输入n的欧拉toticent函数Φ(n)是{1,2,3,…,n}中与n相对素数的数的计数,即,与n的GCD(最大公约数)为1的数。
例如:
Φ(1) = 1 gcd(1, 1) is 1Φ(2) = 1gcd(1, 2) is 1, but gcd(2, 2) is 2.Φ(3) = 2gcd(1, 3) is 1 and gcd(2, 3) is 1Φ(4) = 2gcd(1, 4) is 1 and gcd(3, 4) is 1Φ(5) = 4gcd(1, 5) is 1, gcd(2, 5) is 1, gcd(3, 5) is 1 and gcd(4, 5) is 1Φ(6) = 2gcd(1, 6) is 1 and gcd(5, 6) is 1,
如何计算输入nΦ的Φ(n) A. 简单解决方案 就是遍历从1到n-1的所有数字,用gcd计算数字,n为1。下面是计算输入整数n的Euler Toticent函数的简单方法的实现。
C++
// A simple C++ program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function #include <iostream> using namespace std; // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for ( int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) cout << "phi(" <<n<< ") = " << phi(n) << endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed by SHUBHAMSINGH10 |
C
// A simple C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include <stdio.h> // Function to return gcd of a and b int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate Euler Totient Function int phi(unsigned int n) { unsigned int result = 1; for ( int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf ( "phi(%d) = %d" , n, phi(n)); return 0; } |
JAVA
// A simple java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0 ) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi( int n) { int result = 1 ; for ( int i = 2 ; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1 ) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1 ; n <= 10 ; n++) System.out.println( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by sunnusingh |
Python3
# A simple Python3 program # to calculate Euler's # Totient Function # Function to return # gcd of a and b def gcd(a, b): if (a = = 0 ): return b return gcd(b % a, a) # A simple method to evaluate # Euler Totient Function def phi(n): result = 1 for i in range ( 2 , n): if (gcd(i, n) = = 1 ): result + = 1 return result # Driver Code for n in range ( 1 , 11 ): print ( "phi(" ,n, ") = " , phi(n), sep = "") # This code is contributed # by Smitha |
C#
// A simple C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { // Function to return GCD of a and b static int gcd( int a, int b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function static int phi( int n) { int result = 1; for ( int i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver code public static void Main() { for ( int n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal |
PHP
<Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd( $a , $b ) { if ( $a == 0) return $b ; return gcd( $b % $a , $a ); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi( $n ) { $result = 1; for ( $i = 2; $i < $n ; $i ++) if (gcd( $i , $n ) == 1) $result ++; return $result ; } // Driver Code for ( $n = 1; $n <= 10; $n ++) echo "phi(" . $n . ") =" . phi( $n ). "" ; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ> |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // Function to return // gcd of a and b function gcd(a, b) { if (a == 0) return b; return gcd(b % a, a); } // A simple method to evaluate // Euler Totient Function function phi(n) { let result = 1; for (let i = 2; i < n; i++) if (gcd(i, n) == 1) result++; return result; } // Driver Code for (let n = 1; n <= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} <br>`); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal </script> |
输出:
phi(1) = 1phi(2) = 1phi(3) = 2phi(4) = 2phi(5) = 4phi(6) = 2phi(7) = 6phi(8) = 4 phi(9) = 6phi(10) = 4
上述代码调用gcd函数O(n)次。gcd函数的时间复杂度为O(h),其中“h”是给定两个数字中较小数字的位数。因此,上述解的时间复杂度的上界是O(N logn)[如何Φ最多可以有log 10 n位数字,从1到n] 下面是一个例子 更好的解决方案 这个想法是基于欧拉的乘积公式,该公式指出,toticent函数的值低于n的乘积总素数p。

该公式基本上表示,对于n的所有素数p,Φ(n)的值等于n乘以(1-1/p)的乘积。例如Φ(6)=6*(1-1/2)*(1-1/3)=2。 我们可以用这个概念找到所有的主要因素 这 邮递
1) Initialize : result = n2) Run a loop from 'p' = 2 to sqrt(n), do following for every 'p'. a) If p divides n, then Set: result = result * (1.0 - (1.0 / (float) p)); Divide all occurrences of p in n.3) Return result
下面是欧拉乘积公式的实现。
C++
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function using Euler's // product formula #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and for every prime factor p, // multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )n)); return ( int )result; } // Driver code int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) { cout << "Phi" << "(" << n << ")" << " = " << phi(n) <<endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu |
C
// C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula #include <stdio.h> int phi( int n) { float result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1/p) for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )n)); return ( int )result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf ( "phi(%d) = %d" , n, phi(n)); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n and for // every prime factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ( int p = 2 ; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0 ) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0 ) n /= p; result *= ( 1.0 - ( 1.0 / ( float )p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n > 1 ) result *= ( 1.0 - ( 1.0 / ( float )n)); return ( int )result; } // Driver program to test above function public static void main(String args[]) { int n; for (n = 1 ; n <= 10 ; n++) System.out.println( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by Nikita Tiwari. |
Python3
# Python 3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function # using Euler's product formula def phi(n) : result = n # Initialize result as n # Consider all prime factors # of n and for every prime # factor p, multiply result with (1 - 1 / p) p = 2 while p * p< = n : # Check if p is a prime factor. if n % p = = 0 : # If yes, then update n and result while n % p = = 0 : n = n / / p result = result * ( 1.0 - ( 1.0 / float (p))) p = p + 1 # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most one # such prime factor) if n > 1 : result = result * ( 1.0 - ( 1.0 / float (n))) return int (result) # Driver program to test above function for n in range ( 1 , 11 ) : print ( "phi(" , n, ") = " , phi(n)) # This code is contributed # by Nikita Tiwari. |
C#
// C# program to calculate Euler's Totient // Function using Euler's product formula using System; class GFG { static int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n float result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1 / p) for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= ( float )(1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )p)); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result *= ( float )(1.0 - (1.0 / ( float )n)); return ( int )result; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by nitin mittal. |
PHP
<Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi( $n ) { // Initialize result as n $result = $n ; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for ( $p = 2; $p * $p <= $n ; ++ $p ) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ( $n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while ( $n % $p == 0) $n /= $p ; $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $p )); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ( $n > 1) $result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / $n )); return intval ( $result ); } // Driver Code for ( $n = 1; $n <= 10; $n ++) echo "phi(" . $n . ") =" . phi( $n ). "" ; // This code is contributed by Sam007 Φ> |
Javascript
// Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function // using Euler's product formula function phi(n) { // Initialize result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and for every prime // factor p, multiply result // with (1 - 1/p) for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / p)); } } // If n has a prime factor greater // than sqrt(n) (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result *= (1.0 - (1.0 / n)); return parseInt(result); } // Driver Code for (let n = 1; n <= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} <br>`); // This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal |
输出:
phi(1) = 1phi(2) = 1phi(3) = 2phi(4) = 2phi(5) = 4phi(6) = 2phi(7) = 6phi(8) = 4phi(9) = 6phi(10) = 4
在上述方法中,我们可以避免浮点计算。其思想是计算所有素因子及其倍数,并从n中减去该计数,以获得totient函数值(素因子和素因子倍数的gcd不为1)
1) Initialize result as n2) Consider every number 'p' (where 'p' varies from 2 to Φn). If p divides n, then do following a) Subtract all multiples of p from 1 to n [all multiples of p will have gcd more than 1 (at least p) with n] b) Update n by repeatedly dividing it by p.3) If the reduced n is more than 1, then remove all multiples of n from result.
下面是上述算法的实现。
C++
// C++ program to calculate Euler's // Totient Function #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors of n // and subtract their multiples // from result for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result -= result / n; return result; } // Driver code int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) { cout << "Phi" << "(" << n << ")" << " = " << phi(n) << endl; } return 0; } // This code is contributed by koulick_sadhu |
C
// C program to calculate Euler's Totient Function #include <stdio.h> int phi( int n) { int result = n; // Initialize result as n // Consider all prime factors of n and subtract their // multiples from result for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result -= result / n; return result; } // Driver program to test above function int main() { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) printf ( "phi(%d) = %d" , n, phi(n)); return 0; } |
JAVA
// Java program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function import java.io.*; class GFG { static int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime factors // of n and subtract their // multiples from result for ( int p = 2 ; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0 ) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0 ) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n > 1 ) result -= result / n; return result; } // Driver Code public static void main (String[] args) { int n; for (n = 1 ; n <= 10 ; n++) System.out.println( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed by ajit |
Python3
# Python3 program to calculate # Euler's Totient Function def phi(n): # Initialize result as n result = n; # Consider all prime factors # of n and subtract their # multiples from result p = 2 ; while (p * p < = n): # Check if p is a # prime factor. if (n % p = = 0 ): # If yes, then # update n and result while (n % p = = 0 ): n = int (n / p); result - = int (result / p); p + = 1 ; # If n has a prime factor # greater than sqrt(n) # (There can be at-most # one such prime factor) if (n > 1 ): result - = int (result / n); return result; # Driver Code for n in range ( 1 , 11 ): print ( "phi(" ,n, ") =" , phi(n)); # This code is contributed # by mits |
C#
// C# program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function using System; class GFG { static int phi( int n) { // Initialize result as n int result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and // subtract their // multiples from result for ( int p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then update // n and result while (n % p == 0) n /= p; result -= result / p; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result -= result / n; return result; } // Driver Code static public void Main () { int n; for (n = 1; n <= 10; n++) Console.WriteLine( "phi(" + n + ") = " + phi(n)); } } // This code is contributed // by akt_mit |
PHP
<Φphp // PHP program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi( $n ) { // Initialize // result as n $result = $n ; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for ( $p = 2; $p * $p <= $n ; ++ $p ) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if ( $n % $p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while ( $n % $p == 0) $n = (int) $n / $p ; $result -= (int) $result / $p ; } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if ( $n > 1) $result -= (int) $result / $n ; return $result ; } // Driver Code for ( $n = 1; $n <= 10; $n ++) echo "phi(" , $n , ") =" , phi( $n ), "" ; // This code is contributed // by ajit Φ> |
Javascript
// Javascript program to calculate // Euler's Totient Function function phi(n) { // Initialize // result as n let result = n; // Consider all prime // factors of n and subtract // their multiples from result for (let p = 2; p * p <= n; ++p) { // Check if p is // a prime factor. if (n % p == 0) { // If yes, then // update n and result while (n % p == 0) n = parseInt(n / p); result -= parseInt(result / p); } } // If n has a prime factor // greater than sqrt(n) // (There can be at-most // one such prime factor) if (n > 1) result -= parseInt(result / n); return result; } // Driver Code for (let n = 1; n <= 10; n++) document.write(`phi(${n}) = ${phi(n)} <br>`); // This code is contributed // by _saurabh_jaiswal |
输出:
phi(1) = 1phi(2) = 1phi(3) = 2phi(4) = 2phi(5) = 4phi(6) = 2phi(7) = 6phi(8) = 4phi(9) = 6phi(10) = 4
让我们举一个例子来理解上述算法。
n = 10. Initialize: result = 102 is a prime factor, so n = n/i = 5, result = 53 is not a prime factor.The for loop stops after 3 as 4*4 is not less than or equalto 10.After for loop, result = 5, n = 5Since n > 1, result = result - result/n = 4
欧拉函数的一些有趣性质
1) 暂时 素数p , ![]()
证据:
, where p is any prime numberWe know that
where k is any random number and
Total number from 1 to p = p Number for which
is
, i.e the number p itself, so subtracting 1 from p
例如:
2) 对于 两个素数a和b ![]() ,用于 RSA算法
,用于 RSA算法
证据:
, where a and b are prime numbers
,
Total number from 1 to ab = ab Total multiples of a from 1 to ab =
=
Total multiples of b from 1 to ab =
=
Example:a = 5, b = 7, ab = 35Multiples of a =
= 7 {5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35}Multiples of b =
= 5 {7, 14, 21, 28, 35}
Can there be any double counting ?(watch above example carefully, try with other prime numbers also for more grasp)Ofcourse, we have counted
twice in multiples of a and multiples of b so, Total multiples = a + b - 1 (with which
with
)
, removing all number with
with
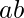
例如:
3) 对于 质数p , ![]()
证据:
, where p is a prime number
Total numbers from 1 to
Total multiples of
Removing these multiples as with them
Example : p = 2, k = 5,
= 32Multiples of 2 (as with them
) = 32 / 2 = 16 {2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32}
例如:
4) 对于 两个数字a和b ![]()
![]()
![]()
特殊情况:gcd(a,b)=1
![]()
例如:
Special Case :,
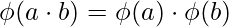
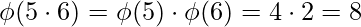
Normal Case :
,
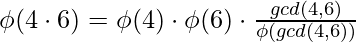
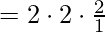
5) n的所有除数之和函数的值之和等于n。

例如:
n = 6 factors = {1, 2, 3, 6} n = 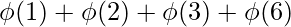 = 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 6
= 1 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 6 n = 8factors = {1, 2, 4, 8}n =
n = 8factors = {1, 2, 4, 8}n = 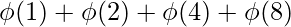 = 1 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 8
= 1 + 1 + 2 + 4 = 8 n = 10factors = {1, 2, 5, 10}n =
n = 10factors = {1, 2, 5, 10}n = 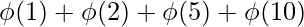 = 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 10
= 1 + 1 + 4 + 4 = 10
6) 最著名、最重要的特征表现在 欧拉定理 :
The theorem states that if n and a are coprime(or relatively prime) positive integers, thenaΦ(n) ≡ 1 (mod n)
这个 RSA密码系统 基于这个定理: 在特殊情况下,当m是素数,比如p时,欧拉定理变成了所谓的 费马小定理 :
ap-1 ≡ 1 (mod p)
7) 模n加法下有限循环群的生成元数为Φ(n) .
相关文章: 所有小于或等于n的数的Euler Toticent函数 用于多重评估的优化Euler Toticent函数
参考资料: http://e-maxx.ru/algo/euler_function http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Euler%27s_totient_function
https://cp-algorithms.com/algebra/phi-function.html
http://mathcenter.oxford.memory.edu/site/math125/chineseRemainderTheorem/ 本文由 安克尔 。如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请发表评论


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



