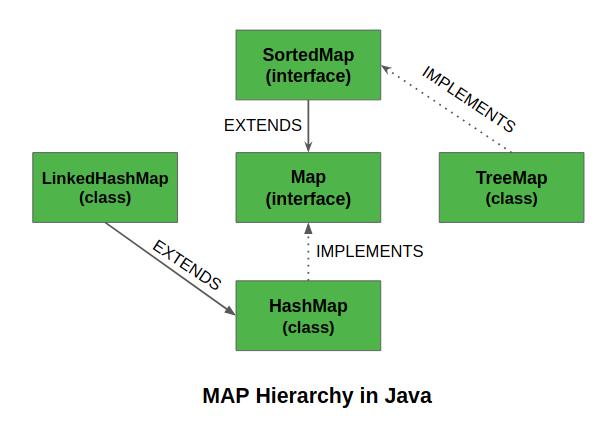
SortedMap是应用程序中的一个接口 收集框架 .此接口扩展了 地图界面 并提供其元素的总顺序(可以按键的排序顺序遍历元素)。实现这个接口的类是 树图 .
SortedMap的主要特点是,它根据密钥的自然顺序或指定的比较器对密钥进行排序。所以考虑使用 树图 当需要满足以下条件的贴图时:
- 不允许使用null键或null值。
- 键可以按自然顺序排序,也可以按指定的比较器排序。
类型参数:
- K–此地图维护的密钥类型
- V–映射值的类型
SortedMap的父接口是 映射
SortedMap的子接口是ConcurrentNavigableMap
SortedMap由ConcurrentSkipListMap实现, 树地图。
宣言:
public interface SortedMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V>
{
Comparator comparator();
SortedMap subMap(K fromKey, K toKey);
SortedMap headMap(K toKey);
SortedMap tailMap(K fromKey);
K firstKey();
K lastKey();
}
例子:
JAVA
// Java code to demonstrate SortedMap Interface import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Set; import java.util.SortedMap; import java.util.TreeMap; public class SortedMapExample { public static void main(String[] args) { SortedMap<Integer, String> sm = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); sm.put( new Integer( 2 ), "practice" ); sm.put( new Integer( 3 ), "quiz" ); sm.put( new Integer( 5 ), "code" ); sm.put( new Integer( 4 ), "contribute" ); sm.put( new Integer( 1 ), "geeksforgeeks" ); Set s = sm.entrySet(); // Using iterator in SortedMap Iterator i = s.iterator(); // Traversing map. Note that the traversal // produced sorted (by keys) output . while (i.hasNext()) { Map.Entry m = (Map.Entry)i.next(); int key = (Integer)m.getKey(); String value = (String)m.getValue(); System.out.println( "Key : " + key + " value : " + value); } } } |
输出:
Key : 1 value : geeksforgeeks Key : 2 value : practice Key : 3 value : quiz Key : 4 value : contribute Key : 5 value : code
创建SortedMap对象
因为SortedMap是一个 界面 ,无法创建SortedMap类型的对象。为了创建一个对象,我们总是需要一个扩展这个列表的类。而且,在Java 1.5中引入泛型之后,可以限制可存储在SortedMap中的对象类型。这种类型的安全地图可以定义为:
//Obj1、Obj2是要存储在SortedMap中的对象类型
SortedMap
set=new TreeMap ();
在SortedMap上执行各种操作
由于SortedMap是一个接口,因此它只能与实现该接口的类一起使用。 树图 是实现SortedMap接口的类。现在,让我们看看如何在树映射上执行一些常用的操作。
1.添加元素: 为了向SortedMap添加元素,我们可以使用 put() 方法但是,树映射中不保留插入顺序。在内部,每个元素的键都会按升序进行比较和排序。
JAVA
// Java program add the elements in the SortedMap import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Default Initialization of a // SortedMap SortedMap tm1 = new TreeMap(); // Initialization of a SortedMap // using Generics SortedMap<Integer, String> tm2 = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); // Inserting the Elements tm1.put( 3 , "Geeks" ); tm1.put( 2 , "For" ); tm1.put( 1 , "Geeks" ); tm2.put( new Integer( 3 ), "Geeks" ); tm2.put( new Integer( 2 ), "For" ); tm2.put( new Integer( 1 ), "Geeks" ); System.out.println(tm1); System.out.println(tm2); } } |
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
2.改变要素: 在添加元素之后,如果我们希望更改元素,可以通过再次添加带有 put() 方法由于SortedMap中的元素使用键进行索引,因此只需插入我们希望更改的键的更新值,即可更改键的值。
JAVA
// Java program to change // the elements in SortedMap import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Initialization of a SortedMap // using Generics SortedMap<Integer, String> tm = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); // Inserting the Elements tm.put( 3 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 2 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 1 , "Geeks" ); System.out.println(tm); tm.put( 2 , "For" ); System.out.println(tm); } } |
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
{1=Geeks, 2=For, 3=Geeks}
3.移除元件: 为了从SortedMap中删除元素,我们可以使用 删除() 方法此方法获取密钥值,并从该SortedMap中删除密钥的映射(如果该映射存在于映射中)。
JAVA
// Java program to remove the // elements from SortedMap import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class GFG { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Initialization of a SortedMap // using Generics SortedMap<Integer, String> tm = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); // Inserting the Elements tm.put( 3 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 2 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 1 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 4 , "For" ); System.out.println(tm); tm.remove( 4 ); System.out.println(tm); } } |
输出:
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks, 4=For}
{1=Geeks, 2=Geeks, 3=Geeks}
4.遍历SortedMap: 有多种方法可以遍历地图。最著名的方法是使用 增强的for循环 拿到钥匙。键的值是通过使用getValue()方法找到的。
JAVA
// Java program to iterate through SortedMap import java.util.*; class GFG { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Initialization of a SortedMap // using Generics SortedMap<Integer, String> tm = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); // Inserting the Elements tm.put( 3 , "Geeks" ); tm.put( 2 , "For" ); tm.put( 1 , "Geeks" ); for (Map.Entry mapElement : tm.entrySet()) { int key = ( int )mapElement.getKey(); // Finding the value String value = (String)mapElement.getValue(); System.out.println(key + " : " + value); } } } |
输出:
1 : Geeks 2 : For 3 : Geeks
实现SortedMap接口的类是TreeMap。
集合框架中实现的TreeMap类是SortedMap接口和SortedMap扩展映射接口的实现。它的行为类似于一个简单的映射,只是它以排序格式存储键。TreeMap使用树数据结构进行存储。对象按排序的升序存储。但我们也可以通过传递一个比较器来按降序存储。让我们看看如何使用这个类创建SortedMap对象。
JAVA
// Java program to demonstrate the // creation of SortedMap object using // the TreeMap class import java.util.*; class GFG { public static void main(String[] args) { SortedMap<String, String> tm = new TreeMap<String, String>( new Comparator<String>() { public int compare(String a, String b) { return b.compareTo(a); } }); // Adding elements into the TreeMap // using put() tm.put( "India" , "1" ); tm.put( "Australia" , "2" ); tm.put( "South Africa" , "3" ); // Displaying the TreeMap System.out.println(tm); // Removing items from TreeMap // using remove() tm.remove( "Australia" ); System.out.println( "Map after removing " + "Australia:" + tm); } } |
输出:
{South Africa=3, India=1, Australia=2}
Map after removing Australia:{South Africa=3, India=1}
DMAP接口的分类方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 比较器() | 返回用于在此映射中对键进行排序的比较器,如果此映射使用其键的自然排序,则返回null。 |
| 入口集() | 返回此映射中包含的映射的集合视图。 |
| firstKey() | 返回此映射中当前的第一个(最低)键。 |
| 头像图(K toKey) | 返回此地图中键严格小于toKey的部分的视图。 |
| 键集() | 返回此映射中包含的键的集合视图。 |
| lastKey() | 返回此映射中当前的最后一个(最高)键。 |
| 子贴图(K fromKey,K toKey) | 返回此地图部分的视图,其关键帧范围为fromKey,inclusive,toKey,exclusive。 |
| 尾图(K fromKey) | 返回此映射中键大于或等于fromKey的部分的视图。 |
| 价值观() | 返回此映射中包含的值的集合视图。 |
方法继承自java接口。util。地图
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 清除() | 此方法用于清除和删除指定映射集合中的所有元素或映射。 |
| 康纳斯基(对象) |
此方法用于检查特定密钥是否映射到映射中。 它将key元素作为参数,如果该元素映射到映射中,则返回True。 |
| containsValue(对象) |
此方法用于检查特定值是否由映射中的单个键或多个键映射。 它将该值作为参数,如果该值由映射中的任何键映射,则返回True。 |
| 入口集() |
此方法用于创建地图中包含的相同元素的集合。它基本上返回地图的集合视图,或者我们可以创建一个新集合,并将地图元素存储到其中。 |
| 相等(对象) |
此方法用于检查两个贴图之间是否相等。它验证作为参数传递的一个映射的元素是否等于此映射的元素。 |
| 获取(对象) |
此方法用于检索或获取由参数中提到的特定键映射的值。当映射不包含密钥的此类映射时,它返回NULL。 |
| hashCode() | 此方法用于为包含键和值的给定映射生成哈希代码。 |
| isEmpty() | 此方法用于检查地图是否有任何键和值对条目。如果不存在映射,则返回true。 |
| 键集() |
此方法用于返回此地图中包含的键的集合视图。集合由映射支持,因此对映射的更改会反映在集合中,反之亦然。 |
| 放置(物体,物体) | 此方法用于将指定值与此映射中的指定键相关联。 |
| putAll(地图) | 此方法用于将指定映射中的所有映射复制到此映射。 |
| 移除(对象) | 此方法用于从映射中删除密钥的映射(如果密钥存在于映射中)。 |
| 大小() | 此方法用于返回映射中可用的键/值对的数量。 |
| 价值观() |
此方法用于根据地图的值创建集合。它基本上返回HashMap中值的集合视图。 |
本文由 普拉蒂克·阿加瓦尔 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 贡献极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄到contribute@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)






