给出一个有向无环图(DAG),求该图的拓扑排序。 拓扑排序 对于有向无环图(DAG),它是顶点的线性排序,因此对于每个有向边uv,顶点u在排序中位于v之前。如果图形不是DAG,则无法对其进行拓扑排序。 例如,下图的拓扑排序为“5 4 2 3 1 0”。一个图可以有多个拓扑排序。例如,下图的另一个拓扑排序是“45 2 3 1 0”。
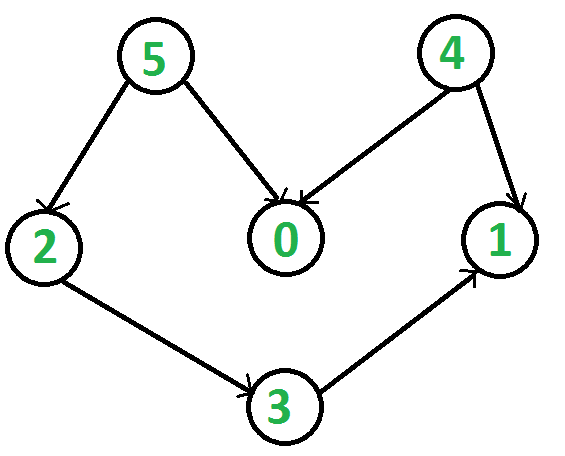
请注意,拓扑排序中的第一个顶点始终是阶数为0的顶点(没有传入边的顶点)。对于上图,顶点4和5没有传入边。
我们已经讨论了一个问题 基于DFS的算法 使用堆栈和 卡恩算法 用于拓扑排序。我们还讨论了如何打印各种拓扑结构的DAG 在这里 .在这篇文章中,通过引入 顶点到达和离开时间的概念 在DFS中。
DFS中顶点的到达时间和离开时间是多少? 在DFS中, 到达时间 是第一次探索顶点的时间 出发时间 是我们已经探索了顶点的所有邻域并准备回溯的时间。
如何利用出发时间求图的拓扑排序? 要找到拓扑类型的图,我们运行 DFS 从所有未访问的顶点逐个开始。对于任何一个顶点,在探索它的任何邻居之前,我们记录该顶点的到达时间,在探索该顶点的所有邻居之后,我们记录其离开时间。请注意,只需要离开时间就可以找到图的拓扑排序,所以我们可以跳过顶点的到达时间。最后,在我们访问了图中的所有顶点之后,我们按照它们离开时间的减少顺序打印这些顶点,这是我们想要的顶点拓扑顺序。 以下是C++实现上述思想的方法——
C++
// A C++ program to print topological sorting of a DAG #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Graph class represents a directed graph using adjacency // list representation class Graph { int V; // No. of vertices // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists list< int >* adj; public : Graph( int ); // Constructor ~Graph(); // Destructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge( int , int ); // The function to do DFS traversal void DFS( int , vector< bool >&, vector< int >&, int &); // The function to do Topological Sort. void topologicalSort(); }; Graph::Graph( int V) { this ->V = V; this ->adj = new list< int >[V]; } Graph::~Graph() { delete [] this ->adj; } void Graph::addEdge( int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to v's list. } // The function to do DFS() and stores departure time // of all vertex void Graph::DFS( int v, vector< bool >& visited, vector< int >& departure, int & time ) { visited[v] = true ; // time++; // arrival time of vertex v for ( int i : adj[v]) if (!visited[i]) DFS(i, visited, departure, time ); // set departure time of vertex v departure[ time ++] = v; } // The function to do Topological Sort. It uses DFS(). void Graph::topologicalSort() { // vector to store departure time of vertex. vector< int > departure(V, -1); // Mark all the vertices as not visited vector< bool > visited(V, false ); int time = 0; // perform DFS on all unvisited vertices for ( int i = 0; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == 0) { DFS(i, visited, departure, time ); } } // print the topological sort for ( int i = V - 1; i >= 0; i--) cout << departure[i] << " " ; } // Driver program to test above functions int main() { // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g(6); g.addEdge(5, 2); g.addEdge(5, 0); g.addEdge(4, 0); g.addEdge(4, 1); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 1); cout << "Topological Sort of the given graph is " ; g.topologicalSort(); return 0; } |
Python3
# A Python3 program to print topological sorting of a DAG def addEdge(u, v): global adj adj[u].append(v) # The function to do DFS() and stores departure time # of all vertex def DFS(v): global visited, departure, time visited[v] = 1 for i in adj[v]: if visited[i] = = 0 : DFS(i) departure[time] = v time + = 1 # The function to do Topological Sort. It uses DFS(). def topologicalSort(): # perform DFS on all unvisited vertices for i in range (V): if (visited[i] = = 0 ): DFS(i) # Print vertices in topological order for i in range (V - 1 , - 1 , - 1 ): print (departure[i], end = " " ) # Driver code if __name__ = = '__main__' : # Create a graph given in the above diagram V,time, adj, visited, departure = 6 , 0 , [[] for i in range ( 7 )], [ 0 for i in range ( 7 )],[ - 1 for i in range ( 7 )] addEdge( 5 , 2 ) addEdge( 5 , 0 ) addEdge( 4 , 0 ) addEdge( 4 , 1 ) addEdge( 2 , 3 ) addEdge( 3 , 1 ) print ( "Topological Sort of the given graph is" ) topologicalSort() # This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 |
Javascript
<script> // A JavaScript program to print topological // sorting of a DAG let adj= new Array(7); for (let i=0;i<adj.length;i++) { adj[i]=[]; } let V=6; let time=0; let visited= new Array(7); let departure = new Array(7); for (let i=0;i<7;i++) { visited[i]=0; departure[i]=-1; } function addEdge(u, v) { adj[u].push(v) } // The function to do DFS() and // stores departure time // of all vertex function DFS(v) { visited[v] = 1; for (let i=0;i<adj[v].length;i++) { if (visited[adj[v][i]]==0) DFS(adj[v][i]); } departure[time] = v time += 1 } // The function to do Topological // Sort. It uses DFS(). function topologicalSort() { //perform DFS on all unvisited vertices for (let i=0;i<V;i++) { if (visited[i] == 0) DFS(i) } //perform DFS on all unvisited vertices for (let i=V-1;i>=0;i--) { document.write(departure[i]+ " " ); } } // Create a graph given in the above diagram addEdge(5, 2); addEdge(5, 0); addEdge(4, 0); addEdge(4, 1); addEdge(2, 3); addEdge(3, 1); document.write( "Topological Sort of the given graph is<br>" ); topologicalSort() // This code is contributed by unknown2108 </script> |
Topological Sort of the given graph is 5 4 2 3 1 0
时间复杂性 上述溶液的浓度为O(V+E)。
本文由 阿迪蒂亚·戈尔 .如果你喜欢GeekSforgek,并想贡献自己的力量,你也可以使用 写极客。组织 或者把你的文章寄去评论-team@geeksforgeeks.org.看到你的文章出现在Geeksforgeks主页上,并帮助其他极客。 如果您发现任何不正确的地方,或者您想分享有关上述主题的更多信息,请写下评论。


![关于”PostgreSQL错误:关系[表]不存在“问题的原因和解决方案-yiteyi-C++库](https://www.yiteyi.com/wp-content/themes/zibll/img/thumbnail.svg)



