在C语言中,以下6个运算符是位运算符(在位级别工作)
null
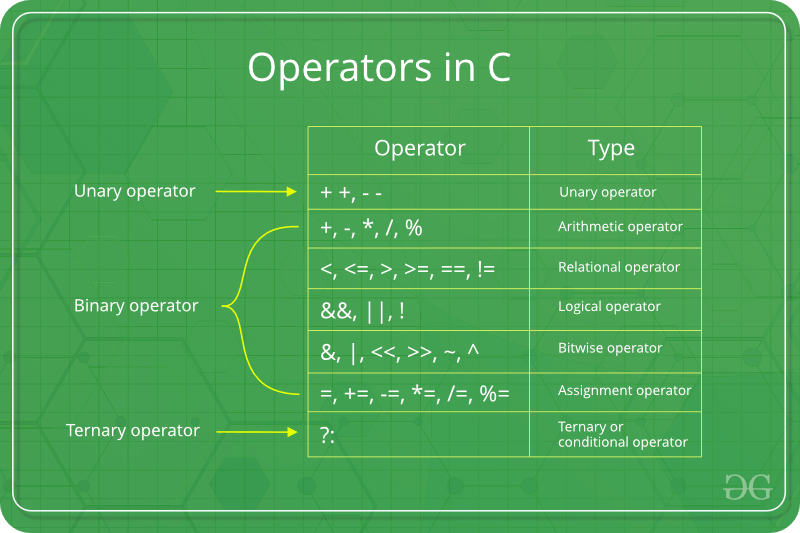
- 这个 &(按位和) 在C或C++中,两个数作为操作数,在两个数的每一个位上进行运算。只有当两位都为1时,AND的结果才为1。
- 这个 |(按位或) 在C或C++中,两个数作为操作数,在两个数的每一位上或每一个数上。如果两位中的任何一位为1,则OR的结果为1。
- 这个 ^(按位异或) 在C或C++中,两个数作为操作数,对两个数的每一个位都进行异或运算。如果两位不同,则异或的结果为1。
- 这个 < 在C或C++中取两个数,左移位第一个操作数的位,第二个操作数决定移位的位置。
- 这个 >>(右移) 在C或C++中取两个数,右移位第一个操作数,第二个操作数决定移位的位置。
- 这个 ~(按位不) 在C或C++中取一个数并反转它的所有位。
例子:
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { // a = 5(00000101), b = 9(00001001) int a = 5, b = 9; // The result is 00000001 cout<< "a = " << a << "," << " b = " << b <<endl; cout << "a & b = " << (a & b) << endl; // The result is 00001101 cout << "a | b = " << (a | b) << endl; // The result is 00001100 cout << "a ^ b = " << (a ^ b) << endl; // The result is 11111010 cout << "~(" << a << ") = " << (~a) << endl; // The result is 00010010 cout<< "b << 1" << " = " << (b << 1) <<endl; // The result is 00000100 cout<< "b >> 1 " << "= " << (b >> 1 )<<endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed by sathiyamoorthics19 |
C
// C Program to demonstrate use of bitwise operators #include <stdio.h> int main() { // a = 5(00000101), b = 9(00001001) unsigned char a = 5, b = 9; // The result is 00000001 printf ( "a = %d, b = %d" , a, b); printf ( "a&b = %d" , a & b); // The result is 00001101 printf ( "a|b = %d" , a | b); // The result is 00001100 printf ( "a^b = %d" , a ^ b); // The result is 11111010 printf ( "~a = %d" , a = ~a); // The result is 00010010 printf ( "b<<1 = %d" , b << 1); // The result is 00000100 printf ( "b>>1 = %d" , b >> 1); return 0; } |
输出:
a = 5, b = 9 a&b = 1 a|b = 13 a^b = 12 ~a = 250 b<<1 = 18 b>>1 = 4
关于位运算符的有趣事实
- 左移和右移运算符不应用于负数 .如果第二个操作数(决定移位数)是负数,则会导致C中的未定义行为。例如,1<-1的结果都未定义。此外,如果数字的移位大于整数的大小,则行为是未定义的。例如,如果使用32位存储整数,则1<<33是未定义的。另一件事是,如果加法表达式(决定移位次数的操作数)为0,则不执行移位操作。看见 这 更多细节。 注: 在里面 C++ ,这种行为定义明确。
- 按位异或运算符是最有用的运算符 A. 技术面试视角。 它被用于许多问题。一个简单的例子是“给定一组数字,其中除一个数字外,所有元素出现偶数次,找到奇数出现的数字”。这个问题可以通过对所有数字进行异或有效地解决。
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; // Function to return the only odd // occurring element int findOdd( int arr[], int n) { int res = 0, i; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) res ^= arr[i]; return res; } // Driver Method int main( void ) { int arr[] = { 12, 12, 14, 90, 14, 14, 14 }; int n = sizeof (arr) / sizeof (arr[0]); cout << "The odd occurring element is " << findOdd(arr, n); return 0; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
C
#include <stdio.h> // Function to return the only odd // occurring element int findOdd( int arr[], int n) { int res = 0, i; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) res ^= arr[i]; return res; } // Driver Method int main( void ) { int arr[] = { 12, 12, 14, 90, 14, 14, 14 }; int n = sizeof (arr) / sizeof (arr[0]); printf ( "The odd occurring element is %d " , findOdd(arr, n)); return 0; } |
输出:
The odd occurring element is 90
- 下面是使用XOR运算符的许多其他有趣问题。
- 不应使用位运算符代替逻辑运算符。 逻辑运算符(&&、| |和!)的结果是0或1,但按位运算符返回整数值。此外,逻辑运算符认为任何非零操作数为1。例如,考虑下面的程序,对于相同操作数的结果& & &是不同的。
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x = 2, y = 5; (x & y) ? cout << "True " : cout << "False " ; (x && y) ? cout << "True " : cout << "False " ; return 0; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
C
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int x = 2, y = 5; (x & y) ? printf ( "True " ) : printf ( "False " ); (x && y) ? printf ( "True " ) : printf ( "False " ); return 0; } |
输出:
False True
1.左移位和右移位运算符分别相当于乘2和除2。 如第1点所述,只有当数字为正数时,它才有效。
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x = 19; cout<< "x << 1 = " << (x << 1) <<endl; cout<< "x >> 1 = " << (x >> 1) <<endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed by sathiyamoorthics19 |
C
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int x = 19; printf ( "x << 1 = %d" , x << 1); printf ( "x >> 1 = %d" , x >> 1); return 0; } |
输出:
x << 1 = 38 x >> 1 = 9
2.&运算符可用于快速检查数字是奇数还是偶数。 只有当x为奇数时,表达式(x&1)的值才会非零,否则该值将为零。
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int x = 19 ; (x & 1) ? cout<< "Odd" : cout<< "Even" ; return 0; } // This code is contributed by sathiyamoorthics19 |
C
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int x = 19; (x & 1) ? printf ( "Odd" ) : printf ( "Even" ); return 0; } |
输出:
Odd
3.操作人员应小心使用。 如果结果存储在无符号变量中,则小数值上的~运算符的结果可能是大数值。如果结果存储在有符号变量中,则结果可能是负数(假设负数以2的补码形式存储,其中最左边的位是符号位)
C++
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { unsigned int x = 1; signed int a = 1; cout<< "Signed Result " << ~a <<endl ; cout<< "Unsigned Result " << ~x ; return 0; } // This code is contributed by sathiyamoorthics19 |
C
// Note that the output of the following // program is compiler dependent #include <stdio.h> int main() { unsigned int x = 1; printf ( "Signed Result %d " , ~x); printf ( "Unsigned Result %ud " , ~x); return 0; } |
输出:
Signed Result -2 Unsigned Result 4294967294d
© 版权声明
文章版权归作者所有,未经允许请勿转载。
THE END


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)





