封装被定义为将数据封装在单个单元下。正是这种机制将代码及其处理的数据绑定在一起。考虑封装的另一种方式是,它是一个保护屏蔽,防止数据被屏蔽之外的代码访问。
null
- 从技术上讲,在封装中,一个类的变量或数据对任何其他类都是隐藏的,并且只能通过声明它的自己的类的任何成员函数来访问。
- 与封装一样,一个类中的数据使用数据隐藏概念从其他类中隐藏,这是通过使一个类的成员或方法私有来实现的,并且该类向最终用户或世界公开,而不提供使用抽象概念实现背后的任何细节,因此它也被称为 数据隐藏和抽象的结合 .
- 封装可以通过将类中的所有变量声明为私有,并在类中编写公共方法来设置和获取变量的值来实现
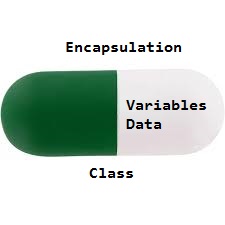
下面显示了访问类enclosedEMO变量的程序:
JAVA
// Java program to demonstrate encapsulation class Encapsulate { // private variables declared // these can only be accessed by // public methods of class private String geekName; private int geekRoll; private int geekAge; // get method for age to access // private variable geekAge public int getAge() { return geekAge; } // get method for name to access // private variable geekName public String getName() { return geekName; } // get method for roll to access // private variable geekRoll public int getRoll() { return geekRoll; } // set method for age to access // private variable geekage public void setAge( int newAge) { geekAge = newAge; } // set method for name to access // private variable geekName public void setName(String newName) { geekName = newName; } // set method for roll to access // private variable geekRoll public void setRoll( int newRoll) { geekRoll = newRoll; } } public class TestEncapsulation { public static void main(String[] args) { Encapsulate obj = new Encapsulate(); // setting values of the variables obj.setName( "Harsh" ); obj.setAge( 19 ); obj.setRoll( 51 ); // Displaying values of the variables System.out.println( "Geek's name: " + obj.getName()); System.out.println( "Geek's age: " + obj.getAge()); System.out.println( "Geek's roll: " + obj.getRoll()); // Direct access of geekRoll is not possible // due to encapsulation // System.out.println("Geek's roll: " + // obj.geekName); } } |
输出
Geek's name: HarshGeek's age: 19Geek's roll: 51
在上面的程序中,当变量声明为私有时,封装类被封装。getAge()、getName()、getRoll()等get方法被设置为public,这些方法用于访问这些变量。setName()、setAge()和setRoll()等setter方法也被声明为public,用于设置变量的值。
封装的优点 :
- 数据隐藏: 用户将不知道该类的内部实现。用户将看不到该类如何在变量中存储值。用户只知道我们正在将值传递给setter方法,并且变量正在用该值初始化。
- 增加灵活性: 根据我们的要求,我们可以使类的变量只读或只写。如果我们希望使变量为只读,那么我们必须从上面的程序中省略setName()、setAge()等setter方法,或者如果我们希望使变量为只读,那么我们必须从上面的程序中省略getName()、getAge()等get方法
- 可重用性: 封装还提高了可重用性,并且易于根据新需求进行更改。
- 测试代码很容易: 封装的代码很容易进行单元测试。
本文由 严酷的阿加瓦尔 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 写极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄去评论-team@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)






