一个系统中有两个单链表。由于编程错误,其中一个链表的结束节点链接到了第二个链表,形成了一个倒Y形链表。编写一个程序来获取两个链表合并的点。
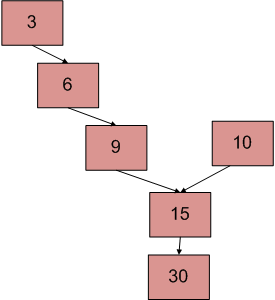
上图显示了一个示例,其中两个链表的交点为15。
方法1(只需使用两个循环) 使用2个嵌套循环。外循环将用于第一个列表的每个节点,内循环将用于第二个列表。在内部循环中,检查第二个列表的任何节点是否与第一个链表的当前节点相同。该方法的时间复杂度为O(M*N),其中M和N是两个列表中的节点数。
方法2(标记访问的节点) 此解决方案需要修改基本的链表数据结构。每个节点都有一个访问标志。遍历第一个链表,并继续标记已访问的节点。现在遍历第二个链表,如果再次看到一个已访问的节点,则有一个交点,返回相交节点。这一解决方案适用于 O(m+n) 但需要每个节点的附加信息。此解决方案的一个变体不需要修改基本数据结构,可以使用哈希实现。遍历第一个链表,并将访问节点的地址存储在散列中。现在遍历第二个链表,如果看到哈希中已经存在的地址,则返回相交节点。
方法3(使用节点计数的差异)
- 获取第一个列表中节点的计数,让计数为c1。
- 获取第二个列表中节点的计数,让计数为c2。
- 得到计数的差异 d=防抱死制动系统(c1-c2)
- 现在,从第一个节点到d个节点遍历较大的列表,这样从这里开始,两个列表的节点数相等
- 然后我们可以并行遍历这两个列表,直到遇到一个公共节点。(请注意,获取公共节点是通过比较节点的地址完成的)
下图是上述方法的试运行:
![图片[2]-编写一个函数来获取两个链表的交点-yiteyi-C++库](https://media.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/cdn-uploads/20190626143630/IntersectionYtwoLinkedList1.png)
以下是上述方法的实施情况:
C++
// C++ program to get intersection point of two linked list #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; /* Link list node */ class Node { public : int data; Node* next; }; /* Function to get the counts of node in a linked list */ int getCount(Node* head); /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, Node* head1, Node* head2); /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 */ int getIntesectionNode(Node* head1, Node* head2) { // Count the number of nodes in // both the linked list int c1 = getCount(head1); int c2 = getCount(head2); int d; // If first is greater if (c1 > c2) { d = c1 - c2; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head1, head2); } else { d = c2 - c1; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head2, head1); } } /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, Node* head1, Node* head2) { // Stand at the starting of the bigger list Node* current1 = head1; Node* current2 = head2; // Move the pointer forward for ( int i = 0; i < d; i++) { if (current1 == NULL) { return -1; } current1 = current1->next; } // Move both pointers of both list till they // intersect with each other while (current1 != NULL && current2 != NULL) { if (current1 == current2) return current1->data; // Move both the pointers forward current1 = current1->next; current2 = current2->next; } return -1; } /* Takes head pointer of the linked list and returns the count of nodes in the list */ int getCount(Node* head) { Node* current = head; // Counter to store count of nodes int count = 0; // Iterate till NULL while (current != NULL) { // Increase the counter count++; // Move the Node ahead current = current->next; } return count; } // Driver Code int main() { /* Create two linked lists 1st 3->6->9->15->30 2nd 10->15->30 15 is the intersection point */ Node* newNode; // Addition of new nodes Node* head1 = new Node(); head1->data = 10; Node* head2 = new Node(); head2->data = 3; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 6; head2->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 9; head2->next->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 15; head1->next = newNode; head2->next->next->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 30; head1->next->next = newNode; head1->next->next->next = NULL; cout << "The node of intersection is " << getIntesectionNode(head1, head2); } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
C
// C program to get intersection point of two linked list #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* Link list node */ struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; /* Function to get the counts of node in a linked list */ int getCount( struct Node* head); /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2); /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 */ int getIntesectionNode( struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { int c1 = getCount(head1); int c2 = getCount(head2); int d; if (c1 > c2) { d = c1 - c2; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head1, head2); } else { d = c2 - c1; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head2, head1); } } /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, struct Node* head1, struct Node* head2) { int i; struct Node* current1 = head1; struct Node* current2 = head2; for (i = 0; i < d; i++) { if (current1 == NULL) { return -1; } current1 = current1->next; } while (current1 != NULL && current2 != NULL) { if (current1 == current2) return current1->data; current1 = current1->next; current2 = current2->next; } return -1; } /* Takes head pointer of the linked list and returns the count of nodes in the list */ int getCount( struct Node* head) { struct Node* current = head; int count = 0; while (current != NULL) { count++; current = current->next; } return count; } /* IGNORE THE BELOW LINES OF CODE. THESE LINES ARE JUST TO QUICKLY TEST THE ABOVE FUNCTION */ int main() { /* Create two linked lists 1st 3->6->9->15->30 2nd 10->15->30 15 is the intersection point */ struct Node* newNode; struct Node* head1 = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); head1->data = 10; struct Node* head2 = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); head2->data = 3; newNode = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); newNode->data = 6; head2->next = newNode; newNode = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); newNode->data = 9; head2->next->next = newNode; newNode = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); newNode->data = 15; head1->next = newNode; head2->next->next->next = newNode; newNode = ( struct Node*) malloc ( sizeof ( struct Node)); newNode->data = 30; head1->next->next = newNode; head1->next->next->next = NULL; printf ( " The node of intersection is %d " , getIntesectionNode(head1, head2)); getchar (); } |
JAVA
// Java program to get intersection point of two linked list class LinkedList { static Node head1, head2; static class Node { int data; Node next; Node( int d) { data = d; next = null ; } } /*function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 */ int getNode() { int c1 = getCount(head1); int c2 = getCount(head2); int d; if (c1 > c2) { d = c1 - c2; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head1, head2); } else { d = c2 - c1; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head2, head1); } } /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, Node node1, Node node2) { int i; Node current1 = node1; Node current2 = node2; for (i = 0 ; i < d; i++) { if (current1 == null ) { return - 1 ; } current1 = current1.next; } while (current1 != null && current2 != null ) { if (current1.data == current2.data) { return current1.data; } current1 = current1.next; current2 = current2.next; } return - 1 ; } /*Takes head pointer of the linked list and returns the count of nodes in the list */ int getCount(Node node) { Node current = node; int count = 0 ; while (current != null ) { count++; current = current.next; } return count; } public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); // creating first linked list list.head1 = new Node( 3 ); list.head1.next = new Node( 6 ); list.head1.next.next = new Node( 9 ); list.head1.next.next.next = new Node( 15 ); list.head1.next.next.next.next = new Node( 30 ); // creating second linked list list.head2 = new Node( 10 ); list.head2.next = new Node( 15 ); list.head2.next.next = new Node( 30 ); System.out.println( "The node of intersection is " + list.getNode()); } } // This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal |
蟒蛇3
# defining a node for LinkedList class Node: def __init__( self ,data): self .data = data self . next = None def getIntersectionNode(head1,head2): #finding the total number of elements in head1 LinkedList c1 = getCount(head1) #finding the total number of elements in head2 LinkedList c2 = getCount(head2) #Traverse the bigger node by 'd' so that from that node onwards, both LinkedList #would be having same number of nodes and we can traverse them together. if c1 > c2: d = c1 - c2 return _getIntersectionNode(d,head1,head2) else : d = c2 - c1 return _getIntersectionNode(d,head2,head1) def _getIntersectionNode(d,head1,head2): current1 = head1 current2 = head2 for i in range (d): if current1 is None : return - 1 current1 = current1. next while current1 is not None and current2 is not None : # Instead of values, we need to check if there addresses are same # because there can be a case where value is same but that value is #not an intersecting point. if current1 is current2: return current1.data # or current2.data ( the value would be same) current1 = current1. next current2 = current2. next # Incase, we are not able to find our intersecting point. return - 1 #Function to get the count of a LinkedList def getCount(node): cur = node count = 0 while cur is not None : count + = 1 cur = cur. next return count if __name__ = = '__main__' : # Creating two LinkedList # 1st one: 3->6->9->15->30 # 2nd one: 10->15->30 # We can see that 15 would be our intersection point # Defining the common node common = Node( 15 ) #Defining first LinkedList head1 = Node( 3 ) head1. next = Node( 6 ) head1. next . next = Node( 9 ) head1. next . next . next = common head1. next . next . next . next = Node( 30 ) # Defining second LinkedList head2 = Node( 10 ) head2. next = common head2. next . next = Node( 30 ) print ( "The node of intersection is " ,getIntersectionNode(head1,head2)) # The code is contributed by Ansh Gupta. |
C#
// C# program to get intersection point of two linked list using System; class LinkedList { Node head1, head2; public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node( int d) { data = d; next = null ; } } /*function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 */ int getNode() { int c1 = getCount(head1); int c2 = getCount(head2); int d; if (c1 > c2) { d = c1 - c2; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head1, head2); } else { d = c2 - c1; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head2, head1); } } /* function to get the intersection point of two linked lists head1 and head2 where head1 has d more nodes than head2 */ int _getIntesectionNode( int d, Node node1, Node node2) { int i; Node current1 = node1; Node current2 = node2; for (i = 0; i < d; i++) { if (current1 == null ) { return -1; } current1 = current1.next; } while (current1 != null && current2 != null ) { if (current1.data == current2.data) { return current1.data; } current1 = current1.next; current2 = current2.next; } return -1; } /*Takes head pointer of the linked list and returns the count of nodes in the list */ int getCount(Node node) { Node current = node; int count = 0; while (current != null ) { count++; current = current.next; } return count; } public static void Main(String[] args) { LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); // creating first linked list list.head1 = new Node(3); list.head1.next = new Node(6); list.head1.next.next = new Node(9); list.head1.next.next.next = new Node(15); list.head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30); // creating second linked list list.head2 = new Node(10); list.head2.next = new Node(15); list.head2.next.next = new Node(30); Console.WriteLine( "The node of intersection is " + list.getNode()); } } // This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu |
Javascript
<script> class Node { constructor(item) { this .data=item; this .next= null ; } } let head1,head2; function getNode() { let c1 = getCount(head1); let c2 = getCount(head2); let d; if (c1 > c2) { d = c1 - c2; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head1, head2); } else { d = c2 - c1; return _getIntesectionNode(d, head2, head1); } } function _getIntesectionNode(d,node1,node2) { let i; let current1 = node1; let current2 = node2; for (i = 0; i < d; i++) { if (current1 == null ) { return -1; } current1 = current1.next; } while (current1 != null && current2 != null ) { if (current1.data == current2.data) { return current1.data; } current1 = current1.next; current2 = current2.next; } return -1; } function getCount(node) { let current = node; let count = 0; while (current != null ) { count++; current = current.next; } return count; } head1 = new Node(3); head1.next = new Node(6); head1.next.next = new Node(9); head1.next.next.next = new Node(15); head1.next.next.next.next = new Node(30); // creating second linked list head2 = new Node(10); head2.next = new Node(15); head2.next.next = new Node(30); document.write( "The node of intersection is " + getNode()); // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 </script> |
The node of intersection is 15
时间复杂性: O(m+n) 辅助空间: O(1)
方法4(在第一个列表中画圆圈) 幸亏 萨拉瓦南人 用于提供以下解决方案。 1.遍历第一个链表(计算元素)并制作一个循环链表。(记住最后一个节点,以便我们以后可以打破这个圆)。 2.现在将问题视为在第二个链表中查找循环。所以问题解决了。 3.由于我们已经知道循环的长度(第一个链表的大小),我们可以遍历第二个链表中的许多节点,然后从第二个链表的开头开始另一个指针。我们必须穿过,直到它们相等,这就是所需的交点。 4.从链表中删除圆圈。
时间复杂性: O(m+n) 辅助空间: O(1)
方法5(颠倒第一个列表并建立方程式) 幸亏 萨拉瓦南·马尼 为了提供这种方法。
1) Let X be the length of the first linked list until intersection point. Let Y be the length of the second linked list until the intersection point. Let Z be the length of the linked list from the intersection point to End of the linked list including the intersection node. We Have X + Z = C1; Y + Z = C2;2) Reverse first linked list.3) Traverse Second linked list. Let C3 be the length of second list - 1. Now we have X + Y = C3 We have 3 linear equations. By solving them, we get X = (C1 + C3 – C2)/2; Y = (C2 + C3 – C1)/2; Z = (C1 + C2 – C3)/2; WE GOT THE INTERSECTION POINT.4) Reverse first linked list.
优点:指针没有可比性。 缺点:修改链表(反向列表)。 时间复杂性: O(m+n) 辅助空间: O(1)
方法6(遍历两个列表并比较最后一个节点的地址) 该方法仅用于检测是否存在交点。(感谢NeoTheSaviour的建议)
1) Traverse the list 1, store the last node address2) Traverse the list 2, store the last node address.3) If nodes stored in 1 and 2 are same then they are intersecting.
该方法的时间复杂度为O(m+n),使用的辅助空间为O(1)
方法7(使用哈希) 基本上,我们需要找到两个链表的公共节点。所以我们散列第一个列表的所有节点,然后检查第二个列表。 1) 创建一个空哈希集。 2) 遍历第一个链表,并在哈希集中插入所有节点的地址。 3) 遍历第二个列表。对于每个节点,检查它是否存在于哈希集中。如果我们在散列集中找到一个节点,就返回该节点。
JAVA
// Java program to get intersection point of two linked list import java.util.*; class Node { int data; Node next; Node( int d) { data = d; next = null ; } } class LinkedListIntersect { public static void main(String[] args) { // list 1 Node n1 = new Node( 1 ); n1.next = new Node( 2 ); n1.next.next = new Node( 3 ); n1.next.next.next = new Node( 4 ); n1.next.next.next.next = new Node( 5 ); n1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node( 6 ); n1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node( 7 ); // list 2 Node n2 = new Node( 10 ); n2.next = new Node( 9 ); n2.next.next = new Node( 8 ); n2.next.next.next = n1.next.next.next; Print(n1); Print(n2); System.out.println(MegeNode(n1, n2).data); } // function to print the list public static void Print(Node n) { Node cur = n; while (cur != null ) { System.out.print(cur.data + " " ); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); } // function to find the intersection of two node public static Node MegeNode(Node n1, Node n2) { // define hashset HashSet<Node> hs = new HashSet<Node>(); while (n1 != null ) { hs.add(n1); n1 = n1.next; } while (n2 != null ) { if (hs.contains(n2)) { return n2; } n2 = n2.next; } return null ; } } |
蟒蛇3
# Python program to get intersection # point of two linked list class Node : def __init__( self , d): self .data = d; self . next = None ; # Function to print the list def Print (n): cur = n; while (cur ! = None ) : print (cur.data, end = " " ); cur = cur. next ; print (""); # Function to find the intersection of two node def MegeNode(n1, n2): # Define hashset hs = set (); while (n1 ! = None ): hs.add(n1); n1 = n1. next ; while (n2 ! = None ): if (n2 in hs): return n2; n2 = n2. next ; return None ; # Driver code # list 1 n1 = Node( 1 ); n1. next = Node( 2 ); n1. next . next = Node( 3 ); n1. next . next . next = Node( 4 ); n1. next . next . next . next = Node( 5 ); n1. next . next . next . next . next = Node( 6 ); n1. next . next . next . next . next . next = Node( 7 ); # list 2 n2 = Node( 10 ); n2. next = Node( 9 ); n2. next . next = Node( 8 ); n2. next . next . next = n1. next . next . next ; Print (n1); Print (n2); print (MegeNode(n1, n2).data); # This code is contributed by _saurabh_jaiswal |
C#
// C# program to get intersection point of two linked list using System; using System.Collections.Generic; public class Node { public int data; public Node next; public Node( int d) { data = d; next = null ; } } public class LinkedListIntersect { public static void Main(String[] args) { // list 1 Node n1 = new Node(1); n1.next = new Node(2); n1.next.next = new Node(3); n1.next.next.next = new Node(4); n1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); n1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); n1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); // list 2 Node n2 = new Node(10); n2.next = new Node(9); n2.next.next = new Node(8); n2.next.next.next = n1.next.next.next; Print(n1); Print(n2); Console.WriteLine(MegeNode(n1, n2).data); } // function to print the list public static void Print(Node n) { Node cur = n; while (cur != null ) { Console.Write(cur.data + " " ); cur = cur.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } // function to find the intersection of two node public static Node MegeNode(Node n1, Node n2) { // define hashset HashSet<Node> hs = new HashSet<Node>(); while (n1 != null ) { hs.Add(n1); n1 = n1.next; } while (n2 != null ) { if (hs.Contains(n2)) { return n2; } n2 = n2.next; } return null ; } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar |
Javascript
<script> // Javascript program to get intersection // point of two linked list class Node { constructor(d) { this .data = d; this .next = null ; } } // Function to print the list function Print(n) { let cur = n; while (cur != null ) { document.write(cur.data + " " ); cur = cur.next; } document.write( "<br>" ); } // Function to find the intersection of two node function MegeNode(n1, n2) { // Define hashset let hs = new Set(); while (n1 != null ) { hs.add(n1); n1 = n1.next; } while (n2 != null ) { if (hs.has(n2)) { return n2; } n2 = n2.next; } return null ; } // Driver code // list 1 let n1 = new Node(1); n1.next = new Node(2); n1.next.next = new Node(3); n1.next.next.next = new Node(4); n1.next.next.next.next = new Node(5); n1.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6); n1.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7); // list 2 let n2 = new Node(10); n2.next = new Node(9); n2.next.next = new Node(8); n2.next.next.next = n1.next.next.next; Print(n1); Print(n2); document.write(MegeNode(n1, n2).data); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script> |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 10 9 8 4 5 6 7 4
这种方法需要O(n)个额外的空间,如果一个列表很大,则效率不是很高。
方法8(双指针技术):
使用两个指针:
- 在头1和头2处初始化两个指针ptr1和ptr2。
- 遍历列表,一次遍历一个节点。
- 当ptr1到达列表的末尾时,将其重定向到head2。
- 同样,当ptr2到达列表的末尾时,将其重定向到head1。
- 一旦他们两人都经历了重新分配,他们将与 碰撞点
- 如果在任何节点ptr1与ptr2相遇,则为交叉节点。
- 第二次迭代后,如果没有相交节点,则返回NULL。
C++
// CPP program to print intersection of lists #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; /* Link list node */ class Node { public : int data; Node* next; }; // A utility function to return intersection node Node* intersectPoint(Node* head1, Node* head2) { // Maintaining two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 // at the head of A and B, Node* ptr1 = head1; Node* ptr2 = head2; // If any one of head is NULL i.e // no Intersection Point if (ptr1 == NULL || ptr2 == NULL) { return NULL; } // Traverse through the lists until they // reach Intersection node while (ptr1 != ptr2) { ptr1 = ptr1->next; ptr2 = ptr2->next; // If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is // intersection node.Return intersection node. if (ptr1 == ptr2) { return ptr1; } /* Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be equidistant from the collision point.*/ // When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then // reassign it to the head2. if (ptr1 == NULL) { ptr1 = head2; } // When ptr2 reaches the end of a list, then // redirect it to the head1. if (ptr2 == NULL) { ptr2 = head1; } } return ptr1; } // Function to print intersection nodes // in a given linked list void print(Node* node) { if (node == NULL) cout << "NULL" ; while (node->next != NULL) { cout << node->data << "->" ; node = node->next; } cout << node->data; } // Driver code int main() { /* Create two linked lists 1st Linked list is 3->6->9->15->30 2nd Linked list is 10->15->30 15 30 are elements in the intersection list */ Node* newNode; Node* head1 = new Node(); head1->data = 10; Node* head2 = new Node(); head2->data = 3; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 6; head2->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 9; head2->next->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 15; head1->next = newNode; head2->next->next->next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode->data = 30; head1->next->next = newNode; head1->next->next->next = NULL; Node* intersect_node = NULL; // Find the intersection node of two linked lists intersect_node = intersectPoint(head1, head2); cout << "INTERSEPOINT LIST :" ; print(intersect_node); return 0; // This code is contributed by bolliranadheer } |
JAVA
// JAVA program to print intersection of lists import java.util.*; class GFG{ /* Link list node */ static class Node { int data; Node next; }; // A utility function to return intersection node static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // Maintaining two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 // at the head of A and B, Node ptr1 = head1; Node ptr2 = head2; // If any one of head is null i.e // no Intersection Point if (ptr1 == null || ptr2 == null ) { return null ; } // Traverse through the lists until they // reach Intersection node while (ptr1 != ptr2) { ptr1 = ptr1.next; ptr2 = ptr2.next; // If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is // intersection node.Return intersection node. if (ptr1 == ptr2) { return ptr1; } /* Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be equidistant from the collision point.*/ // When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then // reassign it to the head2. if (ptr1 == null ) { ptr1 = head2; } // When ptr2 reaches the end of a list, then // redirect it to the head1. if (ptr2 == null ) { ptr2 = head1; } } return ptr1; } // Function to print intersection nodes // in a given linked list static void print(Node node) { if (node == null ) System.out.print( "null" ); while (node.next != null ) { System.out.print(node.data+ "." ); node = node.next; } System.out.print(node.data); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { /* Create two linked lists 1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30 2nd Linked list is 10.15.30 15 30 are elements in the intersection list */ Node newNode; Node head1 = new Node(); head1.data = 10 ; Node head2 = new Node(); head2.data = 3 ; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 6 ; head2.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 9 ; head2.next.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 15 ; head1.next = newNode; head2.next.next.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 30 ; head1.next.next = newNode; head1.next.next.next = null ; Node intersect_node = null ; // Find the intersection node of two linked lists intersect_node = intersectPoint(head1, head2); System.out.print( "INTERSEPOINT LIST :" ); print(intersect_node); } } // This code is contributed by umadevi9616. |
C#
// C# program to print intersection of lists using System; public class GFG { /* Link list node */ public class Node { public int data; public Node next; }; // A utility function to return intersection node static Node intersectPoint(Node head1, Node head2) { // Maintaining two pointers ptr1 and ptr2 // at the head of A and B, Node ptr1 = head1; Node ptr2 = head2; // If any one of head is null i.e // no Intersection Point if (ptr1 == null || ptr2 == null ) { return null ; } // Traverse through the lists until they // reach Intersection node while (ptr1 != ptr2) { ptr1 = ptr1.next; ptr2 = ptr2.next; // If at any node ptr1 meets ptr2, then it is // intersection node.Return intersection node. if (ptr1 == ptr2) { return ptr1; } /* * Once both of them go through reassigning, they will be equidistant from the * collision point. */ // When ptr1 reaches the end of a list, then // reassign it to the head2. if (ptr1 == null ) { ptr1 = head2; } // When ptr2 reaches the end of a list, then // redirect it to the head1. if (ptr2 == null ) { ptr2 = head1; } } return ptr1; } // Function to print intersection nodes // in a given linked list static void print(Node node) { if (node == null ) Console.Write( "null" ); while (node.next != null ) { Console.Write(node.data + "->" ); node = node.next; } Console.Write(node.data); } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { /* * Create two linked lists * * 1st Linked list is 3.6.9.15.30 2nd Linked list is 10.15.30 * * 15 30 are elements in the intersection list */ Node newNode; Node head1 = new Node(); head1.data = 10; Node head2 = new Node(); head2.data = 3; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 6; head2.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 9; head2.next.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 15; head1.next = newNode; head2.next.next.next = newNode; newNode = new Node(); newNode.data = 30; head1.next.next = newNode; head1.next.next.next = null ; Node intersect_node = null ; // Find the intersection node of two linked lists intersect_node = intersectPoint(head1, head2); Console.Write( "INTERSEPOINT LIST :" ); print(intersect_node); } } // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 |
INTERSEPOINT LIST :15->30
时间复杂性: O(m+n) 辅助空间: O(1)
如果您发现上述算法中存在任何缺陷,或者找到更好的方法来解决相同的问题,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



