destination index if (M[i][j] = = 2 ): d = k k + = 1 # find minimum moves return g.BFS (s, d) # Driver Code N = 4 M = [[ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 ], [ 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 ], [ 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 ], [ 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 ]] print (MinimumPath(M)) # This code is contributed by PranchalK |
输出:
4
另一种方法:(DFS实现) 属于 (问题)
同样可以使用 DFS 在哪里 源代码的完整路径 进行比较,以获得到 目的地 .
方法 :
- 循环输入矩阵中的每个元素,并从该矩阵创建一个图形
- 创建一个有N*N个顶点的图。
- 从边缘添加边 K 顶点到 k+1 / k-1 (如果边位于矩阵中的左侧或右侧元素)或 K 到 k+N/ k-N (如果边位于矩阵中的顶部或底部元素)。
- 始终检查矩阵和元素中是否存在元素!=0
- if(element==1)映射源,if(element==2)映射目标。
- 从源到目标,对形成的图形执行DFS。
- 基本条件:if source==destination返回0作为最小移动次数。
- 最小移动将是最小值(对未访问的相邻顶点执行DFS的结果)。
以下是上述方法的实施情况:
C++
// C++ program for the above approach #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define N 4 // To be used in DFS while comparing the // minimum element #define MAX (INT_MAX - 1) using namespace std; // Graph with the adjacency // list representationo class Graph { private : int V; vector< int >* adj; public : Graph( int V) : V{ V } { // Initializing the // adjacency list adj = new vector< int >[V]; } // Clearing the memory after // its use (best practice) ~Graph() { delete [] adj; } // Adding the element to the // adjacency list matrix // representation void add_edges( int u, int v) { adj[u].push_back(v); } // performing the DFS for the minimum moves int DFS( int s, int d, unordered_set< int >& visited) { // Base condition for the recursion if (s == d) return 0; // Initializing the result int res{ MAX }; visited.insert(s); for ( int item : adj[s]) if (visited.find(item) == visited.end()) // comparing the res with // the result of DFS // to get the minimum moves res = min(res, 1 + DFS(item, d, visited)); return res; } }; // ruling out the cases where the element // to be inserted is outside the matrix bool is_safe( int arr[][4], int i, int j) { if ((i < 0 || i >= N) || (j < 0 || j >= N) || arr[i][j] == 0) return false ; return true ; } int min_moves( int arr[][N]) { int s{ -1 }, d{ -1 }, V{ N * N }; /* k be the variable which represents the positions( 0 - N*N ) inside the graph. */ // k moves from top-left to bottom-right int k{ 0 }; Graph g{ V }; for ( int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for ( int j = 0; j < N; j++) { // Adding the edge if (arr[i][j] != 0) { if (is_safe(arr, i, j + 1)) g.add_edges(k, k + 1); // left if (is_safe(arr, i, j - 1)) g.add_edges(k, k - 1); // right if (is_safe(arr, i + 1, j)) g.add_edges(k, k + N); // bottom if (is_safe(arr, i - 1, j)) g.add_edges(k, k - N); // top } // Source from which DFS to be // performed if (arr[i][j] == 1) s = k; // Destination else if (arr[i][j] == 2) d = k; // Moving k from top-left // to bottom-right k++; } } unordered_set< int > visited; // DFS performed from // source to destination return g.DFS(s, d, visited); } int32_t main() { int arr[][N] = { { 3, 3, 1, 0 }, { 3, 0, 3, 3 }, { 2, 3, 0, 3 }, { 0, 3, 3, 3 } }; // if(min_moves(arr) == MAX) there // doesn't exist a path // from source to destination cout << min_moves(arr) << endl; return 0; // the DFS approach and code // is contributed by Lisho // Thomas } |
Python3
# Python3 program for the above approach # To be used in DFS while comparing the # minimum element # define MAX (I4T_MAX - 1) visited = {} adj = [[] for i in range ( 16 )] # Performing the DFS for the minimum moves def add_edges(u, v): global adj adj[u].append(v) def DFS(s, d): global visited # Base condition for the recursion if (s = = d): return 0 # Initializing the result res = 10 * * 9 visited[s] = 1 for item in adj[s]: if (item not in visited): # Comparing the res with # the result of DFS # to get the minimum moves res = min (res, 1 + DFS(item, d)) return res # Ruling out the cases where the element # to be inserted is outside the matrix def is_safe(arr, i, j): if ((i < 0 or i > = 4 ) or (j < 0 or j > = 4 ) or arr[i][j] = = 0 ): return False return True def min_moves(arr): s, d, V = - 1 , - 1 , 16 # k be the variable which represents the # positions( 0 - 4*4 ) inside the graph. # k moves from top-left to bottom-right k = 0 for i in range ( 4 ): for j in range ( 4 ): # Adding the edge if (arr[i][j] ! = 0 ): if (is_safe(arr, i, j + 1 )): add_edges(k, k + 1 ) # left if (is_safe(arr, i, j - 1 )): add_edges(k, k - 1 ) # right if (is_safe(arr, i + 1 , j)): add_edges(k, k + 4 ) # bottom if (is_safe(arr, i - 1 , j)): add_edges(k, k - 4 ) # top # Source from which DFS to be # performed if (arr[i][j] = = 1 ): s = k # Destination elif (arr[i][j] = = 2 ): d = k # Moving k from top-left # to bottom-right k + = 1 # DFS performed from # source to destination return DFS(s, d) # Driver code if __name__ = = '__main__' : arr = [ [ 3 , 3 , 1 , 0 ], [ 3 , 0 , 3 , 3 ], [ 2 , 3 , 0 , 3 ], [ 0 , 3 , 3 , 3 ] ] # If(min_moves(arr) == MAX) there # doesn't exist a path # from source to destination print (min_moves(arr)) # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 |
输出
4
本文由 尼桑·辛格 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 贡献极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄到contribute@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



