PageRank(PR)是谷歌搜索用来在搜索引擎结果中对网站进行排名的算法。PageRank是以谷歌创始人之一拉里·佩奇的名字命名的。PageRank是衡量网站页面重要性的一种方法。据谷歌称:
PageRank通过计算网页链接的数量和质量来粗略估计网站的重要性。基本假设是,更重要的网站可能会从其他网站收到更多链接。
这并不是谷歌用来订购搜索引擎结果的唯一算法,但它是该公司使用的第一个算法,也是最著名的算法。 上述中心性度量不适用于多个图。
算法 PageRank算法输出一个概率分布,用于表示随机点击链接的人到达任何特定页面的可能性。PageRank可以为任何大小的文档集合计算。在一些研究论文中,假设在计算过程开始时,分布均匀地分布在集合中的所有文档中。PageRank计算需要多次通过集合,称为“迭代”,以调整近似PageRank值,以更接近地反映理论真实值。
简化算法 假设一个由四个web页面组成的小宇宙:a、B、C和D。忽略从一个页面到自身的链接,或从一个页面到另一个页面的多个出站链接。所有页面的PageRank初始化为相同的值。在PageRank的原始形式中,所有页面上的PageRank之和是当时web上的页面总数,因此本例中的每个页面的初始值为1。然而,PageRank的更高版本以及本节的其余部分假设概率分布在0和1之间。因此,本例中每个页面的初始值为0.25。 在下一次迭代中,从给定页面传输到其出站链接目标的PageRank在所有出站链接中平均分配。 如果系统中只有从B、C和D页到A页的链接,那么在下一次迭代时,每个链接将把0.25个PageRank转移到A页,总共0.75个。 ![]() 假设B页有一个指向C页和a页的链接,C页有一个指向a页的链接,D页有指向所有三页的链接。因此,在第一次迭代时,B页将其现有值的一半(或0.125)转移到A页,另一半(或0.125)转移到C页。C页将其所有现有值(或0.25)转移到其链接到的唯一页面A。由于D有三个出站链接,它将其现有值的三分之一(或约0.083)转移到A。在该迭代完成时,页面A的PageRank大约为0.458。
假设B页有一个指向C页和a页的链接,C页有一个指向a页的链接,D页有指向所有三页的链接。因此,在第一次迭代时,B页将其现有值的一半(或0.125)转移到A页,另一半(或0.125)转移到C页。C页将其所有现有值(或0.25)转移到其链接到的唯一页面A。由于D有三个出站链接,它将其现有值的三分之一(或约0.083)转移到A。在该迭代完成时,页面A的PageRank大约为0.458。 ![]() 换句话说,出站链接授予的PageRank等于文档自身的PageRank分数除以出站链接的数量L()。
换句话说,出站链接授予的PageRank等于文档自身的PageRank分数除以出站链接的数量L()。 ![]() 在一般情况下,任何页面u的PageRank值可以表示为:
在一般情况下,任何页面u的PageRank值可以表示为: ![]() , i、 e.页面u的PageRank值取决于集合Bu(包含链接到页面u的所有页面的集合)中包含的每个页面v的PageRank值,除以来自页面v的链接数L(v)。该算法涉及计算PageRank的阻尼因子。这就像是政府从一个人身上提取的所得税,尽管他自己支付。
, i、 e.页面u的PageRank值取决于集合Bu(包含链接到页面u的所有页面的集合)中包含的每个页面v的PageRank值,除以来自页面v的链接数L(v)。该算法涉及计算PageRank的阻尼因子。这就像是政府从一个人身上提取的所得税,尽管他自己支付。
下面是计算页面排名的代码。
python
def pagerank(G, alpha = 0.85 , personalization = None , max_iter = 100 , tol = 1.0e - 6 , nstart = None , weight = 'weight' , dangling = None ): """Return the PageRank of the nodes in the graph. PageRank computes a ranking of the nodes in the graph G based on the structure of the incoming links. It was originally designed as an algorithm to rank web pages. Parameters ---------- G : graph A NetworkX graph. Undirected graphs will be converted to a directed graph with two directed edges for each undirected edge. alpha : float, optional Damping parameter for PageRank, default=0.85. personalization: dict, optional The "personalization vector" consisting of a dictionary with a key for every graph node and nonzero personalization value for each node. By default, a uniform distribution is used. max_iter : integer, optional Maximum number of iterations in power method eigenvalue solver. tol : float, optional Error tolerance used to check convergence in power method solver. nstart : dictionary, optional Starting value of PageRank iteration for each node. weight : key, optional Edge data key to use as weight. If None weights are set to 1. dangling: dict, optional The outedges to be assigned to any "dangling" nodes, i.e., nodes without any outedges. The dict key is the node the outedge points to and the dict value is the weight of that outedge. By default, dangling nodes are given outedges according to the personalization vector (uniform if not specified). This must be selected to result in an irreducible transition matrix (see notes under google_matrix). It may be common to have the dangling dict to be the same as the personalization dict. Returns ------- pagerank : dictionary Dictionary of nodes with PageRank as value Notes ----- The eigenvector calculation is done by the power iteration method and has no guarantee of convergence. The iteration will stop after max_iter iterations or an error tolerance of number_of_nodes(G)*tol has been reached. The PageRank algorithm was designed for directed graphs but this algorithm does not check if the input graph is directed and will execute on undirected graphs by converting each edge in the directed graph to two edges. """ if len (G) = = 0 : return {} if not G.is_directed(): D = G.to_directed() else : D = G # Create a copy in (right) stochastic form W = nx.stochastic_graph(D, weight = weight) N = W.number_of_nodes() # Choose fixed starting vector if not given if nstart is None : x = dict .fromkeys(W, 1.0 / N) else : # Normalized nstart vector s = float ( sum (nstart.values())) x = dict ((k, v / s) for k, v in nstart.items()) if personalization is None : # Assign uniform personalization vector if not given p = dict .fromkeys(W, 1.0 / N) else : missing = set (G) - set (personalization) if missing: raise NetworkXError( 'Personalization dictionary ' 'must have a value for every node. ' 'Missing nodes %s' % missing) s = float ( sum (personalization.values())) p = dict ((k, v / s) for k, v in personalization.items()) if dangling is None : # Use personalization vector if dangling vector not specified dangling_weights = p else : missing = set (G) - set (dangling) if missing: raise NetworkXError( 'Dangling node dictionary ' 'must have a value for every node. ' 'Missing nodes %s' % missing) s = float ( sum (dangling.values())) dangling_weights = dict ((k, v / s) for k, v in dangling.items()) dangling_nodes = [n for n in W if W.out_degree(n, weight = weight) = = 0.0 ] # power iteration: make up to max_iter iterations for _ in range (max_iter): xlast = x x = dict .fromkeys(xlast.keys(), 0 ) danglesum = alpha * sum (xlast[n] for n in dangling_nodes) for n in x: # this matrix multiply looks odd because it is # doing a left multiply x^T=xlast^T*W for nbr in W[n]: x[nbr] + = alpha * xlast[n] * W[n][nbr][weight] x[n] + = danglesum * dangling_weights[n] + ( 1.0 - alpha) * p[n] # check convergence, l1 norm err = sum ([ abs (x[n] - xlast[n]) for n in x]) if err < N * tol: return x raise NetworkXError( 'pagerank: power iteration failed to converge ' 'in %d iterations.' % max_iter) |
以上代码是networkx库中实现的函数。
要在networkx中实现上述功能,必须执行以下操作:
python
>>> import networkx as nx >>> G = nx.barabasi_albert_graph( 60 , 41 ) >>> pr = nx.pagerank(G, 0.4 ) >>> pr |
下面是输出,您可以在需要的安装后在空闲时获得。
python
{ 0 : 0.012774147598875784 , 1 : 0.013359655345577266 , 2 : 0.013157355731377924 , 3 : 0.012142198569313045 , 4 : 0.013160014506830858 , 5 : 0.012973342862730735 , 6 : 0.012166706783753325 , 7 : 0.011985935451513014 , 8 : 0.012973502696061718 , 9 : 0.013374146193499381 , 10 : 0.01296354505412387 , 11 : 0.013163220326063332 , 12 : 0.013368514624403237 , 13 : 0.013169335617283102 , 14 : 0.012752071800520563 , 15 : 0.012951601882210992 , 16 : 0.013776032065400283 , 17 : 0.012356820581336275 , 18 : 0.013151652554311779 , 19 : 0.012551059531065245 , 20 : 0.012583415756427995 , 21 : 0.013574117265891684 , 22 : 0.013167552803671937 , 23 : 0.013165528583400423 , 24 : 0.012584981049854336 , 25 : 0.013372989228254582 , 26 : 0.012569416076848989 , 27 : 0.013165322299539031 , 28 : 0.012954300960607157 , 29 : 0.012776091973397076 , 30 : 0.012771016515779594 , 31 : 0.012953404860268598 , 32 : 0.013364947854005844 , 33 : 0.012370004022947507 , 34 : 0.012977539153099526 , 35 : 0.013170376268827118 , 36 : 0.012959579020039328 , 37 : 0.013155319659777197 , 38 : 0.013567147133137161 , 39 : 0.012171548109779459 , 40 : 0.01296692767996657 , 41 : 0.028089802328702826 , 42 : 0.027646981396639115 , 43 : 0.027300188191869485 , 44 : 0.02689771667021551 , 45 : 0.02650459107960327 , 46 : 0.025971186884778535 , 47 : 0.02585262571331937 , 48 : 0.02565482923824489 , 49 : 0.024939722913691394 , 50 : 0.02458271197701402 , 51 : 0.024263128557312528 , 52 : 0.023505217517258568 , 53 : 0.023724311872578157 , 54 : 0.02312908947188023 , 55 : 0.02298716954828392 , 56 : 0.02270220663300396 , 57 : 0.022060403216132875 , 58 : 0.021932442105075004 , 59 : 0.021643288632623502 } |
以上代码已在空闲(windows的Python IDE)上运行。在运行此代码之前,您需要下载networkx库。大括号内的部分代表输出。它几乎类似于Ipython(适用于Ubuntu用户)。
工具书类
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/PageRank
- http://networkx.readthedocs.io/en/networkx-1.10/index.html
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/ranking-google-search-works/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/google-search-works/
因此,通过这种方式,可以计算给定图的页面排名的中心度度量。这样我们就涵盖了两个中心性度量。我想进一步介绍用于网络分析的各种中心性度量。 本文由 贾扬特·比什特 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 写极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄去评论-team@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。
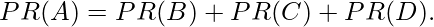


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)





